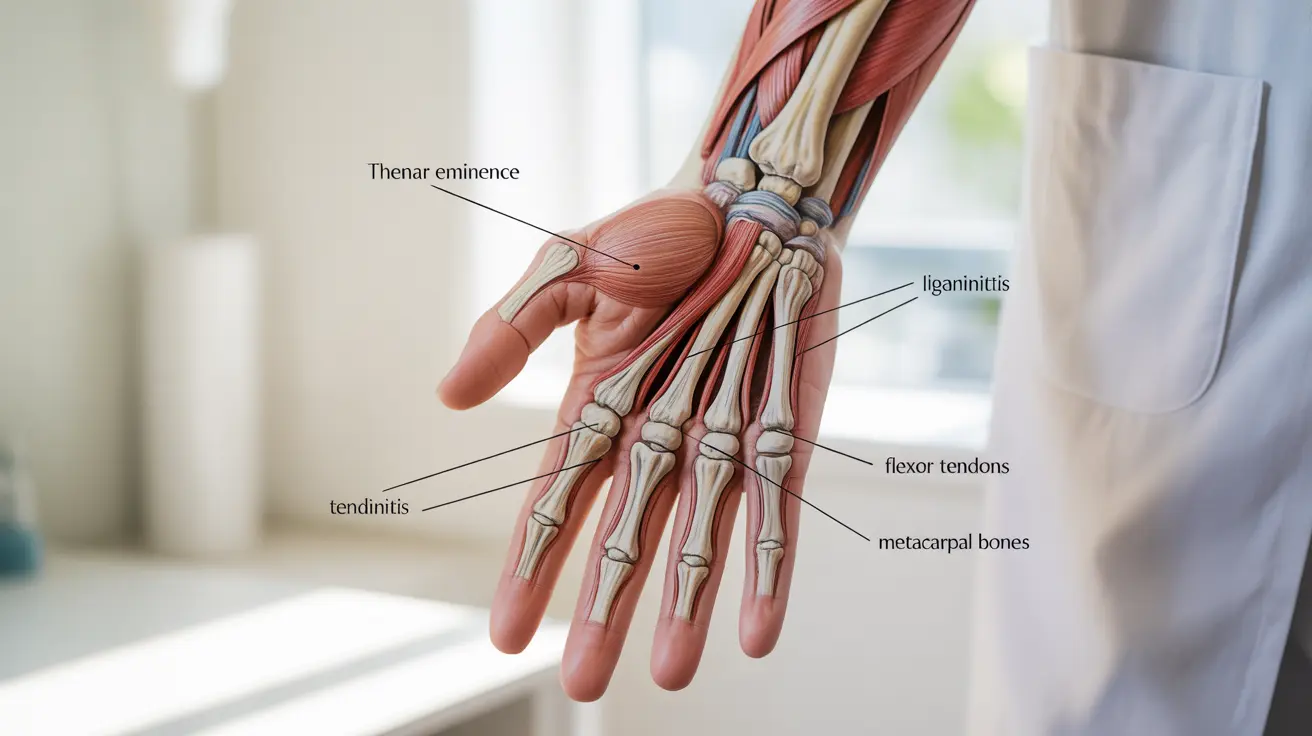
When you experience pain in the fleshy part of your hand under the thumb, it can significantly impact your daily activities and quality of life. This sensitive area, known as the thenar eminence, contains important muscles that control thumb movement and grip strength. Understanding the causes and available treatments for this specific type of hand pain is crucial for proper management and recovery.
Whether you're experiencing sharp, dull, or throbbing sensations in this region, various conditions could be responsible. Let's explore the common causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for pain in this specific area of your hand.
Common Causes of Thumb Base Pain
Several conditions can lead to pain in the fleshy part of the hand under the thumb:
- Thenar muscle strain
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- De Quervain's tenosynovitis
- Thumb arthritis (basal joint arthritis)
- Nerve compression
- Overuse injuries
Each of these conditions presents unique symptoms and requires specific treatment approaches. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment.
Recognizing Symptoms and Warning Signs
The nature and pattern of your thumb pain can provide important clues about its cause:
- Sharp pain during gripping or pinching movements
- Dull ache in the thumb muscle area
- Weakness when trying to grasp objects
- Swelling or inflammation at the base of the thumb
- Reduced range of motion
- Tenderness to touch
Pay attention to when these symptoms occur and what activities might trigger or worsen them, as this information can help with diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options and Pain Management
Medical Treatments
Healthcare providers may recommend various treatment approaches depending on the underlying cause:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Corticosteroid injections
- Physical therapy
- Splinting or bracing
- Surgery (in severe cases)
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Several self-care measures can help manage pain and promote healing:
- Ice therapy for acute pain and inflammation
- Heat therapy for chronic pain
- Gentle stretching exercises
- Activity modification
- Ergonomic adjustments to work setup
Prevention Strategies
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing or aggravating thumb pain:
- Use proper ergonomic tools and equipment
- Take regular breaks during repetitive activities
- Maintain good posture while working
- Perform hand-strengthening exercises
- Practice proper lifting techniques
When to Seek Medical Care
Certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe or persistent pain
- Significant swelling or redness
- Inability to move the thumb
- Numbness or tingling
- Pain that interferes with sleep or daily activities
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of pain in the fleshy part of the hand under my thumb? The most common causes include muscle strain, tendinitis, arthritis, and nerve compression. Overuse injuries and repetitive motions often contribute to pain in this area.
What are the typical symptoms of arthritis or tendinitis at the base of the thumb? Common symptoms include pain during gripping or pinching movements, stiffness, swelling, and reduced strength. Morning stiffness is particularly common with arthritis, while tendinitis often causes pain with specific movements.
How is pain under the thumb treated—are there medications, therapies, or home remedies that help? Treatment options include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, splinting, and activity modification. Home remedies like ice/heat therapy and gentle exercises can also provide relief.
When should I see a doctor for thumb pain, and what tests might they use to diagnose the problem? Seek medical attention if pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by numbness or weakness. Doctors may use physical examination, X-rays, MRI, or nerve conduction studies for diagnosis.
Are there ways to prevent or reduce thumb pain, and what activities should I avoid if my thumb hurts? Prevention includes using ergonomic tools, taking regular breaks, maintaining proper posture, and avoiding repetitive movements. When experiencing pain, avoid activities that require forceful gripping or pinching.