A perinatal stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs either shortly before birth, during the delivery process, or in the first few weeks after birth. This type of stroke can have significant implications for a child's development, making it crucial for parents and healthcare providers to understand its causes, recognize its signs, and know about available treatment options.
While perinatal strokes are relatively rare, affecting approximately 1 in 2,300 to 5,000 live births, early recognition and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for affected infants. Understanding this condition is essential for both medical professionals and parents to ensure the best possible care for newborns.
Understanding the Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of perinatal stroke. These include:
- Blood clotting disorders in either mother or baby
- Infections during pregnancy or early infancy
- Congenital heart problems
- Pregnancy complications
- Blood vessel abnormalities
- Maternal health conditions such as preeclampsia
Understanding these risk factors helps healthcare providers monitor high-risk pregnancies more closely and potentially prevent some cases of perinatal stroke.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Identifying a perinatal stroke can be challenging as newborns cannot communicate their symptoms. However, there are several warning signs parents and healthcare providers should watch for:
Immediate Signs
- Seizures within the first few days of life
- Extreme lethargy or difficulty feeding
- Abnormal muscle tone
- Favoring one side of the body
- Breathing difficulties
Later Signs
- Delayed milestone achievement
- Early hand preference (before 12 months)
- Muscle weakness on one side
- Developmental delays
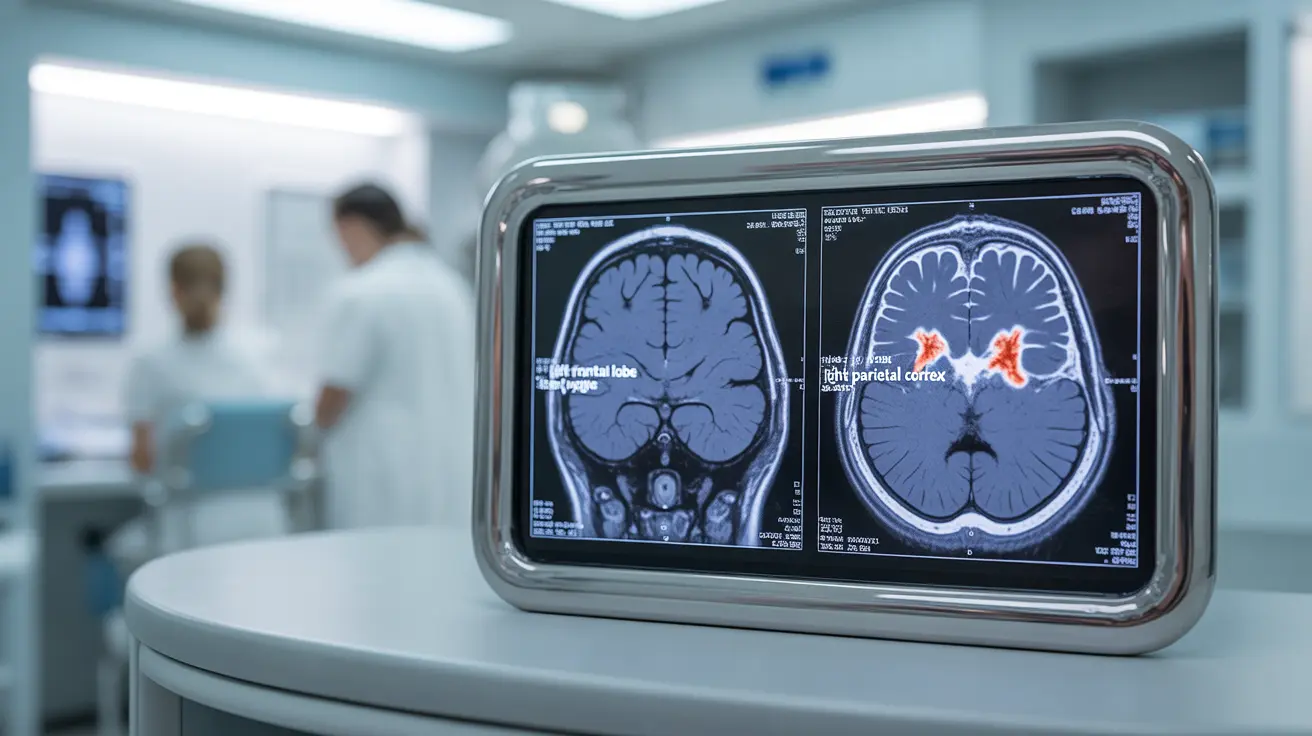
Diagnosis and Testing
When a perinatal stroke is suspected, healthcare providers typically employ several diagnostic tools:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Blood tests to check for clotting disorders
- Cardiac evaluation
These tests help determine the location and extent of the stroke, which is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Approaches and Early Intervention
Treatment for perinatal stroke focuses on both immediate care and long-term rehabilitation. The approach typically includes:
Immediate Medical Care
- Stabilizing vital signs
- Managing seizures if present
- Preventing further complications
- Addressing underlying causes
Long-term Rehabilitation
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech and language therapy
- Developmental intervention programs
Early intervention is crucial in maximizing recovery potential and minimizing long-term effects. The brain's plasticity during infancy and early childhood can help compensate for damaged areas.
Long-term Outlook and Support
The long-term impact of a perinatal stroke varies significantly among children. While some may experience minimal effects, others might face more significant challenges. Regular monitoring and ongoing support are essential for optimal outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes and risk factors of perinatal stroke in newborns? The most common causes include blood clotting disorders, infections, heart problems, and pregnancy complications like preeclampsia. Risk factors can be present in either the mother or baby.
What symptoms should parents watch for that may indicate a perinatal stroke in their baby? Key symptoms include seizures, lethargy, feeding difficulties, favoring one side of the body, and abnormal muscle tone. Later signs may include developmental delays and early hand preference.
How is perinatal stroke diagnosed and what tests are typically used? Diagnosis typically involves MRI or CT scans, EEG monitoring, blood tests, and cardiac evaluations to determine the location and extent of the stroke.
What are the possible long-term effects and outcomes of a perinatal stroke? Long-term effects can range from mild to severe and may include motor difficulties, learning challenges, seizures, or developmental delays. However, many children show significant improvement with early intervention.
How is perinatal stroke treated and can early intervention improve a child's prognosis? Treatment involves immediate medical care to stabilize the condition and prevent complications, followed by long-term rehabilitation services. Early intervention through various therapies can significantly improve outcomes due to the brain's plasticity during early development.