Neurosarcoidosis is a rare but serious condition where inflammation affects the nervous system as part of systemic sarcoidosis. Understanding its symptoms is crucial for early detection and proper treatment, as this condition can impact various parts of the nervous system and lead to significant health complications if left unmanaged.
This comprehensive guide explores the key symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options available for individuals affected by neurosarcoidosis, helping patients and caregivers better understand this complex neurological condition.
Common Symptoms and Manifestations
Neurosarcoidosis can affect different parts of the nervous system, resulting in various symptoms. The most common manifestations include:
- Headaches and facial pain
- Vision problems or blurred vision
- Hearing difficulties or loss
- Weakness or numbness in limbs
- Balance and coordination problems
- Memory issues and confusion
- Seizures in some cases
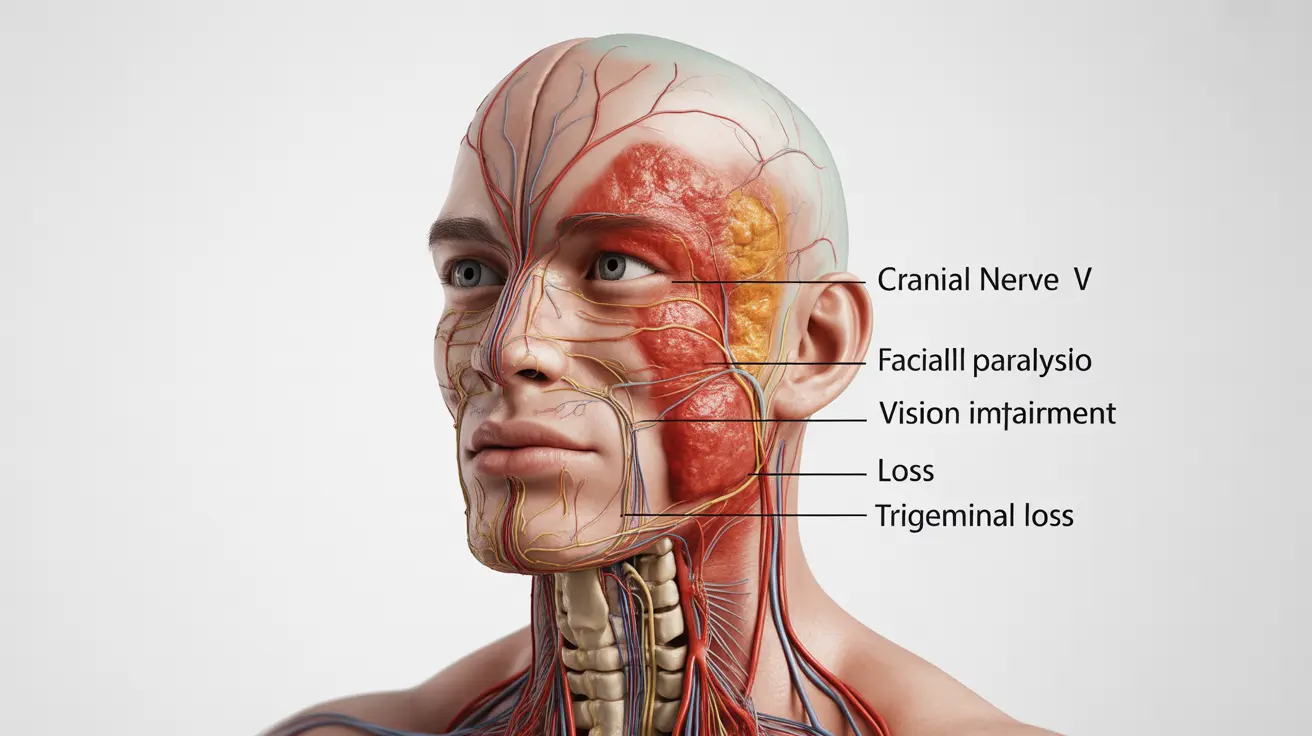
Cranial Nerve Involvement
One of the most significant ways neurosarcoidosis affects patients is through cranial nerve dysfunction. Common issues include:
- Facial weakness or paralysis
- Double vision
- Difficulty swallowing
- Loss of smell or taste
- Hearing impairment
Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing neurosarcoidosis can be challenging because its symptoms often mirror other neurological conditions. Healthcare providers typically use a combination of approaches:
- MRI scans with contrast
- Spinal fluid analysis
- Blood tests for inflammatory markers
- Tissue biopsy when possible
- Comprehensive neurological examination
Differential Diagnosis
Doctors must carefully rule out other conditions that present similar symptoms, including:
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain tumors
- Infectious diseases
- Other inflammatory conditions
Treatment Approaches
Managing neurosarcoidosis typically requires a multi-faceted treatment plan:
Medical Treatments
The primary treatment options include:
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Immunosuppressive medications
- Targeted biological therapies
- Pain management medications when needed
Supportive Care
Additional support measures often include:
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Regular monitoring of symptoms
- Mental health support
Potential Complications
Without proper treatment, neurosarcoidosis can lead to serious complications:
- Permanent nerve damage
- Chronic pain
- Vision loss
- Cognitive difficulties
- Mobility problems
- Reduced quality of life
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of neurosarcoidosis affecting the nervous system?
The most common symptoms include headaches, vision problems, facial weakness, hearing difficulties, and problems with balance and coordination. Patients may also experience numbness or weakness in their limbs, memory issues, and in some cases, seizures.
How is neurosarcoidosis diagnosed when symptoms mimic other neurological diseases like multiple sclerosis?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of MRI scans with contrast, spinal fluid analysis, blood tests, and sometimes tissue biopsy. Doctors also perform detailed neurological examinations and carefully evaluate symptoms to differentiate neurosarcoidosis from similar conditions.
What treatment options are available to manage neurosarcoidosis symptoms and inflammation?
Treatment usually includes corticosteroids as first-line therapy, along with immunosuppressive medications and biological therapies. Supporting treatments may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and pain management strategies.
Can neurosarcoidosis cause facial paralysis or other cranial nerve problems?
Yes, neurosarcoidosis commonly affects cranial nerves, which can lead to facial paralysis, vision problems, hearing loss, and difficulties with swallowing or speaking.
What are the potential complications if neurosarcoidosis is left untreated or progresses?
Untreated neurosarcoidosis can lead to permanent nerve damage, chronic pain, vision loss, cognitive impairment, and significant mobility issues. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to prevent these serious complications.