When an abscess forms in your body, it creates a painful pocket of pus that often requires medical intervention. Understanding the process of pus drainage from an abscess is crucial for anyone facing this common medical condition. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about abscess drainage, from recognizing the need for the procedure to recovery and prevention.
Whether you're dealing with a skin abscess, dental abscess, or internal abscess, proper drainage is often the key to relief and healing. Let's explore the essential aspects of this medical procedure and what you can expect throughout the process.
Signs That Indicate an Abscess Needs Drainage
Recognizing when an abscess requires professional drainage is crucial for proper treatment. Common indicators include:
- Severe pain or throbbing in the affected area
- Noticeable swelling and redness
- Warmth around the abscess site
- Skin that feels tight or stretched
- A visible collection of pus under the skin
- Fever or general feeling of illness
If you experience these symptoms, especially if they worsen over time, it's important to seek medical attention promptly. Attempting to drain an abscess at home can be dangerous and may lead to complications.
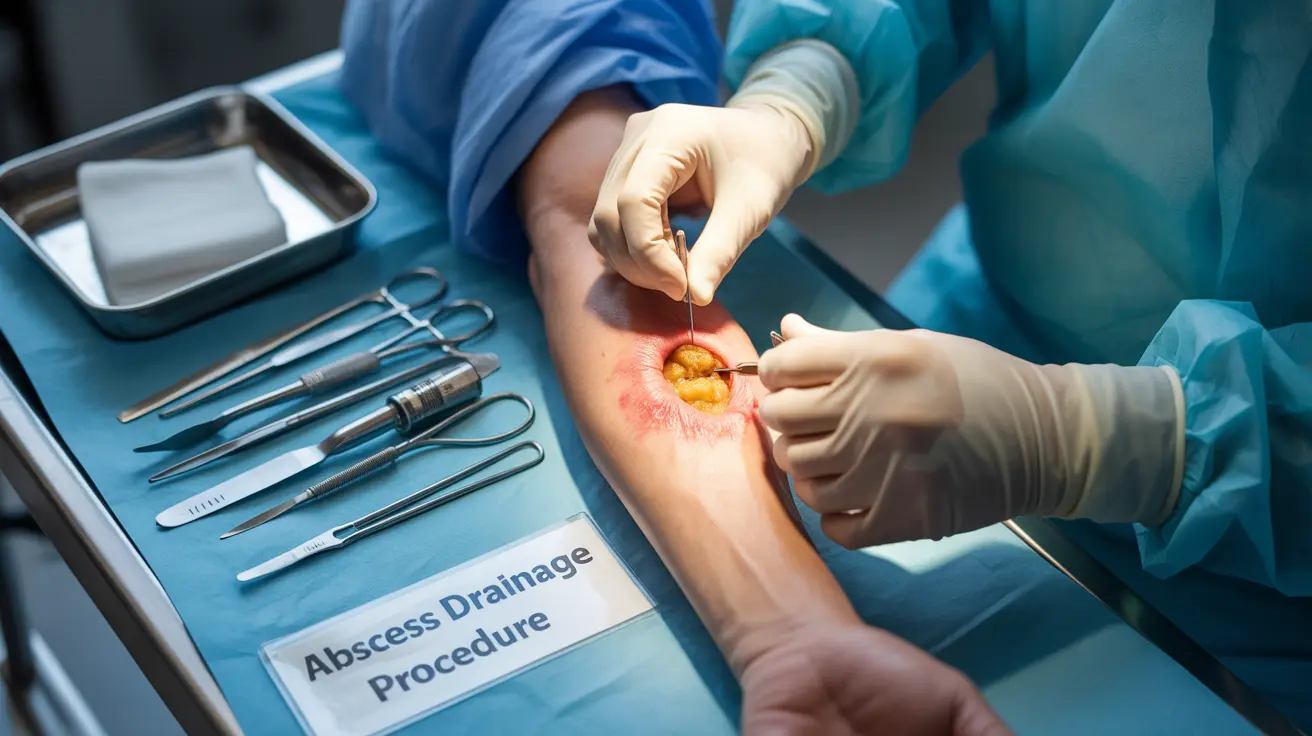
The Abscess Drainage Procedure
Medical professionals follow specific steps when draining an abscess to ensure safety and effectiveness:
Preparation Phase
Before the procedure begins, the healthcare provider will:
- Clean and sterilize the area
- Administer local anesthesia if needed
- Mark the optimal drainage point
During the Procedure
The actual drainage process involves:
- Making a small incision in the abscess
- Allowing the pus to drain completely
- Cleaning the cavity thoroughly
- Possibly inserting a drainage wick or tube
- Applying appropriate dressing
Recovery and Healing Process
The healing timeline after abscess drainage varies depending on the size and location of the abscess. Most patients can expect:
- Initial healing period of 5-7 days
- Regular dressing changes as prescribed
- Gradual reduction in pain and swelling
- Complete healing within 2-4 weeks
Following your healthcare provider's instructions for wound care is essential for proper healing and preventing complications.
Prevention and Long-term Care
To minimize the risk of abscess recurrence, consider these preventive measures:
- Maintain good hygiene practices
- Treat any underlying skin conditions
- Address cuts and scrapes promptly
- Keep your immune system healthy
- Follow up with your healthcare provider as recommended
Role of Antibiotics in Abscess Treatment
While drainage is the primary treatment for most abscesses, antibiotics may be necessary in certain situations:
- When there's significant surrounding infection
- For patients with weakened immune systems
- If the infection is particularly severe
- When the abscess is in a sensitive location
- If there are signs of systemic infection
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common signs and symptoms that indicate an abscess needs to be drained?
The most common signs include severe pain, swelling, redness, warmth in the affected area, and visible collection of pus. If you also have fever or feel generally unwell, these are additional indicators that drainage may be necessary.
How is pus drained from an abscess and what does the procedure involve?
The procedure involves cleaning the area, administering local anesthesia, making a small incision, and allowing the pus to drain completely. The cavity is then cleaned, and sometimes a drainage wick is inserted to ensure continued drainage. The area is finally dressed with appropriate medical bandaging.
What should I expect during recovery after abscess drainage and how long does healing usually take?
Recovery typically involves some initial discomfort that gradually improves over 5-7 days. You'll need to keep the area clean and change dressings as directed. Complete healing usually occurs within 2-4 weeks, depending on the abscess size and location.
Can an abscess come back after drainage, and how can I prevent recurrence?
Yes, abscesses can recur. Prevention involves maintaining good hygiene, treating underlying conditions, proper wound care, and following medical advice. Regular check-ups and prompt treatment of skin injuries can help prevent new abscesses from forming.
When are antibiotics needed in addition to abscess drainage?
Antibiotics are typically prescribed when there's significant surrounding infection, for patients with compromised immune systems, or when the infection shows signs of spreading. Your healthcare provider will determine if antibiotics are necessary based on your specific situation.