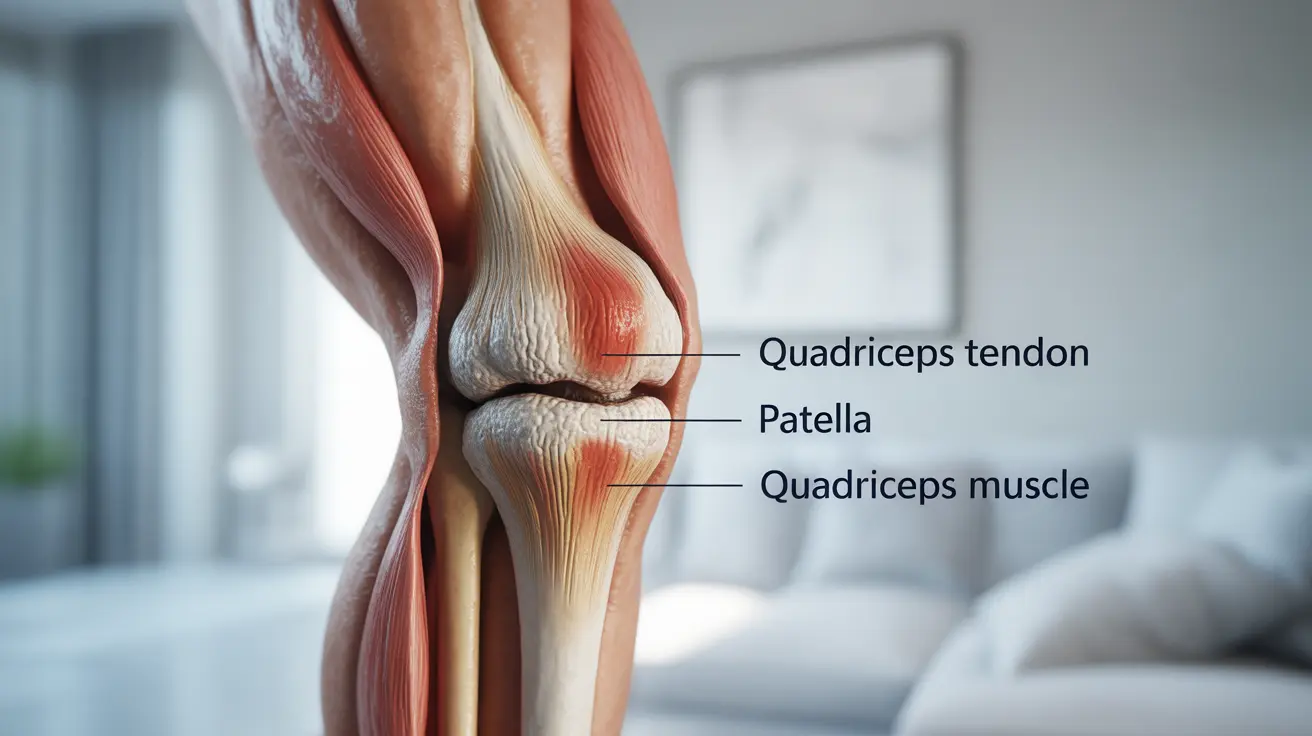
Quadriceps tendonitis is a common overuse injury that affects the thick tendon connecting your quadriceps muscles to your kneecap. This condition can significantly impact daily activities and athletic performance, causing pain and limiting mobility. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for proper management and recovery.
Whether you're an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or someone experiencing knee pain, this comprehensive guide will help you understand quadriceps tendonitis and the steps you can take to address this condition effectively.
What is Quadriceps Tendonitis?
Quadriceps tendonitis, also known as quadriceps tendinopathy, occurs when the tendon connecting your quadriceps muscles to your patella (kneecap) becomes inflamed or irritated. This condition typically develops gradually due to repetitive stress on the tendon, leading to microscopic tears and inflammation.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of quadriceps tendonitis:
- Sudden increases in physical activity
- Repetitive jumping or running
- Poor training techniques
- Muscle imbalances
- Previous knee injuries
- Obesity
- Age-related tendon degeneration
Athletes participating in sports that involve frequent jumping or running are particularly susceptible to developing this condition. Additionally, individuals with poor biomechanics or those who don't properly warm up before exercise may be at increased risk.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of quadriceps tendonitis typically develop gradually and may include:
- Pain above the kneecap, especially during activities
- Tenderness when touching the affected area
- Swelling around the tendon
- Stiffness after periods of inactivity
- Weakness in the quadriceps muscle
- Difficulty with activities like climbing stairs or squatting
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers typically diagnose quadriceps tendonitis through:
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Assessment of pain patterns
- Range of motion tests
- Imaging studies (if necessary)
Your doctor may order additional tests such as MRI or ultrasound to rule out other conditions or assess the severity of tendon damage.
Treatment Approaches
Conservative Treatment
Most cases of quadriceps tendonitis respond well to conservative treatment methods:
- Rest and activity modification
- Ice therapy for pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy exercises
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Proper stretching techniques
- Gradual return to activity
Advanced Treatment Options
For more severe or persistent cases, additional treatments may include:
- Corticosteroid injections
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy
- Surgery (in rare cases)
Prevention and Recovery Strategies
Preventing quadriceps tendonitis and supporting recovery involves:
- Proper warm-up before exercise
- Gradual progression of activity intensity
- Regular stretching and strengthening exercises
- Maintaining healthy body weight
- Using appropriate equipment and footwear
- Listening to your body and avoiding overtraining
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes and risk factors for developing quadriceps tendonitis?
Quadriceps tendonitis commonly develops from overuse, sudden increases in physical activity, poor training techniques, and repetitive stress on the tendon. Risk factors include age, obesity, previous injuries, and participation in high-impact sports.
What symptoms should make me suspect I have quadriceps tendonitis?
Key symptoms include pain above the kneecap that worsens with activity, tenderness to touch, swelling around the tendon, morning stiffness, and difficulty with activities like climbing stairs or squatting.
How is quadriceps tendonitis diagnosed by healthcare professionals?
Healthcare providers diagnose quadriceps tendonitis through physical examination, medical history review, and assessment of symptoms. They may also use imaging studies like MRI or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions.
What are the most effective treatments for quadriceps tendonitis, and when is surgery needed?
Effective treatments include rest, ice therapy, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. Surgery is rarely needed and is only considered when conservative treatments fail after several months or in cases of complete tendon tears.
How can I prevent quadriceps tendonitis and aid recovery after injury?
Prevention and recovery strategies include proper warm-up, gradual activity progression, regular stretching and strengthening exercises, maintaining healthy body weight, and avoiding overtraining. Following a structured rehabilitation program is crucial for successful recovery.