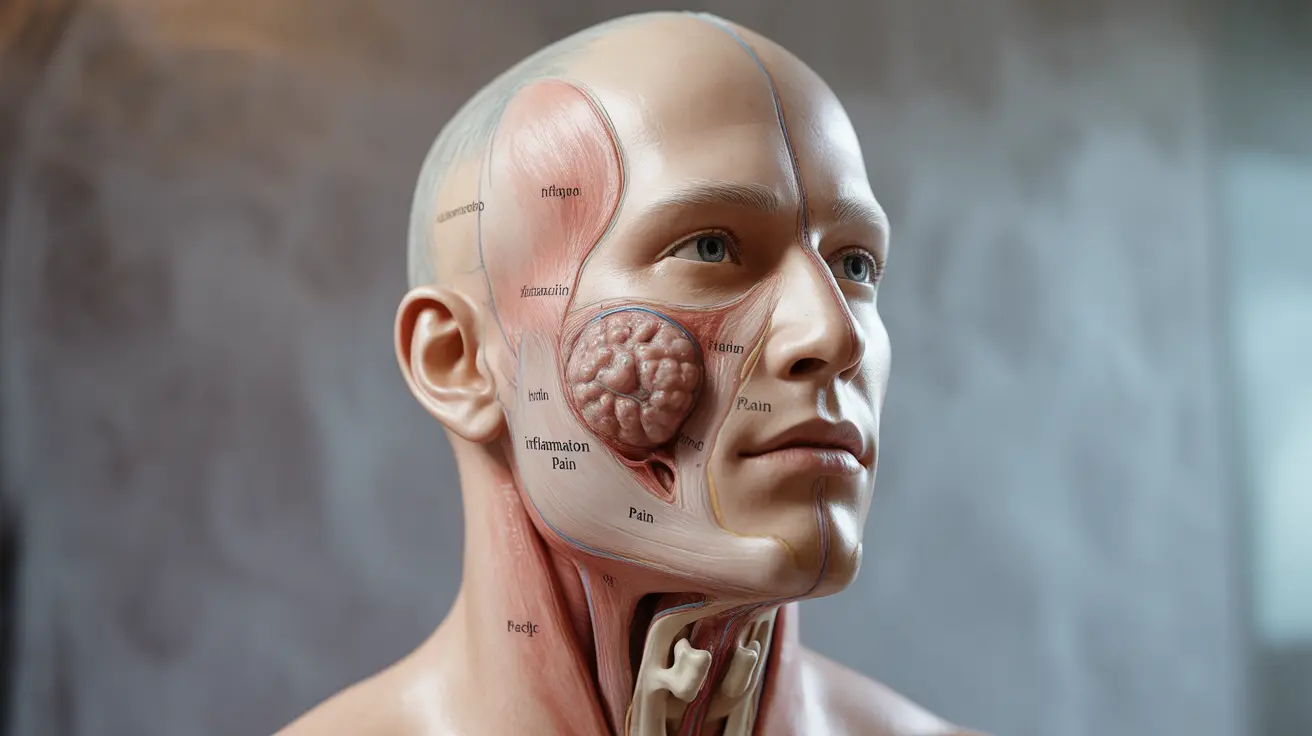
A parotid tumor develops in the parotid glands, the largest of your salivary glands, located in front of and below each ear. While these tumors can be concerning, understanding their nature, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for anyone facing this diagnosis. The majority of parotid tumors are benign, though some can be malignant, making proper medical evaluation essential.
Early detection and appropriate treatment are key factors in managing parotid tumors successfully. This comprehensive guide will help you understand what to look for, what to expect during diagnosis, and the various treatment approaches available.
Signs and Symptoms of Parotid Tumors
Recognizing the signs of a parotid tumor is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- A painless lump near or below the ear
- Gradual swelling in the face or jaw area
- Numbness or weakness in facial muscles
- Difficulty opening the mouth fully
- Changes in facial movement or expression
- Pain in the affected area (less common)
While many of these symptoms can be mild or develop slowly, it's important to seek medical attention if you notice any unusual changes in your face or neck area.
Diagnostic Process for Parotid Tumors
Healthcare providers use various diagnostic tools and procedures to evaluate parotid tumors:
Physical Examination
Your doctor will carefully examine the affected area, checking for lumps, facial muscle function, and any signs of nerve involvement.
Imaging Studies
Several imaging techniques may be used:
- MRI scans
- CT scans
- Ultrasound imaging
- PET scans (in specific cases)
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
This minimally invasive procedure involves taking a small tissue sample from the tumor for laboratory analysis to determine if the growth is benign or malignant.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on whether the tumor is benign or malignant, its size, and location:
Surgical Options
The primary treatment for most parotid tumors is surgical removal (parotidectomy). Types of surgery include:
- Superficial parotidectomy
- Total parotidectomy
- Partial parotidectomy
Additional Treatments
For malignant tumors, additional treatments may include:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Post-Treatment Care and Recovery
Recovery from parotid tumor treatment typically involves:
- Regular follow-up appointments
- Facial exercises (if recommended)
- Careful wound care
- Monitoring for potential complications
- Lifestyle modifications as needed
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a parotid tumor and how can I tell if it might be cancerous?
A painless lump near the ear is the most common symptom. While it's difficult to determine if a tumor is cancerous without medical testing, rapid growth, pain, facial weakness, or paralysis may suggest malignancy.How is a parotid tumor diagnosed and what tests will my doctor use?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, imaging studies (MRI, CT, or ultrasound), and often a fine needle aspiration biopsy to determine the tumor's nature.What are the treatment options for benign versus malignant parotid tumors?
Benign tumors are usually treated with surgical removal alone, while malignant tumors may require a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.What risks and complications should I expect from parotid tumor surgery (parotidectomy)?
Potential complications include temporary or permanent facial nerve weakness, numbness, Frey's syndrome (sweating while eating), and scarring. Your surgeon will discuss specific risks based on your case.How can I reduce the risk of parotid tumor recurrence after treatment?
Regular follow-up appointments, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding tobacco use, and promptly reporting any new symptoms to your healthcare provider are essential for preventing or catching recurrence early.