Overactive bladder affects millions of people worldwide, causing sudden urges to urinate that can be difficult to control. This condition can significantly impact daily life, causing embarrassment and limiting social activities. Fortunately, scheduled toileting has emerged as an effective, non-invasive treatment approach that can help regain bladder control and improve quality of life.
Scheduled toileting, also known as timed voiding or bladder training, represents a behavioral therapy technique that gradually retrains the bladder to hold urine for longer periods. This evidence-based approach offers hope for those seeking alternatives to medication or surgical interventions for managing overactive bladder symptoms.
Understanding Scheduled Toileting for Overactive Bladder
Scheduled toileting is a structured behavioral intervention designed to help individuals with overactive bladder regain control over their urinary habits. This technique involves establishing predetermined bathroom visits at regular intervals, regardless of whether the urge to urinate is present. The primary goal is to gradually increase the time between bathroom visits, thereby training the bladder to hold larger volumes of urine.
The method works by breaking the cycle of frequent urination that characterizes overactive bladder. When someone experiences urgent urges repeatedly, the bladder muscle can become hypersensitive, contracting at smaller volumes than normal. Scheduled toileting helps desensitize these muscle responses while building confidence in bladder control.
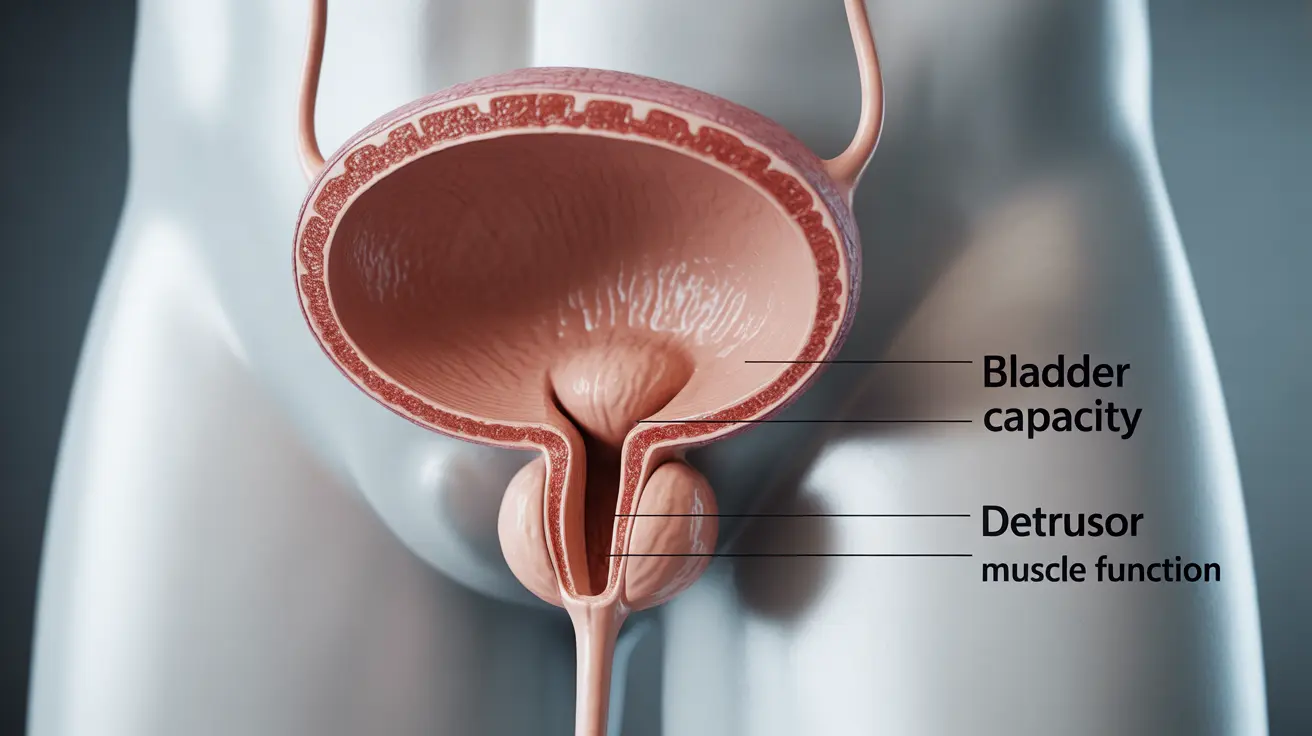
The Science Behind Bladder Retraining
The bladder is a remarkable organ that can typically hold between 300 to 500 milliliters of urine comfortably. In overactive bladder conditions, this capacity becomes compromised due to involuntary detrusor muscle contractions. Scheduled toileting works by gradually conditioning the bladder to accommodate normal volumes again.
Research demonstrates that consistent implementation of scheduled toileting can lead to significant improvements in bladder capacity, reduced urgency episodes, and decreased frequency of urination. The technique essentially reprograms the communication between the brain and bladder, restoring more normal voiding patterns.
Establishing Your Scheduled Toileting Routine
Beginning a scheduled toileting program requires careful planning and commitment. The initial step involves tracking current bathroom habits for several days to establish a baseline. This information helps determine the appropriate starting interval between scheduled bathroom visits.
Most healthcare providers recommend starting with intervals that are slightly longer than your current natural voiding pattern. For example, if you typically urinate every hour, you might begin with scheduled visits every 1.5 hours. This gradual approach prevents overwhelming the bladder while still challenging it to hold urine for extended periods.
Creating a Practical Schedule
A successful scheduled toileting routine should be realistic and sustainable. Consider your daily activities, work schedule, and sleep patterns when designing your program. Many people find success with the following approach:
- Start with shorter intervals and gradually increase by 15-30 minutes weekly
- Maintain consistent timing throughout the day
- Set reminders on your phone or watch to stay on track
- Plan bathroom visits around meals and regular daily activities
- Adjust the schedule as needed based on your progress and comfort level
Advanced Strategies for Bladder Training Success
Beyond basic scheduling, several additional techniques can enhance the effectiveness of your overactive bladder scheduled toileting program. Urge suppression techniques play a crucial role in managing sudden urges that occur between scheduled visits. These methods include deep breathing exercises, pelvic floor muscle contractions, and distraction techniques.
Dietary modifications can also support your bladder training efforts. Reducing caffeine intake, limiting acidic foods, and maintaining proper hydration levels all contribute to bladder health. However, avoid drastically reducing fluid intake, as this can lead to concentrated urine that irritates the bladder.
Pelvic Floor Exercise Integration
Combining scheduled toileting with pelvic floor muscle exercises can significantly improve outcomes. These muscles support the bladder and help control urination. Regular Kegel exercises strengthen these muscles, providing better voluntary control over bladder function.
To perform Kegel exercises effectively, contract the pelvic floor muscles as if stopping the flow of urine, hold for 5-10 seconds, then relax. Repeat this 10-15 times, three times daily. Integrating these exercises with your scheduled toileting routine creates a comprehensive bladder training program.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Your Approach
Tracking your progress is essential for successful bladder training. Maintain a detailed bladder diary that records scheduled bathroom visits, unexpected urges, any accidents, and fluid intake. This information helps identify patterns and determine when to advance to longer intervals between visits.
Progress in scheduled toileting is typically gradual, with most people experiencing initial improvements within 2-4 weeks. However, significant changes may take 8-12 weeks of consistent practice. Patience and persistence are key factors in achieving long-term success with this approach.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Many individuals encounter obstacles during their bladder training journey. Common challenges include scheduling conflicts, social situations, and occasional setbacks. Developing strategies to handle these situations beforehand increases the likelihood of maintaining consistency in your program.
For work environments, communicate with supervisors about your health needs if necessary. Many employers are understanding and accommodating when approached professionally. Planning bathroom locations in advance when traveling or attending social events can also reduce anxiety and maintain schedule adherence.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Bladder Training
Several lifestyle changes can complement your scheduled toileting routine and improve overall bladder health. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the bladder and pelvic floor muscles. Regular physical activity, particularly low-impact exercises, can improve overall muscle tone and circulation.
Sleep hygiene also plays a role in bladder training success. Establishing consistent bedtime routines and limiting fluid intake in the evening can reduce nighttime urination frequency. However, ensure adequate daytime hydration to maintain optimal bladder function.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is scheduled toileting and how does it help with overactive bladder?
Scheduled toileting is a behavioral therapy technique that involves urinating at predetermined times throughout the day, regardless of whether you feel the urge. It helps with overactive bladder by gradually training the bladder to hold larger amounts of urine and reducing the hypersensitivity that causes frequent, urgent urges. This method breaks the cycle of frequent urination and helps restore normal bladder function over time.
How often should I go to the bathroom when doing scheduled voiding for overactive bladder?
The frequency of scheduled bathroom visits should start slightly longer than your current natural voiding pattern. Most people begin with intervals of 1.5 to 2 hours during waking hours, then gradually increase the time between visits by 15-30 minutes each week as tolerance improves. The goal is to eventually achieve normal voiding intervals of 3-4 hours during the day.
Can scheduled toileting reduce the urgency and frequency of urination in overactive bladder?
Yes, scheduled toileting can significantly reduce both urgency and frequency of urination in people with overactive bladder. Studies show that consistent practice of this technique can decrease urgent episodes by 50-80% and reduce overall voiding frequency. The method works by retraining the bladder muscle to respond normally to filling, reducing hypersensitivity and involuntary contractions.
What are the best tips for starting a bladder training program with scheduled voiding?
The best tips for starting include: keeping a bladder diary for 3-7 days before beginning to establish your baseline, setting realistic initial intervals, using phone alarms or reminders to maintain consistency, combining the program with pelvic floor exercises, staying properly hydrated, and being patient with the process. It's also important to have a plan for managing urges between scheduled times using distraction techniques or Kegel exercises.
How long does it take to see results from scheduled toileting for overactive bladder?
Most people begin to notice improvements within 2-4 weeks of consistent scheduled toileting practice. However, significant and lasting results typically take 8-12 weeks of dedicated effort. Some individuals may experience benefits sooner, while others may need up to 16 weeks to achieve optimal outcomes. The key is maintaining consistency and gradually increasing intervals between bathroom visits as tolerance improves.