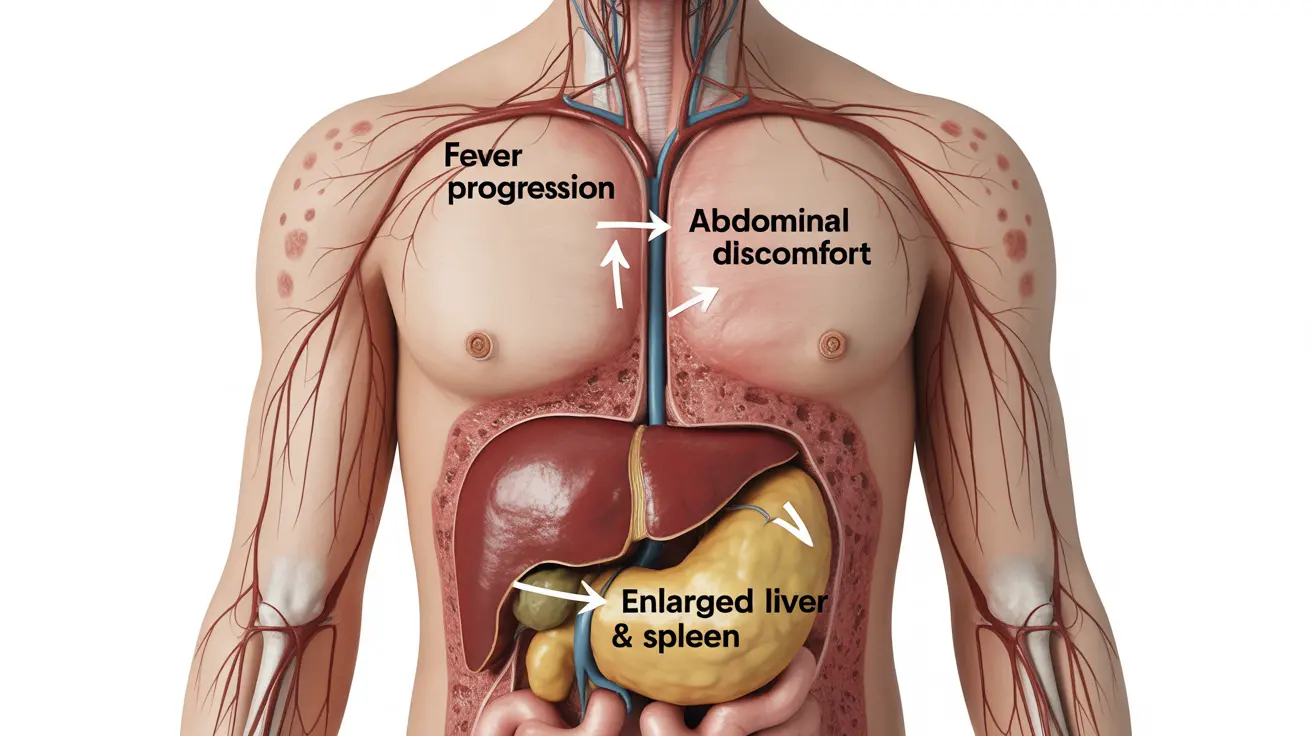
Recognizing typhoid symptoms early can be crucial for proper treatment and preventing serious complications. This potentially severe bacterial infection requires prompt medical attention, especially if you've traveled to regions where typhoid fever is common. Understanding the progression of symptoms and knowing when to seek help can make a significant difference in recovery outcomes.
Early Warning Signs of Typhoid Fever
The initial symptoms of typhoid fever typically develop gradually over several days to weeks after exposure to the bacteria. Common early warning signs include:
- Persistent fever that increases gradually
- Headaches and fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Mild abdominal pain
- Dry cough
- Muscle aches
These symptoms often start mild but progressively worsen if left untreated. Many people initially mistake these signs for common flu or other less serious illnesses.
Progressive Symptoms and Complications
As typhoid fever advances, symptoms become more severe and distinct. The progression typically follows a characteristic pattern:
Week 1
- Rising fever (up to 104°F/40°C)
- Weakness and fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort
- Decreased appetite
Week 2-3
Without treatment, symptoms intensify to include:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Rash (rose-colored spots)
- Enlarged spleen and liver
- Mental confusion
Typhoid Symptoms in Different Age Groups
Children
Children often experience milder symptoms but may show:
- Lower fever compared to adults
- More pronounced gastrointestinal symptoms
- Lethargy and irritability
- Poor appetite and weight loss
Adults
Adults typically present with more classic symptoms:
- High sustained fever
- Severe headaches
- Significant abdominal pain
- More frequent complications if untreated
When to Seek Medical Care
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you experience:
- Fever above 103°F (39.4°C)
- Severe abdominal pain
- Persistent vomiting
- Confusion or mental changes
- Particularly if you've recently traveled to high-risk areas
Distinguishing Typhoid from Other Illnesses
Several key features help distinguish typhoid fever from other conditions:
- Gradually increasing fever pattern
- Relative bradycardia (slow heart rate despite fever)
- Rose-colored spots on the trunk
- Recent travel history to endemic areas
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early and common symptoms of typhoid fever to watch for?
Early typhoid symptoms include gradually increasing fever, headache, weakness, dry cough, and loss of appetite. These symptoms typically develop 6-30 days after exposure and worsen progressively if untreated.
How does typhoid fever typically progress and what severe symptoms indicate complications?
Typhoid fever progresses from mild symptoms to severe complications over weeks. Severe symptoms indicating complications include very high fever, severe abdominal pain, mental confusion, and intestinal bleeding or perforation.
What are the differences in typhoid symptoms between children and adults?
Children often show milder symptoms with lower fever and more pronounced gastrointestinal issues. Adults typically experience higher sustained fever, severe headaches, and are at greater risk for complications.
When should someone seek medical care for typhoid symptoms or after traveling to high-risk areas?
Seek immediate medical care if you experience high fever, severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, or mental changes, especially after traveling to regions where typhoid is common.
How can typhoid fever symptoms be distinguished from other common illnesses with fever and stomach pain?
Typhoid fever can be distinguished by its gradually increasing fever pattern, relative bradycardia, rose-colored spots on the trunk, and typical progression of symptoms, especially when combined with relevant travel history.