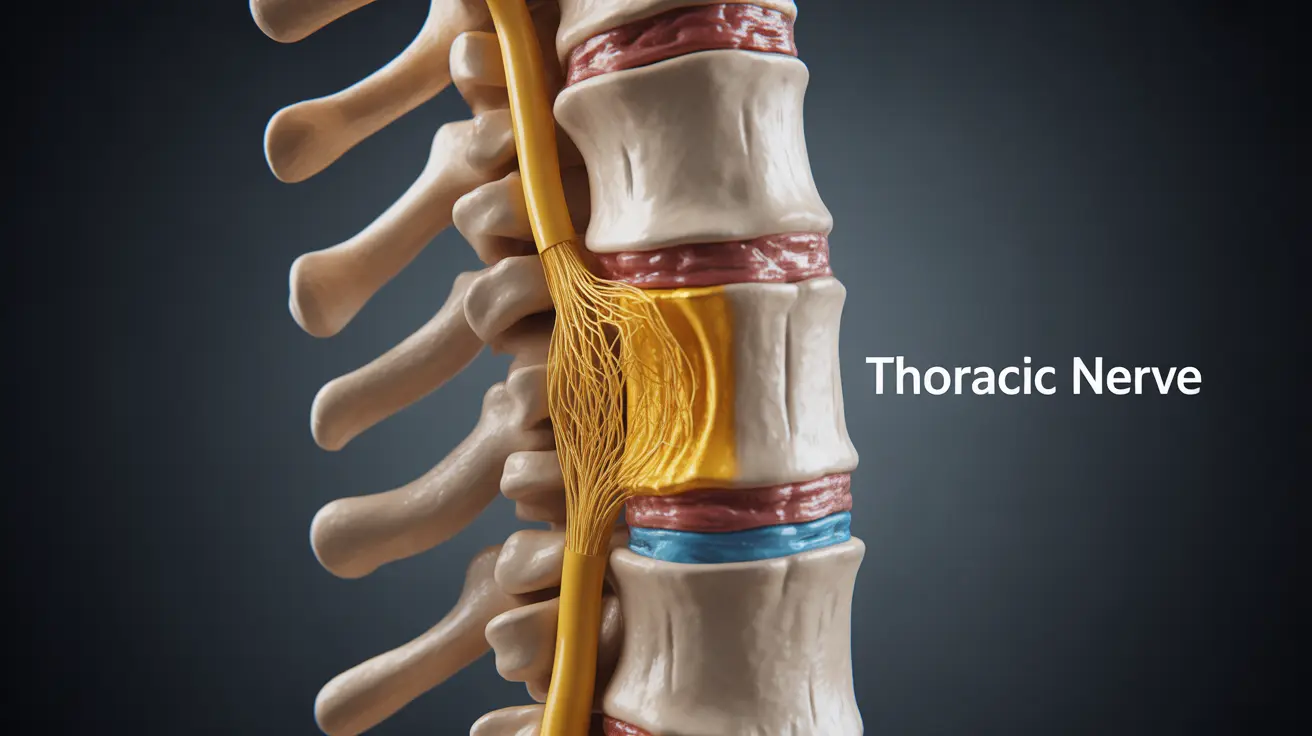
A pinched nerve in the upper back can be an incredibly uncomfortable and concerning condition that affects your daily activities and quality of life. When nerve tissue becomes compressed or irritated in the thoracic spine (upper back), it can lead to various symptoms that require proper attention and care.
Understanding this condition is crucial for seeking appropriate treatment and preventing future occurrences. This comprehensive guide will explore the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies for managing a pinched nerve in the upper back.
Understanding the Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the upper back is the first step toward getting appropriate treatment. Common indicators include:
- Sharp, burning pain in the upper back
- Radiating pain that travels along the affected nerve
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Muscle weakness in the affected area
- Increased pain with certain movements
- "Pins and needles" sensation
- Reduced range of motion
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to developing a pinched nerve in the upper back:
Physical Factors
- Poor posture
- Herniated discs
- Bone spurs
- Spinal stenosis
- Traumatic injury
Lifestyle and Health Factors
- Obesity
- Repetitive movements
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes
- Occupational hazards
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose a pinched nerve in the upper back accurately:
Physical Examination
During the initial consultation, your doctor will perform a thorough physical examination, checking your:
- Range of motion
- Muscle strength
- Reflexes
- Sensation in affected areas
Imaging Tests
Additional diagnostic tools may include:
- X-rays
- MRI scans
- CT scans
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Nerve conduction studies
Treatment Approaches
Conservative Treatment Options
Initial treatment typically focuses on non-invasive approaches:
- Rest and activity modification
- Physical therapy exercises
- Over-the-counter pain medications
- Ice and heat therapy
- Gentle stretching routines
Advanced Treatment Methods
If conservative treatments don't provide relief, your healthcare provider might recommend:
- Prescription medications
- Steroid injections
- Professional physical therapy
- Chiropractic care
- In severe cases, surgical intervention
Prevention Strategies
Preventing a pinched nerve involves maintaining good habits and proper body mechanics:
Posture Improvement
- Maintain proper sitting and standing posture
- Use ergonomic furniture
- Take regular breaks from prolonged sitting
- Practice proper lifting techniques
Exercise and Stretching
- Regular strength training for back muscles
- Gentle stretching exercises
- Core-strengthening activities
- Low-impact aerobic exercise
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a pinched nerve in the upper back?
Common symptoms include sharp or burning pain, numbness, tingling sensations, muscle weakness, and radiating pain along the affected nerve pathway. You might also experience reduced range of motion and increased discomfort with certain movements.
What causes a pinched nerve in the upper back and how can poor posture contribute?
A pinched nerve can be caused by various factors, including herniated discs, bone spurs, and trauma. Poor posture significantly contributes by creating unnecessary pressure on nerves and surrounding tissues, leading to compression and inflammation over time.
How is a pinched nerve in the upper back diagnosed by doctors?
Doctors diagnose a pinched nerve through a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans. They may also use nerve conduction studies or EMG to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of nerve involvement.
What are the most effective treatments for relieving a pinched nerve in the upper back?
Effective treatments include a combination of rest, physical therapy, pain management techniques, and in some cases, medication or steroid injections. Conservative treatments are typically tried first, with surgery reserved for severe cases that don't respond to other treatments.
How can I prevent a pinched nerve in the upper back through lifestyle or exercises?
Prevention strategies include maintaining good posture, regular exercise focusing on core and back strength, proper ergonomics at work, and avoiding repetitive movements that strain the upper back. Regular stretching and maintaining a healthy weight also help reduce the risk of developing a pinched nerve.