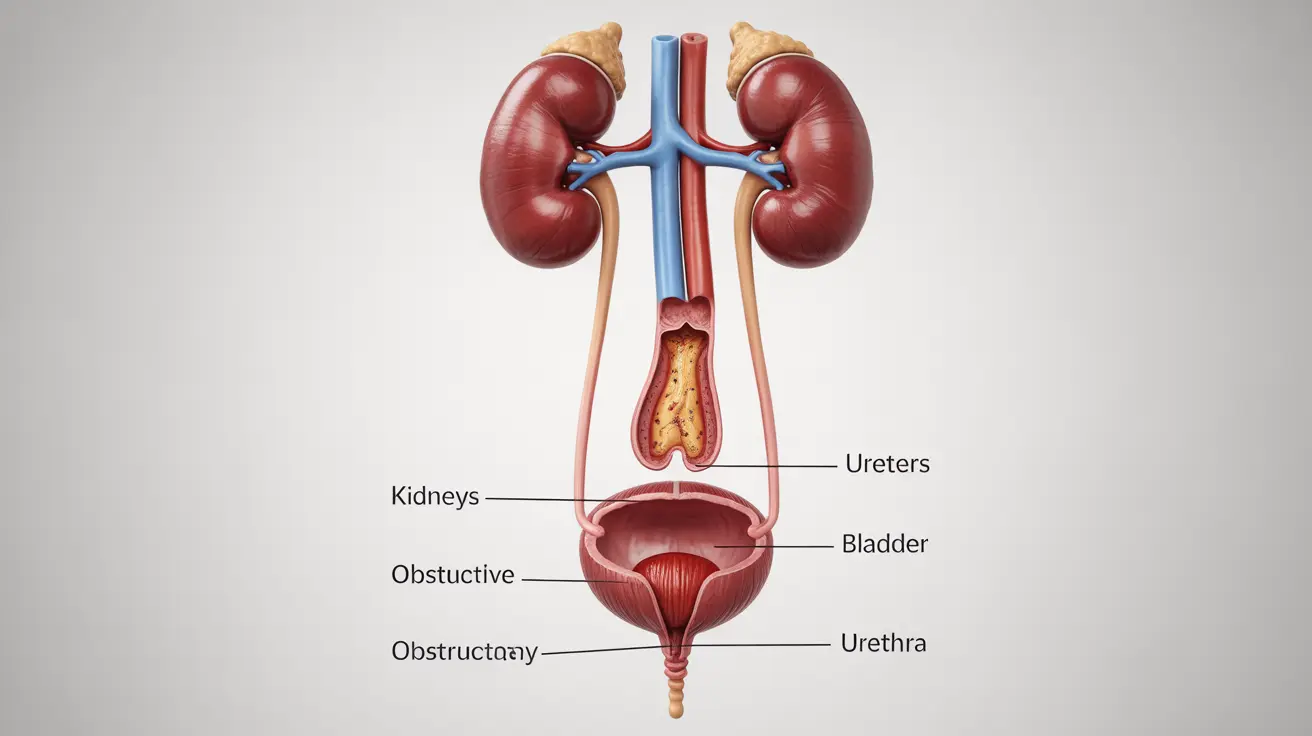
Obstructive uropathy is a serious medical condition that affects the urinary system, potentially leading to severe complications if left untreated. This article will explore the various aspects of obstructive uropathy, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. By understanding this condition, you can better recognize its signs and seek timely medical attention.
What is Obstructive Uropathy?
Obstructive uropathy occurs when there is a blockage in the urinary tract that impedes the normal flow of urine. This obstruction can happen anywhere along the urinary system, from the kidneys to the urethra. As a result, urine backs up, potentially causing damage to the kidneys and other parts of the urinary system.
Symptoms of Obstructive Uropathy
Recognizing the symptoms of obstructive uropathy is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include:
- Pain or discomfort in the lower back or side
- Difficulty urinating or a weak urine stream
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Urgent need to urinate
- Blood in the urine
- Swelling in the legs or abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever (if infection is present)
It's important to note that symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the obstruction. Some individuals may experience sudden, severe symptoms, while others might have a gradual onset of milder symptoms.
Common Causes of Obstructive Uropathy
Understanding the causes of obstructive uropathy can help in prevention and early detection. Some common causes include:
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are one of the most frequent causes of urinary obstruction. These hard deposits can form anywhere in the urinary tract and block the flow of urine.
Enlarged Prostate
In men, an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) can compress the urethra, making it difficult for urine to pass through.
Tumors
Cancerous or non-cancerous growths in the urinary tract or surrounding organs can cause obstruction by pressing on the urinary system.
Congenital Abnormalities
Some people are born with structural abnormalities in their urinary system that can lead to obstructive uropathy.
Scarring
Previous injuries, surgeries, or infections can cause scar tissue to form, potentially narrowing or blocking parts of the urinary tract.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing obstructive uropathy typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and various tests such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or urodynamic studies. Once diagnosed, treatment focuses on relieving the obstruction and preventing further damage to the urinary system.
Treatment Approaches
The choice of treatment depends on the cause and severity of the obstruction. Common treatment options include:
- Catheterization to drain urine
- Medication to shrink an enlarged prostate
- Lithotripsy to break up kidney stones
- Surgery to remove tumors or correct structural abnormalities
- Stent placement to keep the urinary tract open
In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary to fully address the obstruction and its underlying cause.
Long-term Effects and Complications
If left untreated, obstructive uropathy can lead to serious complications, including:
- Chronic kidney disease or kidney failure
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Permanent damage to the urinary system
- Sepsis (in severe cases)
Regular follow-up care and monitoring are essential to prevent these long-term effects and ensure the best possible outcomes for patients with obstructive uropathy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of obstructive uropathy and how does it affect the body?
Symptoms of obstructive uropathy include lower back or side pain, difficulty urinating, frequent urination, blood in urine, and swelling in the legs or abdomen. It affects the body by causing urine to back up in the urinary system, potentially leading to kidney damage, infections, and other complications if left untreated.
How is obstructive uropathy treated and what are the most effective options for removing blockages?
Treatment for obstructive uropathy depends on the cause but may include catheterization, medications, lithotripsy for kidney stones, or surgery. The most effective options vary based on the specific blockage, but often involve a combination of these approaches to relieve the obstruction and address its underlying cause.
Can an enlarged prostate cause obstructive uropathy, and what treatments are available?
Yes, an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) can cause obstructive uropathy in men. Treatments include medications to shrink the prostate or relax muscles, minimally invasive procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), or in severe cases, open surgery to remove part of the prostate gland.
What are some common causes of obstructive uropathy, and how can they be prevented?
Common causes include kidney stones, enlarged prostate, tumors, and congenital abnormalities. Prevention strategies vary but may include staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking. Regular check-ups, especially for men over 50, can help detect prostate issues early.
How does obstructive uropathy affect kidney function, and what are the long-term risks if left untreated?
Obstructive uropathy can severely impact kidney function by causing urine to back up, leading to increased pressure in the kidneys. This can damage kidney tissue and impair their ability to filter waste and excess fluid. Long-term risks of untreated obstructive uropathy include chronic kidney disease, kidney failure, recurrent infections, and in severe cases, sepsis.