Phlebitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of a vein, can range from a minor inconvenience to a serious medical concern requiring immediate attention. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the different types of phlebitis, recognize its symptoms, and learn about effective treatment approaches.
Whether you're dealing with superficial phlebitis or the more serious deep vein phlebitis, early recognition and proper medical care are essential for preventing complications and ensuring the best possible outcome.
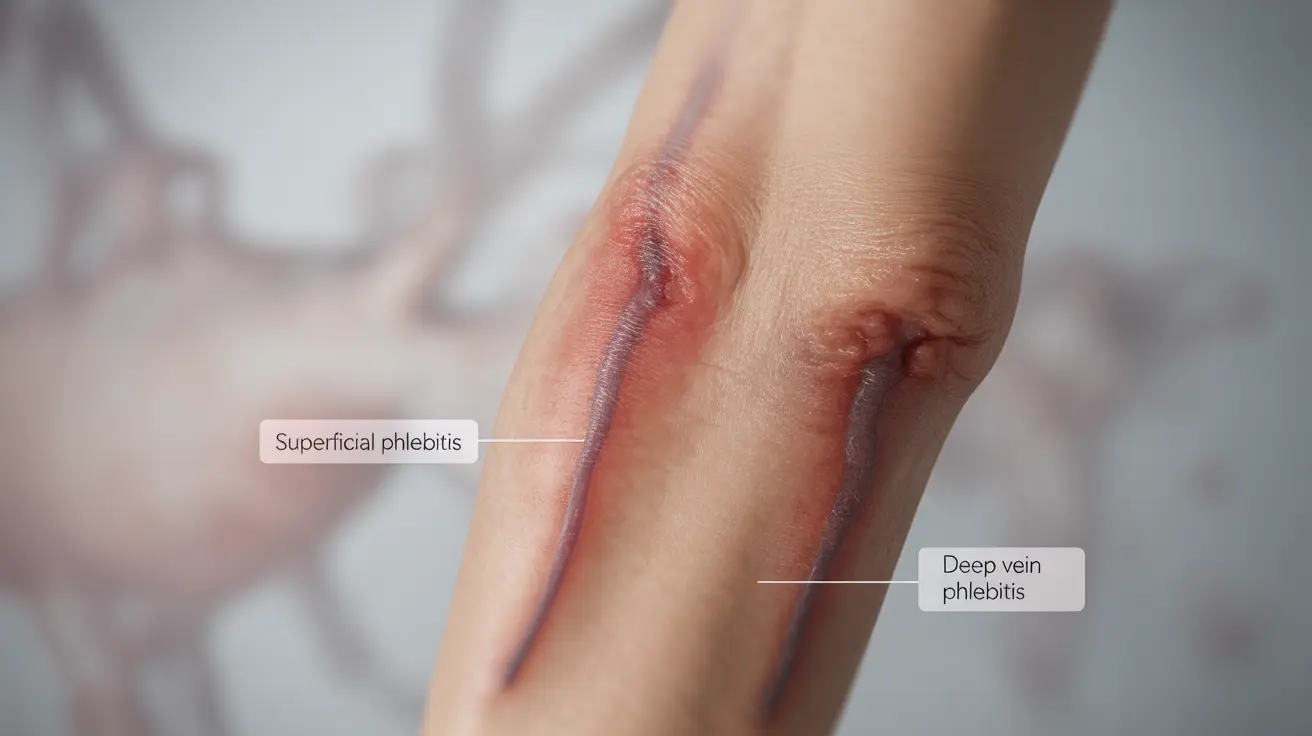
Understanding Phlebitis and Its Types
Phlebitis occurs in two main forms: superficial phlebitis, affecting veins near the skin's surface, and deep vein phlebitis, which impacts larger veins deeper in the body. Each type presents different risks and requires specific treatment approaches.
Superficial phlebitis typically causes localized discomfort and visible symptoms but rarely leads to serious complications. However, deep vein phlebitis requires immediate medical attention as it can lead to dangerous blood clots.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Early detection of phlebitis symptoms can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Common indicators include:
- Redness along the affected vein
- Warmth and tenderness in the area
- Swelling of the affected limb
- Pain or discomfort that may worsen when touching the area
- Hardening of the vein
- Skin discoloration
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can increase your likelihood of developing phlebitis:
- Recent surgery or injury
- Extended periods of inactivity
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Varicose veins
- Recent IV placement
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose phlebitis accurately. These may include:
- Physical examination
- Ultrasound imaging
- Blood tests
- Venography in some cases
Treatment Approaches
Superficial Phlebitis Treatment
Treatment for superficial phlebitis typically involves:
- Warm compresses to reduce inflammation
- Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications
- Compression stockings
- Regular movement and elevation of the affected area
Deep Vein Phlebitis Management
Deep vein phlebitis requires more aggressive treatment, including:
- Blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants)
- Hospital admission in severe cases
- Close medical monitoring
- Possible surgical intervention
Prevention Strategies
Taking proactive steps can help reduce your risk of developing phlebitis:
- Stay active and avoid prolonged immobility
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stay well-hydrated
- Exercise regularly
- Wear compression stockings when recommended
- Move frequently during long trips
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of phlebitis and how can I recognize it?
Common symptoms include redness, warmth, tenderness along the vein, swelling, and pain in the affected area. The vein may feel hard and rope-like under the skin, and the surrounding area might appear discolored.
How is phlebitis diagnosed and what tests might my doctor order?
Doctors typically start with a physical examination and medical history review. They may order ultrasound imaging to assess blood flow and clot formation, and blood tests to check for inflammation or clotting disorders.
What are the treatment options for superficial versus deep vein phlebitis?
Superficial phlebitis usually requires conservative treatment with warm compresses, anti-inflammatory medications, and compression stockings. Deep vein phlebitis needs more intensive treatment, including blood thinners, possible hospitalization, and careful monitoring.
What causes phlebitis and what factors increase my risk of developing it?
Phlebitis can be caused by injury, surgery, prolonged immobility, obesity, pregnancy, or underlying medical conditions. Risk factors include smoking, varicose veins, recent IV placement, and certain medical conditions affecting blood clotting.
How can I prevent phlebitis, especially if I have risk factors like varicose veins or prolonged inactivity?
Prevention strategies include staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, wearing compression stockings when recommended, and taking frequent breaks to move during long periods of sitting. If you have varicose veins, following your doctor's management plan is crucial.