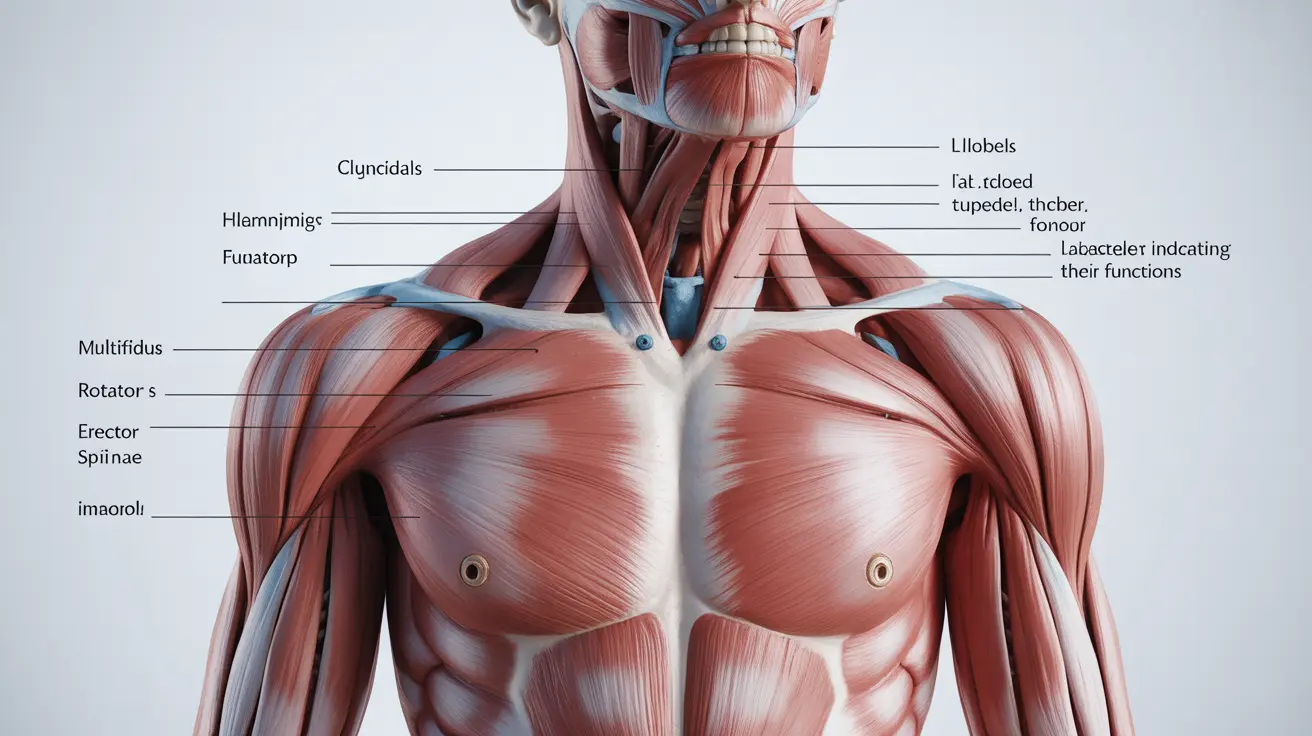
The paraspinal muscles play a crucial role in supporting your spine and enabling proper posture and movement. These essential muscles run along both sides of your vertebral column, from your neck down to your lower back, working together to help you stand, bend, and twist while maintaining spinal stability.
Whether you're dealing with back pain or simply want to maintain a healthy spine, understanding how to care for and strengthen your paraspinal muscles is vital for overall back health and mobility. This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about these important muscles.
Anatomy and Function of Paraspinal Muscles
Paraspinal muscles consist of several muscle groups that run parallel to your spine. These include the multifidus, rotators, and erector spinae muscles. Each group serves specific functions in maintaining spinal health and stability:
- Multifidus: Deep stabilizing muscles that support individual vertebrae
- Rotators: Small muscles that assist in spinal rotation
- Erector spinae: Larger muscles that help with extension and side-bending
Common Paraspinal Muscle Problems
Several conditions can affect your paraspinal muscles, leading to discomfort and reduced mobility:
Muscle Strain
Muscle strain often occurs due to sudden movements, heavy lifting, or repetitive motions. Common symptoms include:
- Localized pain and tenderness
- Muscle stiffness
- Reduced range of motion
- Muscle spasms
Muscle Fatigue
Extended periods of poor posture or overuse can lead to muscle fatigue, causing:
- Dull, aching pain
- Weakness in the back muscles
- Difficulty maintaining good posture
- Increased risk of injury
Maintaining Healthy Paraspinal Muscles
Proper Posture Techniques
Maintaining good posture is crucial for paraspinal muscle health. Key practices include:
- Keeping shoulders back and down
- Maintaining a neutral spine position
- Taking regular breaks from sitting
- Using ergonomic furniture and equipment
Strengthening Exercises
Regular exercise can help maintain strong, flexible paraspinal muscles. Some effective exercises include:
- Bird dog pose
- Superman holds
- Bridge exercises
- Gentle back extensions
Stretching Routines
Regular stretching helps maintain flexibility and prevent muscle tension. Beneficial stretches include:
- Cat-cow stretch
- Child's pose
- Seated spinal twists
- Gentle forward folds
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of paraspinal muscle strain or injury?
The main symptoms include acute pain in the back muscles, muscle spasms, stiffness, reduced range of motion, and tenderness to touch. Pain typically worsens with movement and may be accompanied by inflammation in the affected area.
How can I strengthen my paraspinal muscles to improve posture and reduce back pain?
You can strengthen paraspinal muscles through targeted exercises like bird dog pose, bridges, and gentle back extensions. Start with body weight exercises and gradually progress to more challenging movements as strength improves. Always maintain proper form and stop if you experience pain.
What are some effective exercises for relieving paraspinal muscle spasms?
Gentle stretches like cat-cow poses, child's pose, and light walking can help relieve muscle spasms. Apply heat therapy before stretching and cold therapy afterward. Gentle massage and progressive muscle relaxation techniques can also provide relief.
Can poor posture damage my paraspinal muscles, and how can I prevent this?
Yes, poor posture can strain and weaken paraspinal muscles over time. Prevent damage by maintaining good posture, using ergonomic furniture, taking regular movement breaks, and performing posture-strengthening exercises. Consider using posture-tracking devices or setting regular reminders to check your alignment.
Are there any simple stretches I can do at home to maintain flexibility in my paraspinal muscles?
Yes, several effective stretches can be done at home. These include cat-cow stretches, seated spinal twists, child's pose, and gentle forward folds. Perform these stretches daily, holding each position for 15-30 seconds, and never force a stretch beyond comfort.