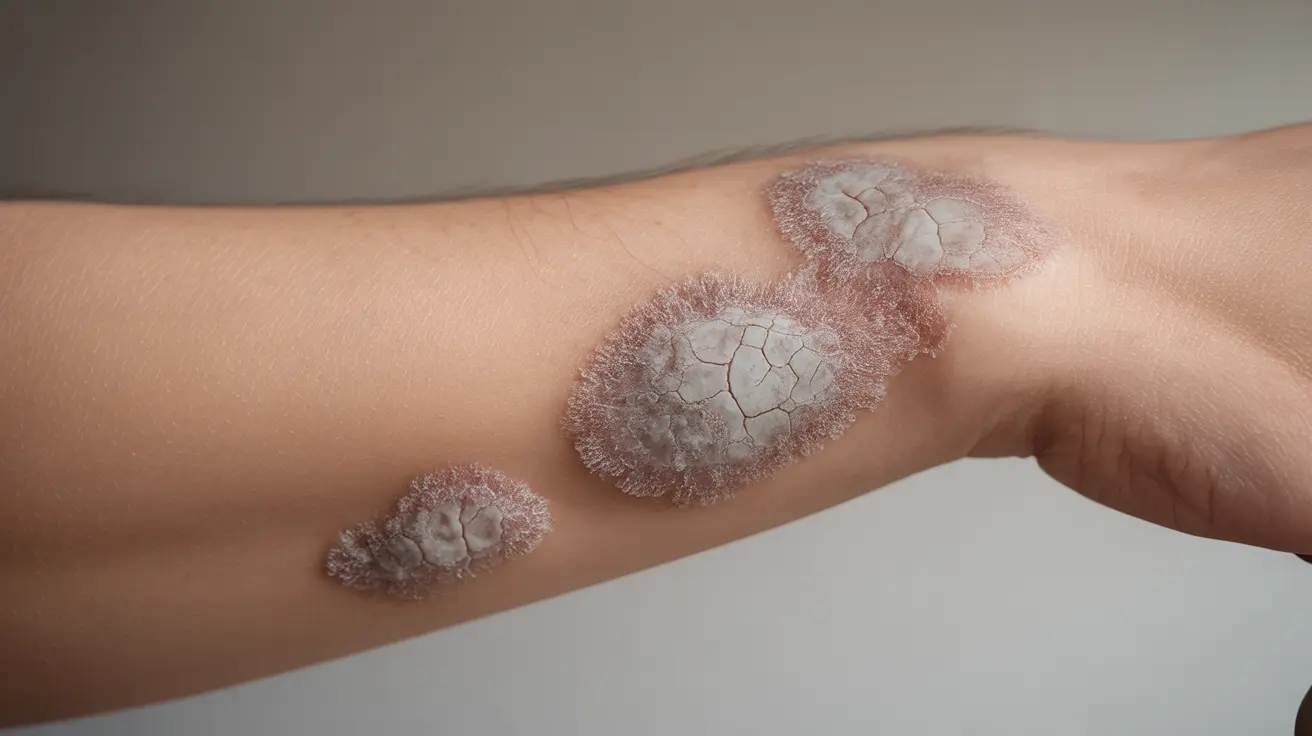
Ostraceous psoriasis is a distinctive and severe form of plaque psoriasis characterized by thick, scaly patches that resemble oyster shells. This chronic inflammatory skin condition can significantly impact a person's quality of life and requires careful medical management. Understanding its unique features and available treatments is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
While less common than other forms of psoriasis, ostraceous psoriasis demands special attention due to its intense presentation and potential complications. This article explores the key aspects of this condition, from its characteristic appearance to effective management strategies.
Distinctive Features and Appearance
Ostraceous psoriasis stands out from other psoriasis variants due to its unique presentation. The lesions typically appear as thick, layered plaques with a distinctive gray or white coloring. These scales build up in a pattern resembling oyster shells, hence the term "ostraceous."
Key visual characteristics include:
- Thick, adherent scales with a shell-like appearance
- Grayish-white to silver coloring
- Well-defined borders around the plaques
- Multiple layers of scaling
- Common locations on elbows, knees, and lower back
Diagnostic Process and Classification
Diagnosing ostraceous psoriasis requires careful examination by a dermatologist. The distinctive appearance often makes it recognizable, but healthcare providers must still conduct a thorough evaluation to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Physical examination of the skin lesions
- Review of medical history
- Sometimes, a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis
- Assessment for associated conditions like psoriatic arthritis
Treatment Approaches
Managing ostraceous psoriasis often requires a combination of treatments due to its severity. Treatment plans are typically tailored to each patient's specific needs and response to therapy.
Topical Treatments
First-line treatments often include:
- High-potency corticosteroids
- Vitamin D analogs
- Moisturizers and emollients
- Salicylic acid preparations to help remove scales
Systemic Treatments
For more severe cases, systemic options may include:
- Oral medications like methotrexate or cyclosporine
- Biologic therapies
- Oral retinoids
- Phototherapy treatments
Managing Associated Conditions
Ostraceous psoriasis can occur alongside other health issues, particularly psoriatic arthritis. Regular monitoring and comprehensive care are essential for addressing both skin symptoms and joint involvement when present.
Prevention and Lifestyle Management
While ostraceous psoriasis cannot be completely prevented, several strategies can help reduce flare-ups and manage symptoms:
- Identifying and avoiding personal triggers
- Maintaining good skin hygiene
- Regular moisturizing
- Stress management
- Healthy lifestyle choices
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms and appearance of ostraceous psoriasis?
Ostraceous psoriasis presents as thick, layered plaques with a distinctive oyster shell-like appearance. The lesions typically have a grayish-white color and well-defined borders, with multiple layers of scaling that are firmly attached to the skin.
How is ostraceous psoriasis diagnosed and differentiated from other psoriasis types?
Diagnosis is primarily based on the characteristic appearance of the lesions during physical examination by a dermatologist. The thick, adherent scales and oyster shell-like appearance distinguish it from other forms of psoriasis. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed for confirmation.
What treatment options are most effective for managing ostraceous psoriasis and associated psoriatic arthritis?
The most effective treatment approach typically combines topical treatments (high-potency corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs) with systemic medications (biologics, methotrexate) when necessary. For associated psoriatic arthritis, additional medications targeting joint inflammation may be prescribed.
Can ostraceous psoriasis cause joint pain or psoriatic arthritis, and how are these conditions related?
Yes, patients with ostraceous psoriasis can develop psoriatic arthritis. Both conditions are driven by similar inflammatory processes, and approximately 30% of people with psoriasis may develop psoriatic arthritis, requiring comprehensive treatment for both skin and joint symptoms.
What factors trigger or worsen ostraceous psoriasis, and how can flare-ups be prevented?
Common triggers include stress, skin injury, certain medications, infections, and weather changes. Prevention strategies include identifying and avoiding personal triggers, maintaining good skin care, managing stress, and following prescribed treatment plans consistently.