When diagnosed with a non-cancerous brain tumor, one of the first questions patients and their families ask is about survival rates and long-term outcomes. While these tumors are generally less aggressive than their malignant counterparts, understanding the factors that influence survival rates is crucial for making informed healthcare decisions.
This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of non-cancerous brain tumor prognosis, treatment options, and factors that affect survival rates. By understanding these elements, patients can better navigate their healthcare journey and work more effectively with their medical team.
Understanding Non-Cancerous Brain Tumors
Non-cancerous brain tumors, also known as benign brain tumors, are abnormal cell growths that don't spread to other parts of the body. These tumors typically grow more slowly than malignant tumors and often have clear boundaries, making them easier to remove surgically in many cases.
Common Types and Their Prognosis
Different types of benign brain tumors have varying survival rates and treatment outcomes:
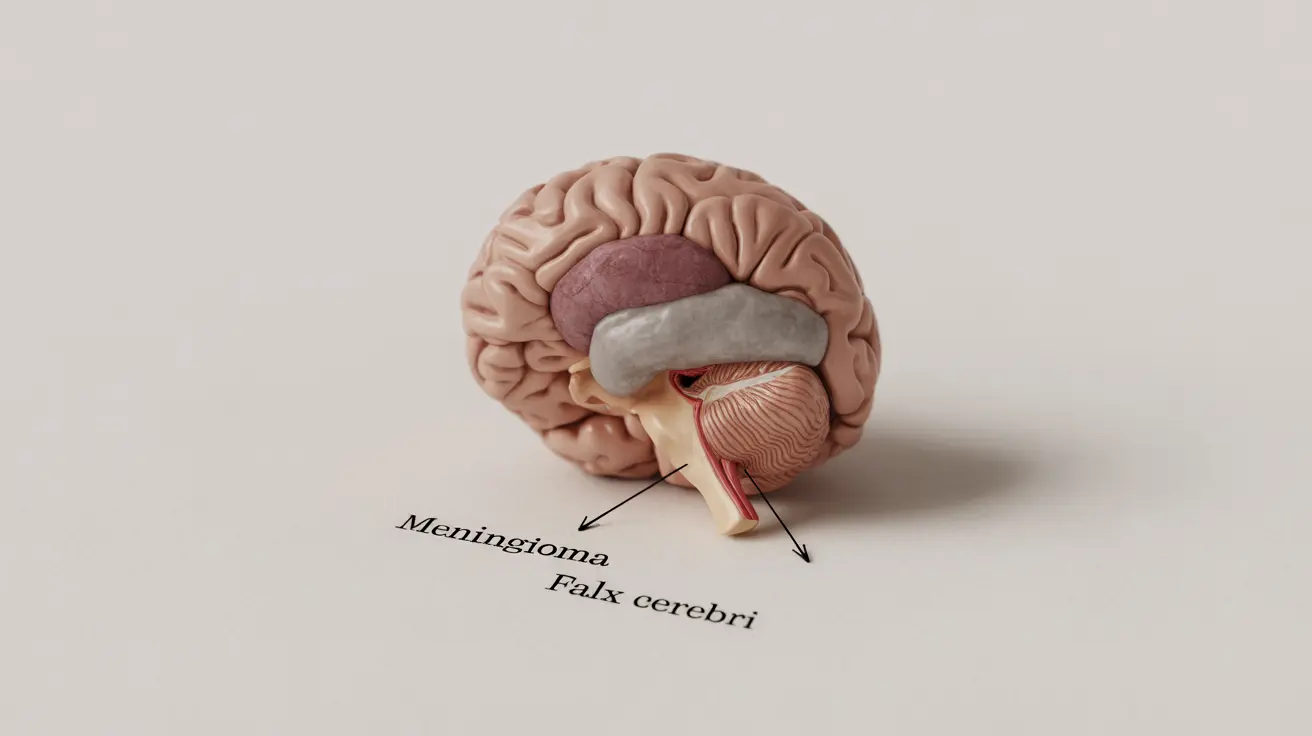
Meningiomas
These tumors develop in the meninges, the protective layers covering the brain. They typically have excellent survival rates, with many patients living normal lifespans after treatment. The five-year survival rate for meningiomas can exceed 90% with appropriate treatment.
Pituitary Adenomas
These tumors form in the pituitary gland and generally have very favorable outcomes. The survival rate for patients with pituitary adenomas is notably high, often approaching normal life expectancy when properly treated.
Acoustic Neuromas
Also known as vestibular schwannomas, these tumors typically have excellent survival rates, with most patients living normal lifespans after treatment.
Factors Affecting Survival Rates
Several key factors influence the survival rates for non-cancerous brain tumors:
- Tumor location and accessibility
- Size of the tumor at diagnosis
- Patient's age and overall health
- Timing of diagnosis and treatment
- Access to specialized medical care
- Treatment response
Treatment Options and Success Rates
Modern treatment approaches for non-cancerous brain tumors have significantly improved survival rates:
Surgical Removal
Complete surgical removal often offers the best long-term outcomes, with success rates varying based on tumor location and accessibility. Many patients experience excellent recovery with minimal complications.
Radiation Therapy
When surgery isn't possible, radiation therapy can effectively control tumor growth. This treatment option has shown promising results in maintaining long-term tumor control.
Observation
Some small, slow-growing tumors may only require monitoring, with intervention occurring only if symptoms develop or growth is detected.
Lifestyle and Management Strategies
Maintaining overall health can positively impact survival rates and quality of life:
- Regular medical follow-up
- Healthy diet and exercise
- Stress management
- Regular sleep patterns
- Strong support system
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical symptoms of benign brain tumors, like meningioma or schwannoma?
Common symptoms include headaches, vision changes, balance problems, hearing loss (especially with acoustic neuromas), and potential seizures. The specific symptoms often depend on the tumor's location and size.
How are noncancerous brain tumors usually treated, and what are the success rates?
Treatment typically involves surgical removal, radiation therapy, or a combination of both. Success rates are generally high, with many patients achieving complete tumor removal or control. The specific success rate depends on factors like tumor location, size, and type.
Can benign brain tumors, such as pituitary adenomas, cause hormonal imbalances?
Yes, particularly pituitary adenomas can affect hormone production, leading to various endocrine disorders. These may include changes in growth hormone levels, thyroid function, or reproductive hormones.
What are the key factors that influence survival rates for patients with noncancerous brain tumors?
Key factors include tumor location, size, patient age, overall health status, timing of diagnosis, treatment approach, and access to specialized care. Early detection and treatment generally lead to better outcomes.
How do lifestyle and diet impact the risk or management of benign brain tumors?
While lifestyle and diet don't directly prevent benign brain tumors, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support overall treatment success and recovery. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep.