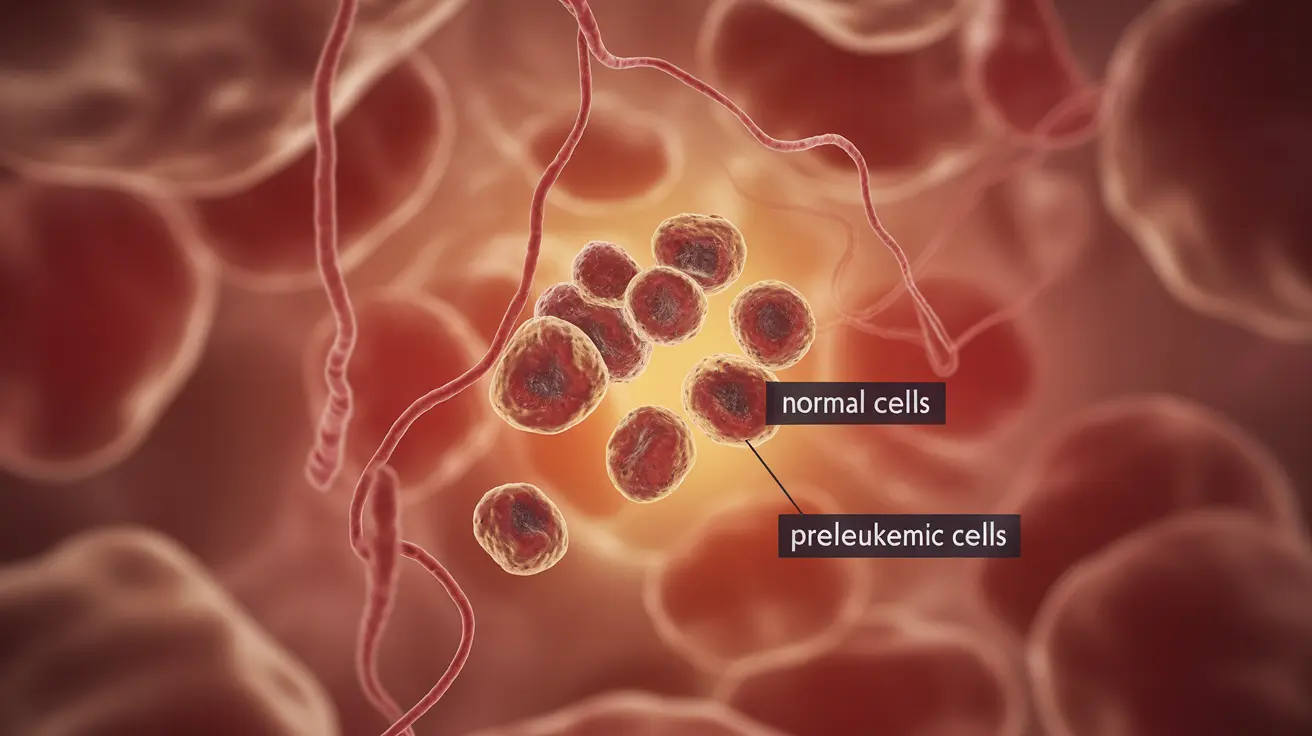
Preleukemia, medically known as myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), is a group of blood disorders that affect the body's ability to produce healthy blood cells. This condition occurs when the bone marrow fails to create enough properly functioning blood cells, potentially leading to serious health complications if left untreated. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and treatment options for preleukemia is crucial for early detection and optimal management.
What is Preleukemia (MDS)?
Preleukemia occurs when blood-forming cells in the bone marrow become abnormal, resulting in the production of immature or defective blood cells. This condition primarily affects older adults and can vary in severity, from mild cases requiring monitoring to more severe forms that may progress to acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Common Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of preleukemia often develop gradually and may initially be subtle. Common indicators include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- Unexplained fever
- Petechiae (small red spots under the skin)
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing preleukemia involves several specialized tests and procedures:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Bone marrow biopsy and aspiration
- Cytogenetic testing
- Flow cytometry
- Molecular testing
These tests help doctors determine the specific type of MDS and its severity, which is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can increase the risk of developing preleukemia:
- Advanced age (most common in people over 60)
- Previous cancer treatment with chemotherapy or radiation
- Exposure to certain chemicals, including benzene
- Smoking
- Genetic disorders
- Male gender (slightly higher risk)
Treatment Approaches
Supportive Care
Many patients benefit from supportive treatments that address specific symptoms:
- Blood transfusions
- Antibiotics for infections
- Growth factors to stimulate blood cell production
- Regular monitoring and preventive care
Disease-Modifying Treatments
More intensive treatments may include:
- Hypomethylating agents
- Lenalidomide
- Chemotherapy
- Stem cell transplantation (for eligible patients)
Prevention and Management
While preleukemia cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle choices and precautions can help manage the condition:
- Regular medical check-ups
- Avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals
- Maintaining good hygiene to prevent infections
- Following a healthy diet and exercise routine
- Quitting smoking
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of preleukemia (myelodysplastic syndrome) that I should watch for? Common symptoms include persistent fatigue, weakness, frequent infections, easy bruising or bleeding, shortness of breath, and pale skin. Some patients may also experience unexplained fever and small red spots under the skin called petechiae.
How is preleukemia (MDS) diagnosed and what tests are involved? Diagnosis typically involves a complete blood count (CBC), bone marrow biopsy and aspiration, cytogenetic testing, flow cytometry, and molecular testing. These tests help determine the type and severity of MDS.
What treatment options are available for managing preleukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome? Treatment options include supportive care (blood transfusions, antibiotics), growth factors, hypomethylating agents, lenalidomide, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation for eligible patients. The choice of treatment depends on the specific type of MDS and individual patient factors.
Can preleukemia (MDS) progress to acute myeloid leukemia, and how can this be prevented? Yes, preleukemia can progress to acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in some cases. While progression cannot always be prevented, early detection and appropriate treatment can help manage the condition and potentially slow its progression. Regular monitoring and following prescribed treatments are essential.
What are the typical causes and risk factors for developing preleukemia (myelodysplastic syndrome)? Risk factors include advanced age (over 60), previous cancer treatments, exposure to certain chemicals like benzene, smoking, genetic disorders, and being male. While some risk factors cannot be modified, others, such as smoking cessation and avoiding chemical exposure, can be controlled.