A navicular fracture, which affects a key bone in the midfoot, can be a challenging injury that often leads to significant discomfort and swelling. Understanding how to recognize and manage the swelling associated with this injury is crucial for proper healing and recovery. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the relationship between navicular fractures and swelling, along with effective management strategies.
Understanding Navicular Fracture and Associated Swelling
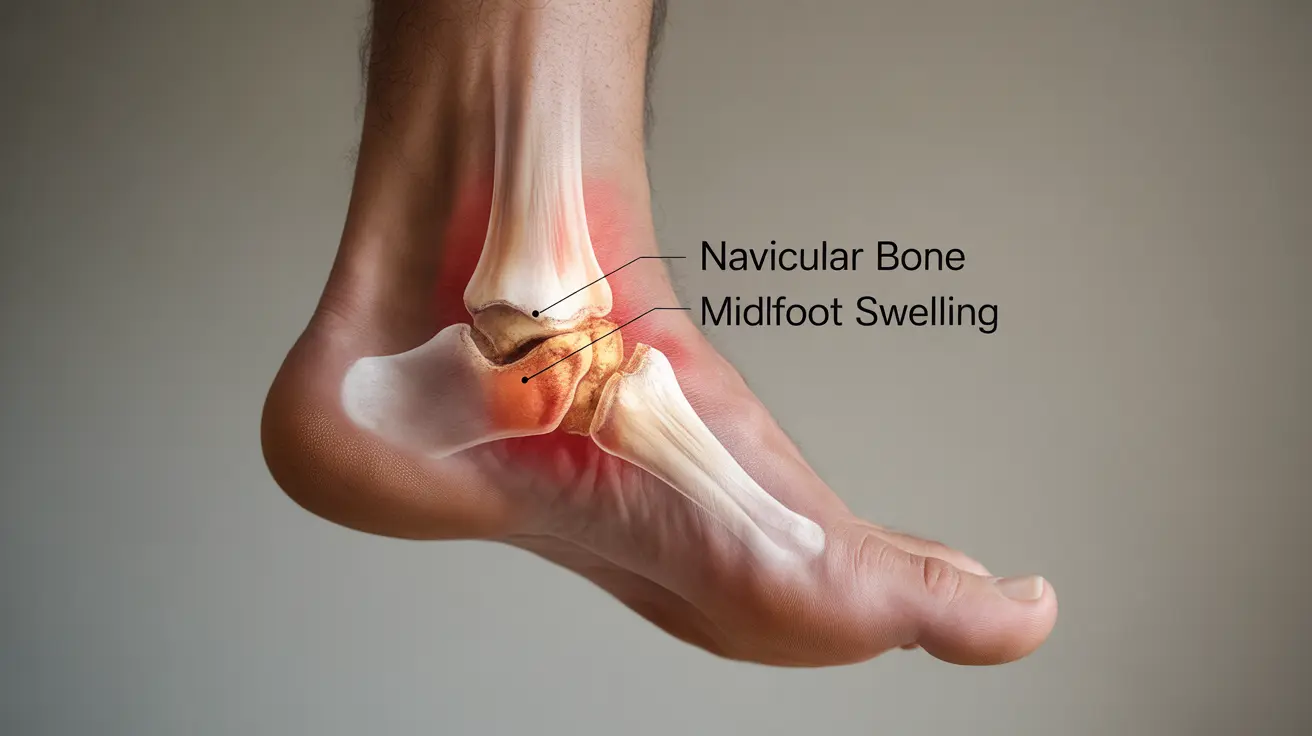
The navicular bone plays a vital role in maintaining the arch of your foot and supporting your weight during movement. When this bone fractures, it typically triggers an inflammatory response, leading to swelling in the midfoot area. This swelling is your body's natural response to injury, but proper management is essential for optimal healing.
Signs and Symptoms of Navicular Fracture
Recognizing the signs of a navicular fracture is crucial for early intervention and proper treatment. The most common indicators include:
- Localized swelling across the top of the midfoot
- Pain that worsens with weight-bearing activities
- Tenderness when touching the affected area
- Difficulty walking or maintaining balance
- Visible bruising around the midfoot region
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose navicular fractures and assess associated swelling. These typically include:
- Physical examination of the foot
- Imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, or CT scans)
- Assessment of range of motion
- Evaluation of weight-bearing capability
Understanding Swelling Patterns
The swelling pattern in navicular fractures can vary significantly among patients. Some may experience immediate and pronounced swelling, while others might notice minimal swelling initially. This variation depends on factors such as:
- Severity of the fracture
- Time elapsed since injury
- Individual healing response
- Previous foot injuries or conditions
Treatment Approaches
Managing a navicular fracture requires a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the bone injury and associated swelling. Common treatment strategies include:
Immediate Care
- RICE protocol (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
- Immobilization using a cast or boot
- Non-weight bearing period
- Pain management
Long-term Management
Long-term treatment focuses on proper healing and preventing complications. This may include:
- Physical therapy exercises
- Gradual return to weight-bearing activities
- Regular monitoring of swelling levels
- Modified footwear or orthotics
Prevention Strategies
Athletes and active individuals can take several steps to reduce their risk of navicular fractures:
- Wearing appropriate supportive footwear
- Gradually increasing activity intensity
- Maintaining proper foot strength and flexibility
- Being mindful of training surface conditions
- Regular foot health check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical signs and symptoms of a navicular fracture, especially regarding swelling and pain?
The most common signs include localized swelling in the midfoot area, sharp pain that intensifies with weight-bearing activities, tenderness to touch, and difficulty walking. The swelling typically develops within hours of the injury and may be accompanied by visible bruising.
How is swelling related to a navicular fracture diagnosed and why might it be minimal or absent?
Healthcare providers assess swelling through physical examination and imaging tests. Swelling might be minimal or absent in some cases due to the deep location of the navicular bone, delayed inflammatory response, or the specific type of fracture. This is why imaging tests are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
What are the most effective treatments for navicular fractures to reduce pain and manage swelling?
The most effective treatments include immediate implementation of the RICE protocol, proper immobilization, and a period of non-weight bearing. Additional treatments may include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and gradually progressive rehabilitation exercises.
How long does swelling last after a navicular fracture and what can help reduce it?
Swelling typically persists for several weeks to months, depending on the severity of the fracture. Regular elevation, compression therapy, ice application, and following medical advice regarding activity levels can help reduce swelling duration and intensity.
What preventative measures can athletes take to avoid navicular fractures and associated swelling?
Athletes should focus on wearing proper footwear, maintaining good foot strength and flexibility, gradually increasing training intensity, and being aware of training surface conditions. Regular rest periods and listening to body signals are also crucial preventative measures.