A pleural friction rub is a distinctive sound that doctors can hear through a stethoscope when the pleural membranes in your lungs become inflamed and rub against each other. This condition often indicates an underlying respiratory or inflammatory condition that requires medical attention. Understanding the characteristics, causes, and implications of a pleural friction rub is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is a Pleural Friction Rub?
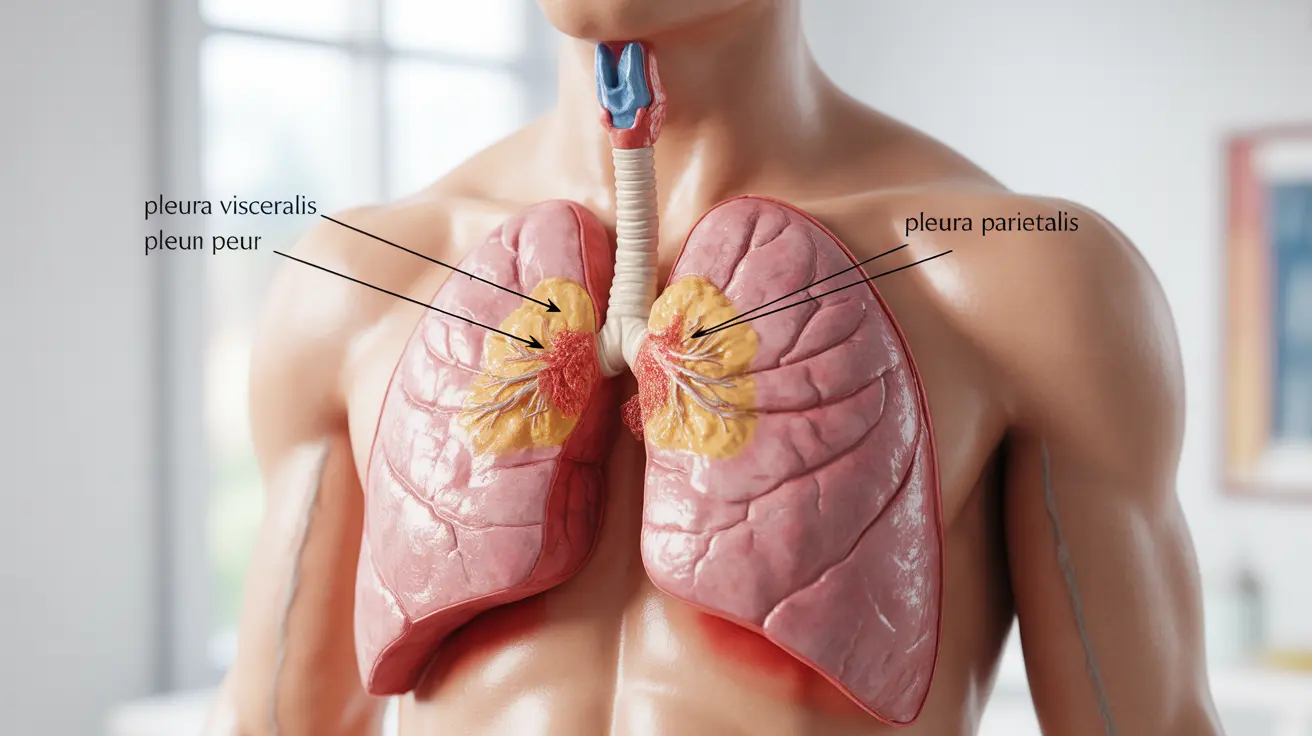
The pleura consists of two thin layers of tissue that surround your lungs. In healthy individuals, these layers glide smoothly against each other during breathing. However, when inflammation or other conditions affect these membranes, they can become rough and create a distinctive scratching or grating sound known as a pleural friction rub.
Characteristics and Sound Description
A pleural friction rub typically produces a creaking or scratching noise that healthcare providers can hear during both inhalation and exhalation. This sound is often described as similar to walking on fresh snow or the sound of leather rubbing against leather. The sound is usually most audible when the patient takes deep breaths.
Common Causes
Several conditions can lead to the development of a pleural friction rub:
- Pleurisy (inflammation of the pleural membranes)
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism
- Lung cancer
- Autoimmune conditions like lupus
- Chest trauma
- Post-cardiac surgery complications
Associated Symptoms
Patients experiencing a pleural friction rub often report various accompanying symptoms:
- Sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Dry cough
- Fever in some cases
- General discomfort in the chest area
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose the underlying cause of a pleural friction rub:
- Physical examination with a stethoscope
- Chest X-rays
- CT scans
- Blood tests
- Pleural fluid analysis if fluid is present
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to rule out cardiac causes
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for a pleural friction rub focuses on addressing the underlying condition:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Pain management
- Treatment of underlying autoimmune conditions
- Surgical intervention when necessary
- Supportive care measures
When to Seek Medical Attention
It's important to seek immediate medical care if you experience:
- Severe chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Persistent cough
- Unexplained fever
- Worsening symptoms despite treatment
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What does a pleural friction rub sound like and what does it indicate? A: A pleural friction rub sounds like a creaking or grating noise, similar to walking on fresh snow. It indicates inflammation or roughening of the pleural membranes surrounding the lungs, often due to an underlying respiratory or inflammatory condition.
Q: What are the common causes of a pleural friction rub? A: Common causes include pleurisy, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, lung cancer, autoimmune conditions, chest trauma, and post-cardiac surgery complications. Each of these conditions can cause inflammation of the pleural membranes.
Q: What symptoms should prompt me to see a doctor if I have a pleural friction rub? A: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, persistent cough, unexplained fever, or worsening symptoms. These could indicate a serious underlying condition requiring prompt treatment.
Q: How is a pleural friction rub diagnosed by doctors? A: Doctors diagnose pleural friction rub through physical examination with a stethoscope, along with additional tests such as chest X-rays, CT scans, blood tests, pleural fluid analysis, and ECGs to determine the underlying cause.
Q: What treatment options are available for conditions causing pleural friction rub? A: Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics for infections, anti-inflammatory medications, pain management, treatment of autoimmune conditions, surgical intervention when necessary, and supportive care measures.