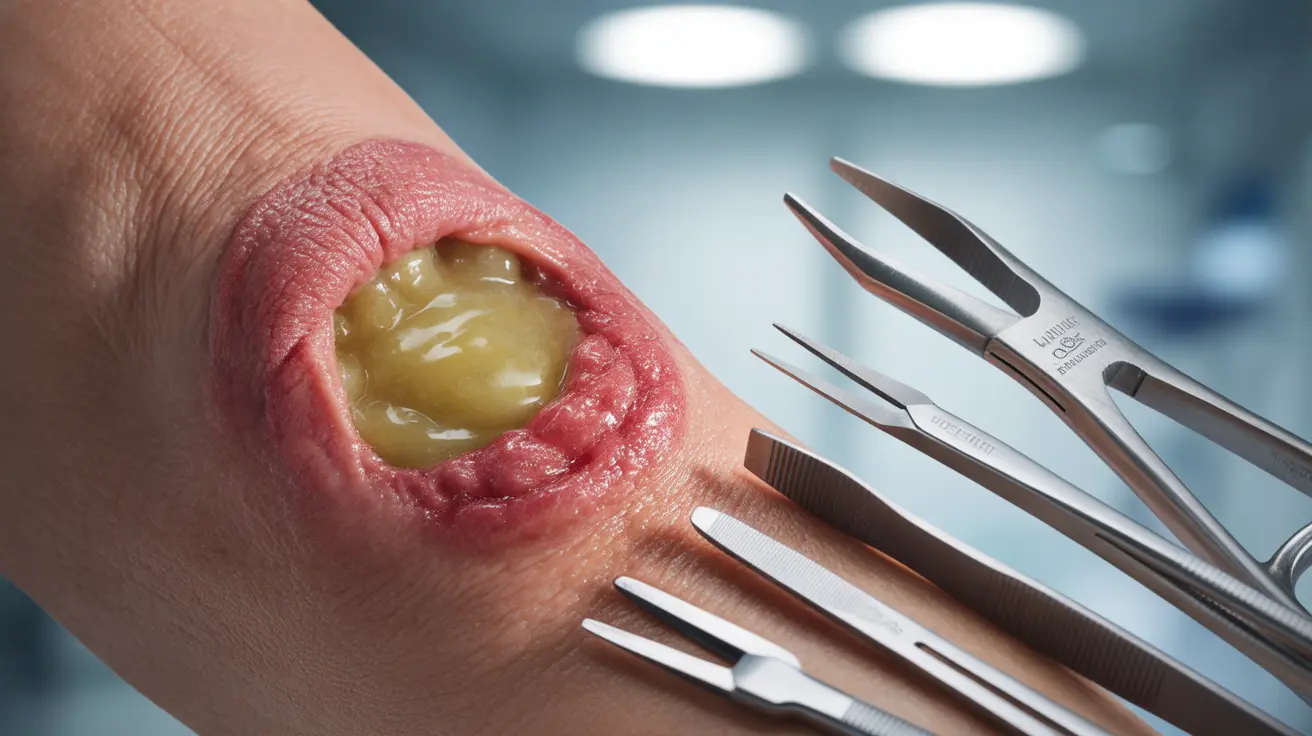
Purulent drainage, also known as pus, is a common sign of infection in wounds that requires careful attention and proper medical care. This thick, cloudy fluid typically indicates that your body is actively fighting against harmful bacteria or other pathogens. Understanding what purulent drainage is, how to identify it, and when to seek medical help is crucial for proper wound healing and preventing complications.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the characteristics of purulent drainage, its causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies to help you maintain proper wound care and recognize when professional medical attention is necessary.
Identifying Purulent Drainage
Purulent drainage has distinct characteristics that set it apart from normal wound drainage. The fluid typically appears:
- Thick and opaque
- Yellow, green, or brownish in color
- Sometimes accompanied by an unpleasant odor
- Creamy or paste-like in consistency
When examining a wound, it's important to distinguish between normal drainage and purulent drainage. Normal wound drainage is typically clear or slightly yellow and thin in consistency, while purulent drainage indicates the presence of white blood cells fighting an infection.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of purulent drainage in wounds:
Bacterial Infections
The most common cause is bacterial infection, which can occur when bacteria enter through breaks in the skin or during surgical procedures.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to contaminated surfaces, poor hygiene, or inadequate wound care can increase the risk of developing purulent drainage.
Medical Conditions
Certain conditions can make you more susceptible to developing infections that lead to purulent drainage:
- Diabetes
- Compromised immune system
- Poor circulation
- Chronic skin conditions
Warning Signs and When to Seek Medical Care
While some wound drainage is normal during the healing process, certain signs indicate the need for immediate medical attention:
- Increased redness or warmth around the wound
- Fever or chills
- Spreading infection or red streaks
- Significant pain or swelling
- Foul-smelling drainage
- Dark or discolored drainage
Treatment Approaches
The treatment of purulent drainage typically involves a multi-faceted approach:
Medical Interventions
Healthcare providers may recommend:
- Prescribed antibiotics (oral or topical)
- Professional wound cleaning and debridement
- Regular wound assessment and monitoring
- Specialized dressing changes
Home Care Measures
Proper wound care at home is essential and may include:
- Regular cleaning with prescribed solutions
- Appropriate dressing changes using sterile techniques
- Keeping the wound clean and dry
- Following medical instructions precisely
Prevention Strategies
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing purulent drainage:
- Practice proper hand hygiene
- Keep wounds clean and covered
- Change dressings as recommended
- Follow post-operative care instructions carefully
- Maintain good overall health and nutrition
Frequently Asked Questions
What does purulent drainage look like, and how can I tell if my wound is infected?
Purulent drainage appears as thick, opaque fluid that's typically yellow, green, or brown in color. Signs of infection include increased redness, warmth around the wound, pain, swelling, and fever. The presence of purulent drainage, especially when accompanied by these symptoms, strongly suggests an infection.
What are the common causes and risk factors for developing purulent drainage in a wound?
Common causes include bacterial infections, poor wound care, compromised immune system, diabetes, and exposure to contaminated environments. Risk factors include chronic medical conditions, poor circulation, and inadequate hygiene practices.
When should I see a doctor for purulent drainage, and what are the signs of a serious infection?
Seek medical attention if you notice fever, increasing pain, spreading redness, red streaks, significant swelling, or foul-smelling drainage. Also consult a healthcare provider if the drainage is excessive or doesn't improve with proper wound care.
How is purulent drainage treated, and what are the options for wound care at home?
Treatment typically involves antibiotics, professional wound cleaning, and proper dressing changes. At home, maintain good wound hygiene, follow prescribed care instructions, and keep the wound clean and properly dressed.
What steps can I take to prevent purulent drainage and reduce the risk of wound infection?
Prevention includes practicing good hand hygiene, keeping wounds clean and covered, changing dressings regularly, following medical instructions carefully, and maintaining overall good health through proper nutrition and lifestyle habits.