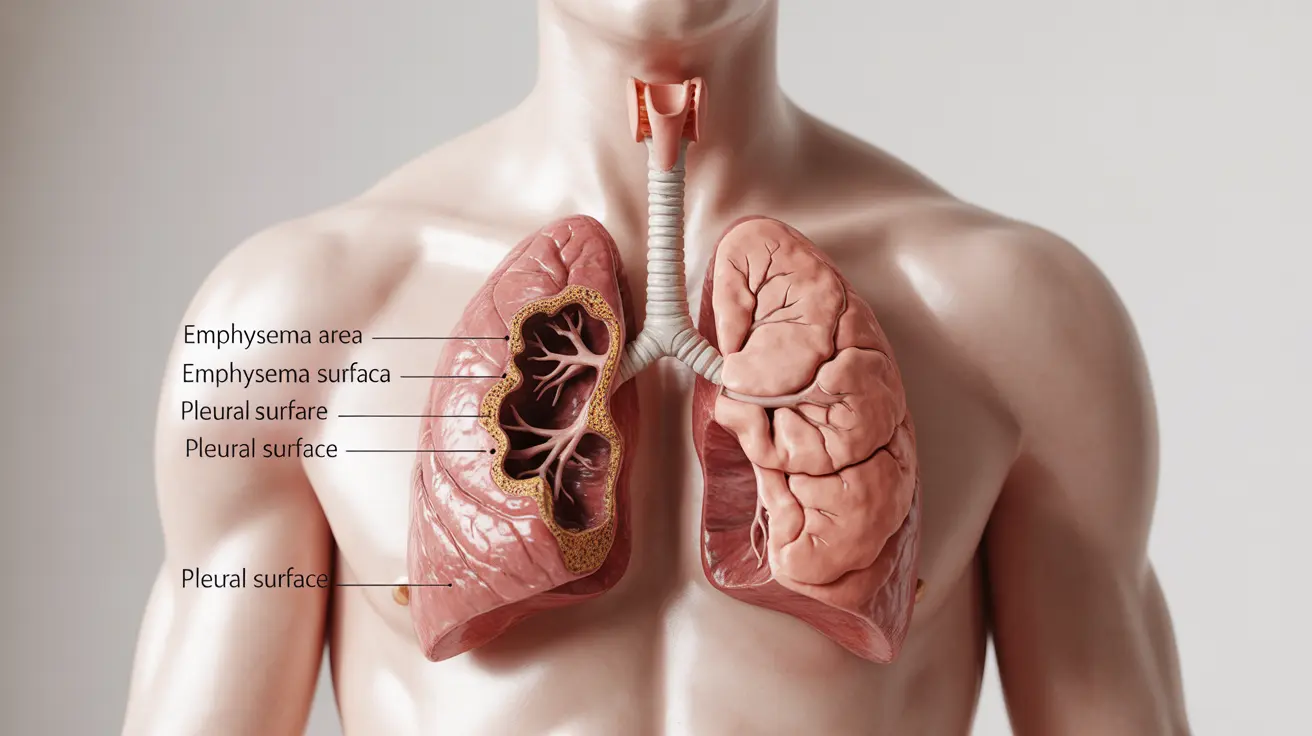
Paraseptal emphysema is a specific type of emphysema that primarily affects the distal airways and alveoli adjacent to the pleura, fissures, and septa of the lungs. This condition can significantly impact respiratory health and requires careful medical attention for proper management and treatment.
While less common than other forms of emphysema, understanding paraseptal emphysema is crucial for early detection and intervention. This article explores the key aspects of this condition, including its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, and treatment options.
What is Paraseptal Emphysema?
Paraseptal emphysema occurs when air sacs (alveoli) near the outer edges of the lungs become damaged and enlarged. This condition specifically affects the areas close to the pleura (the membrane covering the lungs) and the connective tissue that divides the lungs into sections.
Unlike other forms of emphysema that may affect the entire lung more uniformly, paraseptal emphysema has a distinctive pattern of damage that can be identified through medical imaging.
Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of paraseptal emphysema can vary in severity and may develop gradually over time. Common indicators include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Chest tightness or discomfort
- Reduced exercise tolerance
- Persistent cough
- Fatigue
- Wheezing in some cases
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can contribute to the development of paraseptal emphysema:
Primary Risk Factors
- Smoking (both active and passive exposure)
- Occupational exposure to harmful substances
- Genetic predisposition
- Age (more common in older adults)
Environmental Factors
Environmental pollutants and workplace exposures can significantly increase the risk of developing paraseptal emphysema. This includes exposure to:
- Industrial chemicals
- Air pollution
- Dust particles
- Chemical fumes
Diagnosis and Assessment
Accurate diagnosis of paraseptal emphysema typically involves several steps:
Imaging Studies
CT scans are particularly important in diagnosing paraseptal emphysema, as they can clearly show:
- The distribution of affected areas
- The extent of lung damage
- Any associated complications
Additional Tests
- Pulmonary function tests
- Chest X-rays
- Blood oxygen level measurements
- Complete medical history evaluation
Treatment and Management
Managing paraseptal emphysema requires a comprehensive approach that may include:
Medical Interventions
- Bronchodilators to improve breathing
- Anti-inflammatory medications when needed
- Oxygen therapy in advanced cases
- Antibiotics for respiratory infections
Lifestyle Modifications
Important lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition include:
- Smoking cessation programs
- Regular exercise within individual limitations
- Breathing exercises and pulmonary rehabilitation
- Avoiding environmental irritants
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early symptoms and signs of paraseptal emphysema I should watch for? Early signs include gradual onset of shortness of breath during physical activity, chest tightness, and reduced exercise tolerance. Some patients may also experience a persistent cough.
How is paraseptal emphysema diagnosed and what role do CT scans play? Diagnosis primarily relies on high-resolution CT scans, which can clearly show the characteristic pattern of damage near the pleura and septa. CT scans help physicians assess the extent and distribution of the condition.
What are the main causes and risk factors for developing paraseptal emphysema? The primary causes include smoking, exposure to environmental pollutants, genetic factors, and advancing age. Occupational exposure to harmful substances can also increase risk.
How is paraseptal emphysema treated and managed to prevent complications like collapsed lung? Treatment involves a combination of medications (bronchodilators, anti-inflammatories), oxygen therapy when needed, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Regular monitoring and prompt treatment of respiratory infections are crucial for preventing complications.
Can quitting smoking or changing inhalation habits help slow the progression of paraseptal emphysema? Yes, quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to slow disease progression. Avoiding exposure to environmental irritants and maintaining good air quality can also help manage the condition.