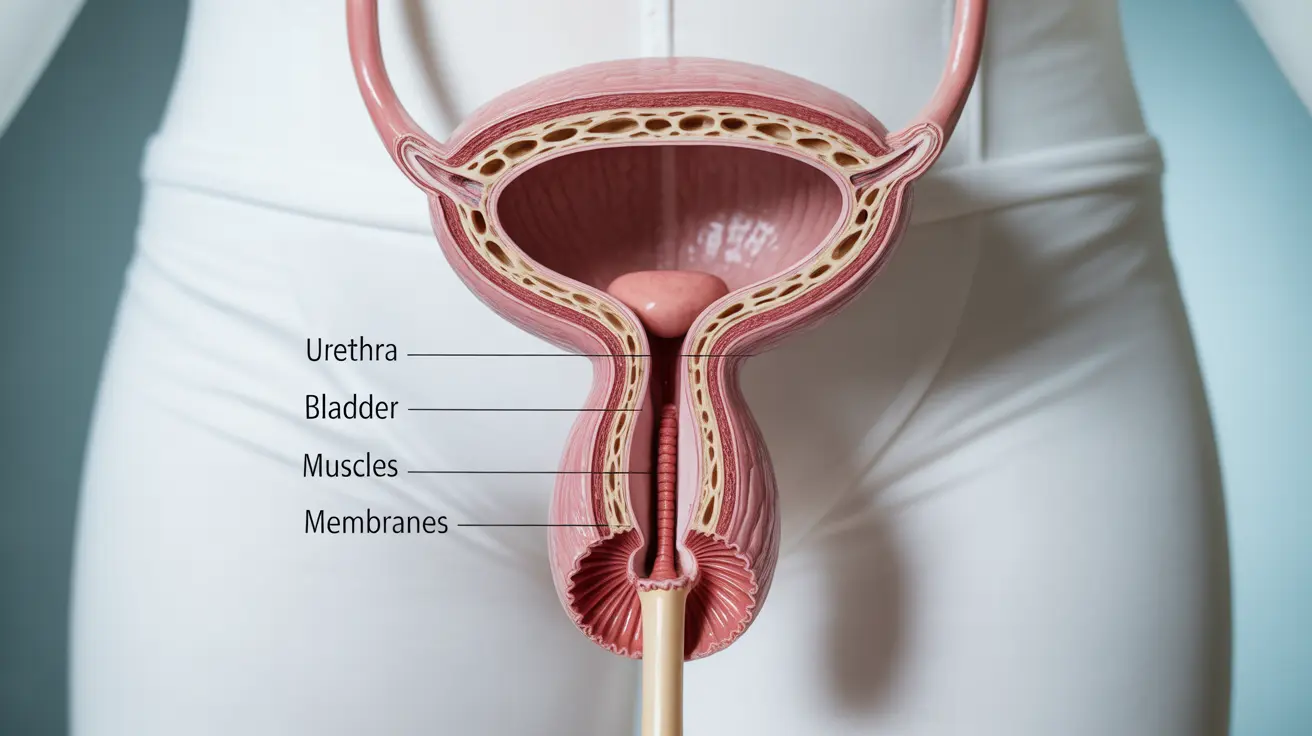
The female urethra plays a crucial role in urinary health, serving as the pathway for urine to exit the body from the bladder. Understanding its structure and function is essential for maintaining optimal urinary health and preventing common infections that can affect women's well-being.
This comprehensive guide explores the normal female urethra, common health concerns, and practical strategies for maintaining urinary tract health.
Anatomy and Function of the Female Urethra
The female urethra is a short tube, typically measuring about 4 centimeters in length, that extends from the bladder to the external urethral opening. This relatively short length, while efficient for urination, can make women more susceptible to urinary tract infections compared to men, whose urethras are significantly longer.
The urethra contains specialized tissue and muscles that help control urination and prevent bacteria from entering the urinary system. It's lined with mucous membranes that produce protective secretions and is surrounded by muscles that help maintain continence.
Common Health Concerns and Symptoms
Women may experience various urethral health issues throughout their lives. Common symptoms that might indicate a problem include:
- Burning or pain during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Lower abdominal pain or pressure
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Discomfort or pain in the pelvic region
Hormonal Influences on Urethral Health
Hormonal changes, particularly during menopause, can significantly impact urethral health. Decreased estrogen levels can lead to:
- Thinning of urethral tissue
- Reduced muscle tone
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Changes in urinary patterns
These changes make it especially important for post-menopausal women to maintain good urinary tract health through proper care and prevention strategies.
Prevention and Maintenance Strategies
Maintaining optimal urethral health involves several key practices:
- Proper wiping technique (front to back)
- Regular urination, especially after sexual activity
- Adequate hydration throughout the day
- Wearing breathable, cotton underwear
- Avoiding irritating feminine products
- Regular exercise to maintain pelvic floor strength
Lifestyle Modifications for Optimal Health
Adopting certain lifestyle habits can significantly improve urethral health:
Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Maintain good personal hygiene practices, and consider incorporating pelvic floor exercises into your routine. These measures can help strengthen the muscles supporting the urethra and maintain proper function.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical symptoms of a female urethra infection, and how can it be treated?
Common symptoms include burning during urination, frequent urination, and pelvic pain. Treatment typically involves antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider, along with increased fluid intake and over-the-counter pain relievers for comfort.
How does the short length of the female urethra impact the risk of developing urinary tract infections?
The shorter length of the female urethra makes it easier for bacteria to travel from the outside environment to the bladder, increasing the risk of urinary tract infections. This anatomical feature means bacteria have a shorter distance to travel to cause infection.
What are some effective ways to prevent urinary tract infections in women?
Effective prevention strategies include proper wiping technique, urinating after sexual activity, staying well-hydrated, wearing breathable underwear, and maintaining good hygiene practices. Regular urination and avoiding holding urine for long periods are also important.
How does hormonal change, such as during menopause, affect the female urethra's health and susceptibility to infections?
Menopause leads to decreased estrogen levels, which can cause thinning of urethral tissue and reduced muscle tone. These changes can increase susceptibility to infections and may lead to urinary symptoms. Some women may benefit from hormonal treatments to address these changes.
What is the role of proper hygiene and lifestyle changes in maintaining the health of the female urethra?
Proper hygiene and lifestyle practices are crucial for urethral health. This includes maintaining clean, dry intimate areas, wearing appropriate clothing, staying hydrated, and practicing good bathroom habits. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight also contribute to overall urinary tract health.