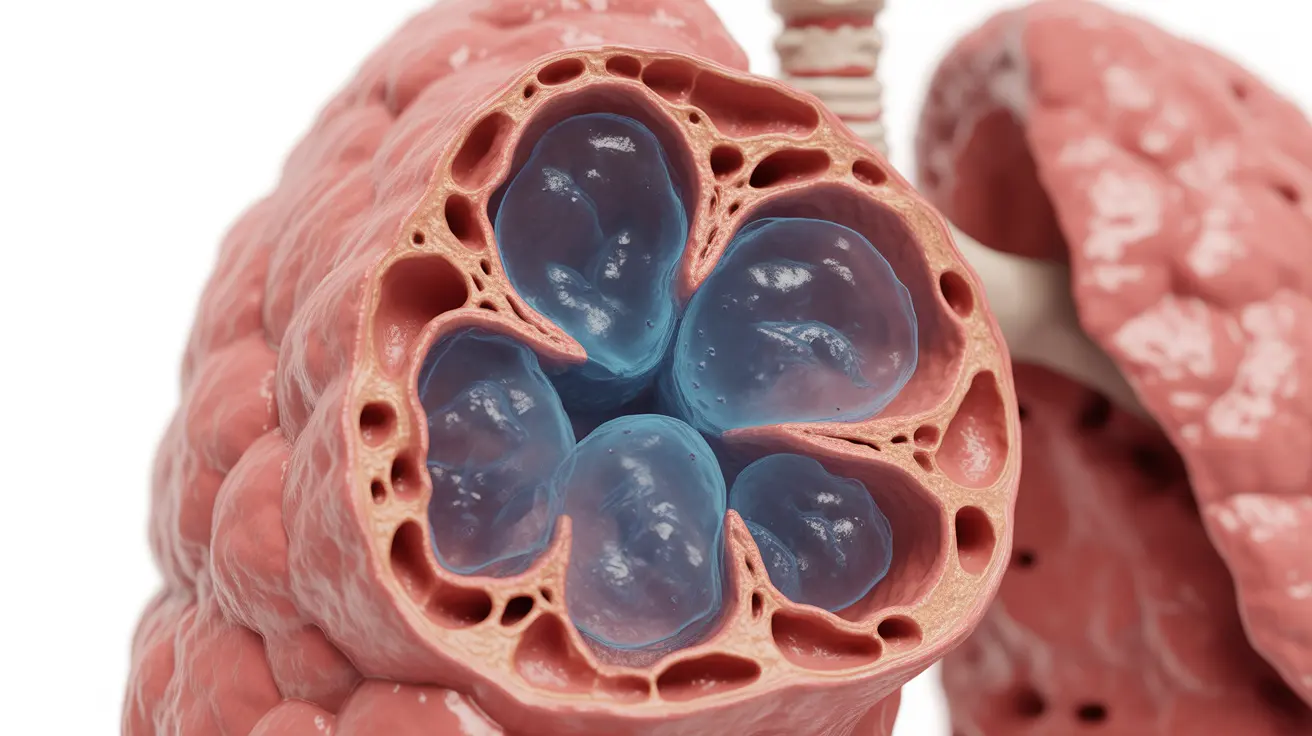
Obstructive emphysema is a serious progressive lung condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This chronic respiratory disease gradually damages the air sacs (alveoli) in your lungs, making it increasingly difficult to breathe. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for both patients and their caregivers.
As part of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), obstructive emphysema requires careful management and lifestyle modifications to maintain quality of life. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about this condition, from early warning signs to the latest treatment approaches.
Understanding the Nature of Obstructive Emphysema
Obstructive emphysema occurs when the walls between air sacs in your lungs become damaged and lose their elasticity. This damage causes the air sacs to collapse during exhalation, trapping air in the lungs and making it difficult to breathe out. The condition progressively worsens over time, leading to increasingly compromised lung function.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
The initial symptoms of obstructive emphysema often develop gradually and may include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Persistent cough
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Reduced exercise tolerance
- Frequent respiratory infections
As the condition progresses, symptoms typically become more severe and may begin to affect daily activities significantly.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors contribute to the development of obstructive emphysema:
Primary Risk Factors
- Smoking (the leading cause)
- Long-term exposure to secondhand smoke
- Occupational exposure to dust and chemicals
- Air pollution
- Genetic factors (Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency)
Diagnostic Process and Testing
Doctors use various methods to diagnose obstructive emphysema and assess its severity:
- Pulmonary function tests (spirometry)
- Chest X-rays
- CT scans
- Blood gas analysis
- Exercise tests
Treatment Approaches
Medications
Several medication options can help manage symptoms:
- Bronchodilators
- Inhaled corticosteroids
- Combination inhalers
- Antibiotics (when necessary)
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
This comprehensive program includes:
- Exercise training
- Breathing techniques
- Nutritional counseling
- Education about the condition
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes is crucial for managing obstructive emphysema:
- Smoking cessation
- Regular exercise within limitations
- Proper nutrition
- Stress management
- Avoiding environmental triggers
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of obstructive emphysema and how do they progress over time?
Common symptoms include progressive shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, and reduced exercise tolerance. These symptoms typically worsen over time, starting with mild breathing difficulties during exercise and potentially progressing to breathing problems even at rest.
What causes obstructive emphysema and who is most at risk for developing it?
The primary cause is smoking, but other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, occupational dust and chemicals, air pollution, and genetic factors. Smokers, especially long-term smokers, and people with frequent exposure to lung irritants are at highest risk.
How is obstructive emphysema diagnosed by doctors and what tests are commonly used?
Doctors diagnose obstructive emphysema through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and various tests including pulmonary function tests (spirometry), chest X-rays, CT scans, and blood gas analysis.
What treatment options are available to manage obstructive emphysema and improve breathing?
Treatment options include medications (bronchodilators and corticosteroids), pulmonary rehabilitation programs, oxygen therapy when needed, and in some cases, surgical interventions. The treatment plan is typically tailored to the individual's specific needs and disease severity.
How can quitting smoking and lifestyle changes help slow the progression of obstructive emphysema?
Quitting smoking is the most important step in slowing disease progression. Additional lifestyle changes like regular exercise, proper nutrition, and avoiding environmental triggers can help maintain lung function and improve quality of life. These modifications, combined with proper medical care, can significantly impact the disease's course.