Experiencing pain above the vaginal area can be concerning and may signal various underlying conditions that require medical attention. This type of discomfort, often described as suprapubic pain, can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms that help identify its cause. Understanding the potential sources of this pain and knowing when to seek medical help is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
While some causes of pain above the vagina may be temporary and benign, others could indicate more serious conditions that need prompt medical intervention. This comprehensive guide will explore the common causes, associated symptoms, and treatment options available for addressing this type of pelvic pain.
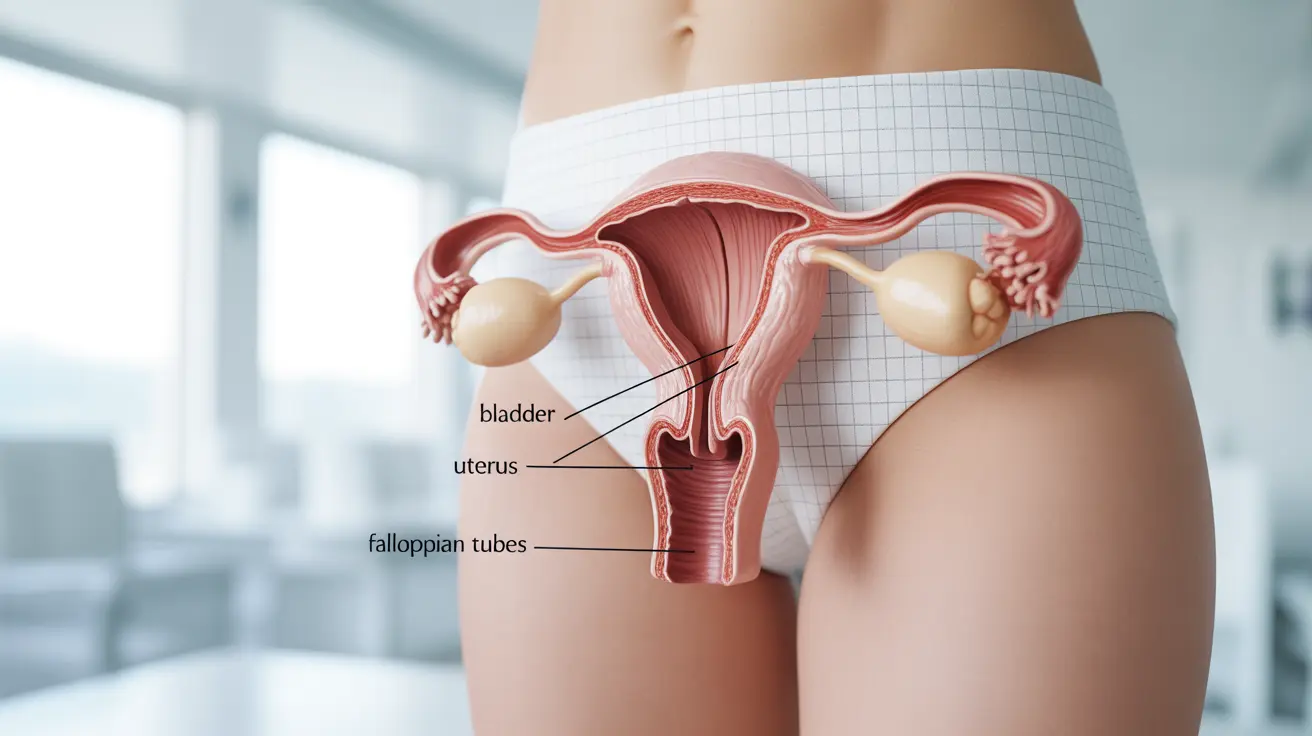
Common Causes of Suprapubic Pain
Several conditions can trigger pain above the vaginal area, including:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Ovarian cysts or masses
- Endometriosis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Bladder conditions
- Uterine fibroids
- Gastrointestinal issues
Urinary System Issues
Urinary tract infections are a frequent cause of pain above the vagina. These infections typically cause a burning sensation during urination, frequent urges to urinate, and pressure or pain in the lower abdomen. Other urinary conditions, such as interstitial cystitis or bladder infections, can also cause similar discomfort.
Reproductive System Conditions
Gynecological conditions often manifest as pain above the vaginal area. Ovarian cysts, endometriosis, and uterine fibroids can all cause persistent or cyclical pain. These conditions may also be accompanied by irregular menstrual cycles, heavy bleeding, or pain during intercourse.
Identifying the Source of Pain
The characteristics of the pain, including its timing, intensity, and associated symptoms, can help determine its cause. Keep track of:
- When the pain occurs
- How long it lasts
- What makes it better or worse
- Any accompanying symptoms
- Relationship to menstrual cycle
When to Seek Medical Attention
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation, including:
- Severe or worsening pain
- Fever or chills
- Heavy vaginal bleeding
- Difficulty urinating
- Severe nausea or vomiting
- Pain that interferes with daily activities
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and may include:
- Antibiotics for infections
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Hormone therapy
- Physical therapy
- Surgical intervention when necessary
- Lifestyle modifications
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of pain above the vagina or in the suprapubic area?
The most common causes include urinary tract infections, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and bladder conditions. Each condition typically presents with distinct additional symptoms that help in diagnosis.
How can I tell if pain above my vagina is due to a urinary tract infection or another condition?
UTIs usually cause burning during urination, frequent urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. Pain from other conditions may be more cyclical (related to menstruation) or constant, and typically doesn't include urinary symptoms.
When should I see a doctor for pain in my lower abdomen or pelvis above the vagina?
Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, fever, heavy bleeding, difficulty urinating, or if the pain interferes with daily activities. Also consult a healthcare provider if the pain persists for more than a few days or keeps returning.
What treatments are available for pelvic pain caused by ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or infections?
Treatment options include antibiotics for infections, hormonal medications for endometriosis, pain relievers, and sometimes surgery. The specific treatment plan depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
Can digestive problems like irritable bowel syndrome cause pain above the vagina, and how is it managed?
Yes, gastrointestinal conditions like IBS can cause pain in the lower abdomen and pelvic area. Management typically involves dietary modifications, stress reduction, medication, and lifestyle changes. Working with a healthcare provider can help develop an effective treatment plan.