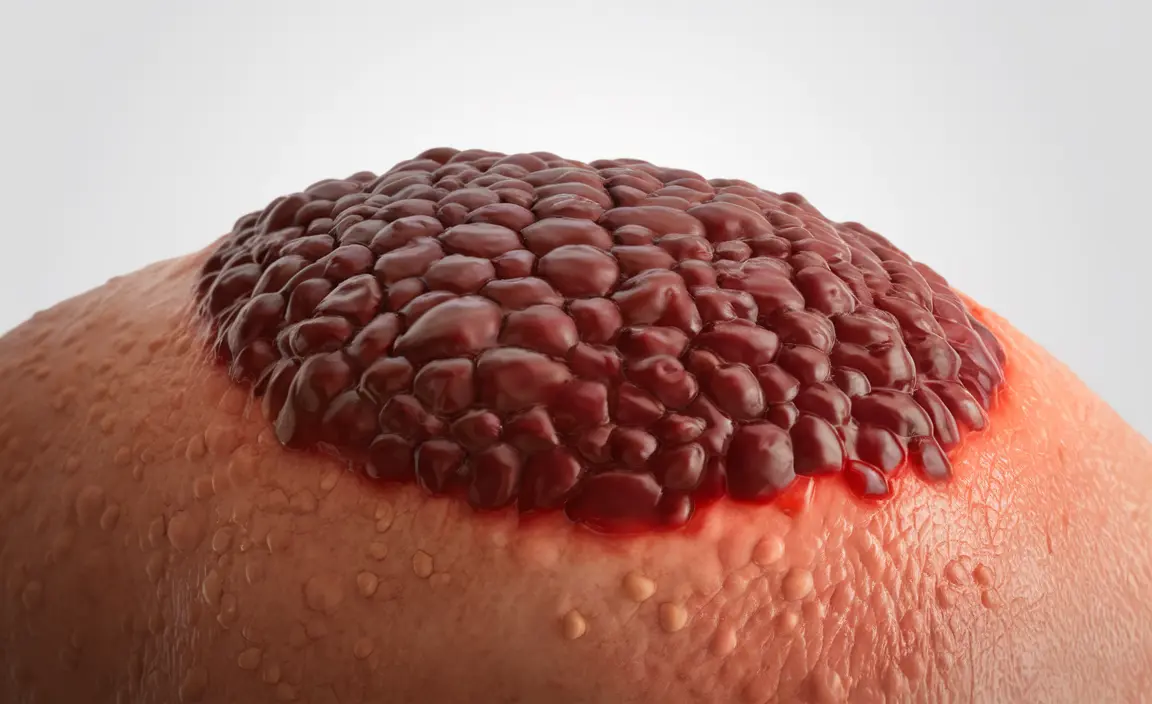
Nodular melanoma is one of the most aggressive forms of skin cancer, requiring immediate medical attention when detected. Understanding its appearance and characteristics is crucial for early detection and successful treatment. This comprehensive guide will help you recognize the visual signs of nodular melanoma and understand its key features.
Visual Characteristics of Nodular Melanoma
Nodular melanoma typically appears as a raised, dark bump on the skin that differs significantly from common moles. These growths often exhibit distinctive features that set them apart from benign skin lesions:
- Symmetrical, dome-shaped appearance
- Dark black, blue, or brown coloring
- Smooth, glossy surface
- Uniform color throughout
- Elevated above the skin's surface
- Well-defined borders
Key Visual Indicators
When examining potential nodular melanoma spots, look for these specific visual cues:
- Rapid growth over weeks or months
- Size typically larger than 6 millimeters
- Firm to the touch
- May bleed easily or ulcerate
- Can appear on any part of the body, including areas not exposed to sun
Signs and Symptoms
Unlike other forms of melanoma, nodular melanoma has unique characteristics that make early identification crucial:
Primary Warning Signs
Watch for these distinctive features:
- Sudden appearance of a new growth
- Notable changes in size or shape
- Tenderness or pain in the affected area
- Breaking of the skin's surface
- Itching or burning sensations
Risk Factors and Causes
Understanding the risk factors can help identify those who may need more frequent skin checks:
- Fair skin and light-colored eyes
- History of significant sun exposure
- Family history of melanoma
- Multiple atypical moles
- Weakened immune system
- Previous skin cancer diagnosis
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Early diagnosis is critical for successful treatment of nodular melanoma. The diagnostic process typically involves:
Diagnostic Procedures
- Complete skin examination
- Dermoscopy evaluation
- Biopsy of suspicious lesions
- Imaging tests for staging
- Lymph node assessment
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary based on the stage and extent of the melanoma:
- Surgical excision
- Lymph node removal when necessary
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Radiation therapy in specific cases
Prevention and Monitoring
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing nodular melanoma:
- Regular self-examination of skin
- Professional skin checks every 6-12 months
- Consistent use of broad-spectrum sunscreen
- Protective clothing when outdoors
- Avoiding peak sun exposure hours
Frequently Asked Questions
What does nodular melanoma look like in pictures and how can I identify its typical features? Nodular melanoma appears as a raised, symmetrical bump that's usually dark in color (black, blue, or brown). It typically has well-defined borders, a smooth surface, and is larger than 6mm in diameter. Unlike regular moles, it grows vertically rather than spreading across the skin's surface.
What are the common symptoms and signs that distinguish nodular melanoma from other skin growths? Nodular melanoma is distinguished by its rapid growth, uniform color, raised appearance, and tendency to bleed easily. Unlike other melanomas, it doesn't follow the typical ABCDE rule completely, as it's usually symmetrical and has regular borders.
How fast does nodular melanoma grow and why is early detection important? Nodular melanoma grows rapidly, often developing within weeks or months. Early detection is crucial because this type of melanoma grows vertically into deeper layers of skin more quickly than other types, making it more likely to spread if not caught early.
What causes nodular melanoma, and can it develop without significant sun exposure? While UV exposure is a major risk factor, nodular melanoma can develop without significant sun exposure. Other factors include genetic predisposition, fair skin type, multiple atypical moles, and a weakened immune system.
How is nodular melanoma diagnosed and what treatment options are available? Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, dermoscopy, and biopsy of suspicious lesions. Treatment options include surgical removal, lymph node evaluation, and possibly immunotherapy or targeted therapy, depending on the stage of the cancer.