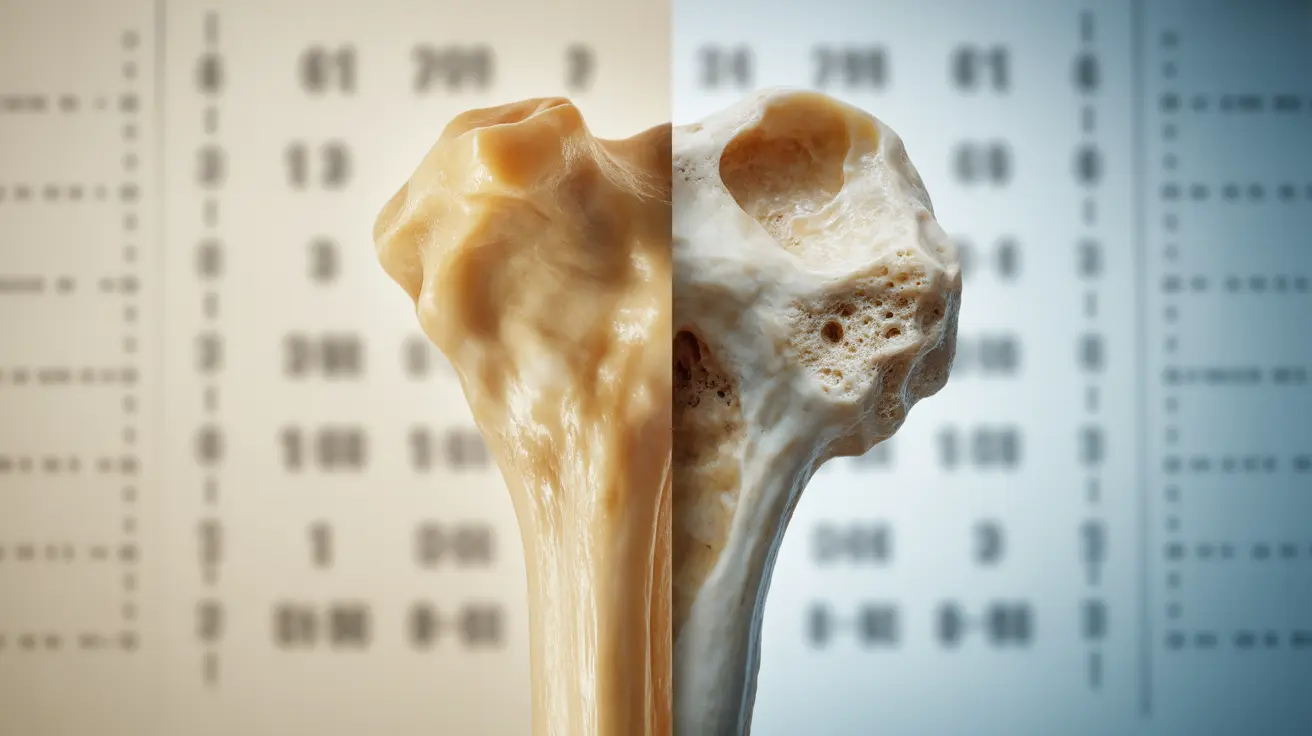
Primary osteoporosis is a progressive bone condition that occurs when bone density and strength naturally decline with age or after menopause. Unlike secondary osteoporosis, which develops due to specific medical conditions or medications, primary osteoporosis is largely related to the natural aging process and hormonal changes.
Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and management, as it affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact quality of life if left untreated. This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects of primary osteoporosis, from recognition to treatment.
Types of Primary Osteoporosis
Primary osteoporosis typically manifests in two main forms:
Postmenopausal Osteoporosis (Type 1)
This type occurs in women after menopause due to decreased estrogen production. The rapid bone loss typically affects trabecular bone, commonly found in the vertebrae and wrist bones.
Age-Related Osteoporosis (Type 2)
Also known as senile osteoporosis, this type affects both men and women over 70. It involves the loss of both cortical and trabecular bone, leading to hip and vertebral fractures.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Early-stage primary osteoporosis often develops without noticeable symptoms, earning it the nickname "silent disease." However, as the condition progresses, several signs may emerge:
- Back pain caused by fractured or collapsed vertebrae
- Loss of height over time
- Stooped posture or kyphosis
- Bones that break more easily than expected
- Reduced grip strength
- Decreased mobility
Diagnostic Procedures and Assessment
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose primary osteoporosis and assess fracture risk:
Bone Density Testing
The primary diagnostic tool is the DXA (Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scan, which measures bone mineral density at key sites like the hip and spine. Results are expressed as T-scores, with scores of -2.5 or lower indicating osteoporosis.
Additional Assessments
- Complete medical history evaluation
- Physical examination
- Blood tests to rule out secondary causes
- FRAX® tool calculation for fracture risk
- Height measurements to track changes
Treatment Approaches
Managing primary osteoporosis typically involves a comprehensive treatment plan:
Medication Options
Several medications can help slow bone loss or build new bone:
- Bisphosphonates
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
- Hormone therapy
- Bone-forming agents
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements
Lifestyle Modifications
Essential lifestyle changes can help manage the condition:
- Regular weight-bearing exercise
- Balance training to prevent falls
- Proper nutrition rich in calcium and vitamin D
- Smoking cessation
- Limited alcohol consumption
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms and signs of primary osteoporosis?
The most common signs include height loss, stooped posture, back pain, and increased susceptibility to fractures. Early stages may be symptomless, which makes regular screening crucial for at-risk individuals.
How is primary osteoporosis diagnosed and what tests are used to assess bone loss?
Primary osteoporosis is mainly diagnosed through DXA scans, which measure bone mineral density. Additional assessments may include blood tests, medical history review, and physical examination to evaluate overall bone health and fracture risk.
What treatment options are effective for slowing bone loss in primary osteoporosis?
Effective treatments include medications like bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, and bone-forming agents, combined with calcium and vitamin D supplementation. These treatments are most successful when paired with appropriate lifestyle modifications.
How can lifestyle changes help prevent fractures in people with primary osteoporosis?
Regular weight-bearing exercise, balance training, proper nutrition, fall prevention strategies, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce fracture risk. Environmental modifications at home can also help prevent falls.
What are the differences between postmenopausal osteoporosis and senile osteoporosis?
Postmenopausal osteoporosis occurs in women after menopause due to estrogen decline and primarily affects trabecular bone. Senile osteoporosis affects both men and women over 70 and involves the loss of both cortical and trabecular bone.