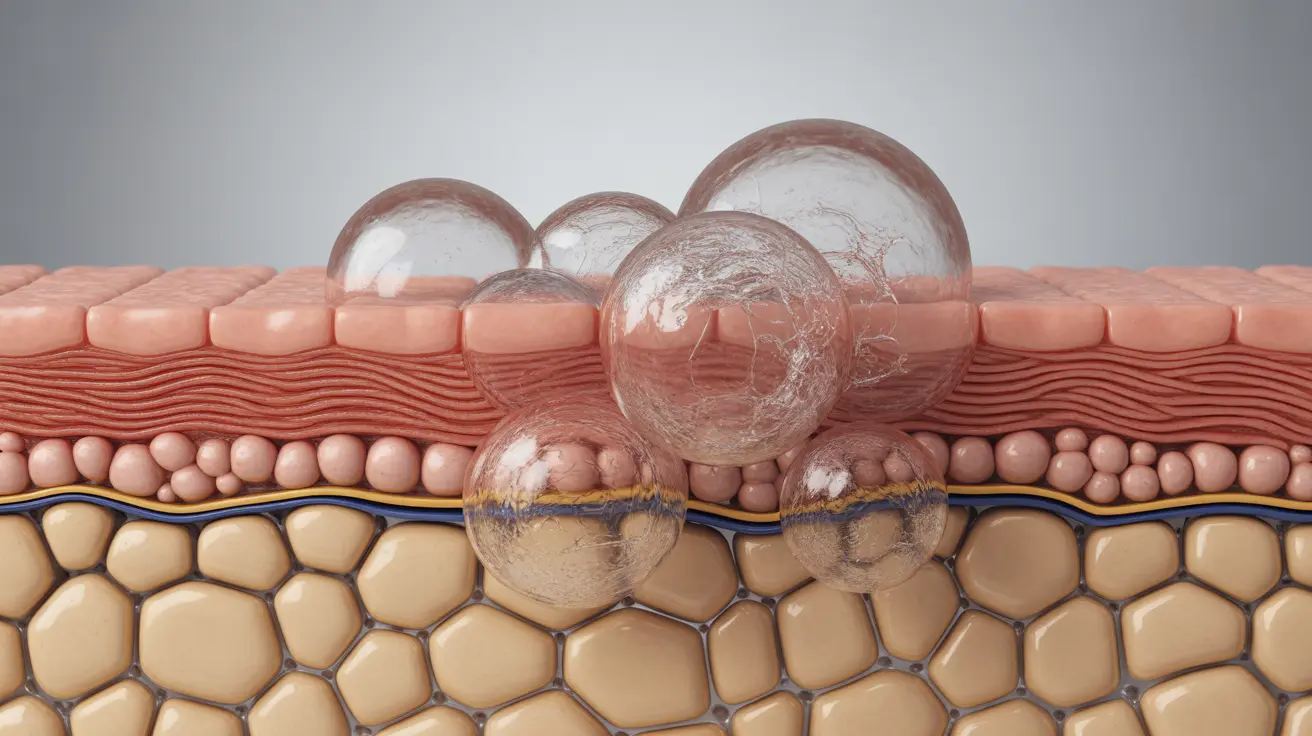
Bullous pemphigoid is a rare but serious autoimmune skin condition that primarily affects older adults, causing large, fluid-filled blisters to develop on the skin. This chronic condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the connection between the outer and inner layers of skin, leading to characteristic blistering and inflammation.
While the condition can be distressing, understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing it effectively. Early recognition and proper medical intervention can help control symptoms and prevent complications.
Understanding the Nature of Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid develops when the body's immune system mistakenly targets specific proteins that help hold layers of skin together. This autoimmune response leads to inflammation and the formation of blisters between the epidermis and dermis layers of skin.
The condition typically affects people over 60 years of age, though younger adults and children can occasionally develop it. While the exact trigger isn't always clear, certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
The initial signs of bullous pemphigoid often begin with redness, itching, and inflammation of the skin. As the condition progresses, characteristic symptoms include:
- Large, fluid-filled blisters that don't break easily
- Itchy, red, or inflamed skin around the blisters
- Blisters commonly appearing on the abdomen, groin, arms, and legs
- Potential involvement of mucous membranes in some cases
Diagnostic Process and Testing
Accurate diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid requires several steps and specialized tests. Healthcare providers typically use:
- Skin biopsy
- Direct immunofluorescence testing
- Blood tests for specific antibodies
- Detailed medical history evaluation
Treatment Approaches and Management
Treatment for bullous pemphigoid typically involves a combination of medications and careful skin care. The main treatment options include:
- Corticosteroids (topical and oral)
- Immunosuppressive medications
- Antibiotics when necessary
- Proper wound care and skin protection
Managing Side Effects of Treatment
While corticosteroids are effective in treating bullous pemphigoid, they can cause significant side effects. Healthcare providers carefully monitor patients and may adjust treatment plans to minimize complications while maintaining effectiveness.
Lifestyle Management and Self-Care
People with bullous pemphigoid can take several steps to support their treatment and protect their skin:
- Gentle skin care routines
- Avoiding trauma to the skin
- Regular medical follow-up
- Proper nutrition and hydration
- Protecting the skin from sun exposure
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and early signs of bullous pemphigoid?
Early signs include redness, itching, and skin inflammation, followed by the development of large, tense blisters. These blisters typically appear on the trunk, arms, legs, and in skin folds. Initial symptoms may resemble eczema or hives before blisters develop.
How is bullous pemphigoid diagnosed by doctors?
Doctors diagnose bullous pemphigoid through a combination of physical examination, skin biopsy, direct immunofluorescence testing, and blood tests that look for specific antibodies associated with the condition. A detailed medical history is also important for accurate diagnosis.
What treatments are most effective for managing bullous pemphigoid and its symptoms?
The most effective treatments include topical and oral corticosteroids, along with immunosuppressive medications. Treatment plans are typically tailored to each patient's specific situation and may include a combination of medications to control symptoms while minimizing side effects.
Can certain medications or factors trigger bullous pemphigoid?
Yes, certain medications, ultraviolet light exposure, radiation therapy, and some medical procedures can trigger bullous pemphigoid. Some medications associated with triggering the condition include certain antibiotics, diuretics, and blood pressure medications.
What are the potential side effects of corticosteroids used to treat bullous pemphigoid and how can they be minimized?
Common side effects of corticosteroids include increased risk of infections, bone loss, diabetes, and skin thinning. These can be minimized through careful dosing, regular monitoring, using the lowest effective dose, and implementing protective measures such as calcium and vitamin D supplementation when appropriate.