Rheumatism is a broad term that encompasses various conditions affecting joints, muscles, and connective tissues throughout the body. While many people use the terms rheumatism and arthritis interchangeably, understanding the distinct meaning of rheumatism is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive guide explores what rheumatism means, its various forms, and how it impacts those affected.
What is Rheumatism?
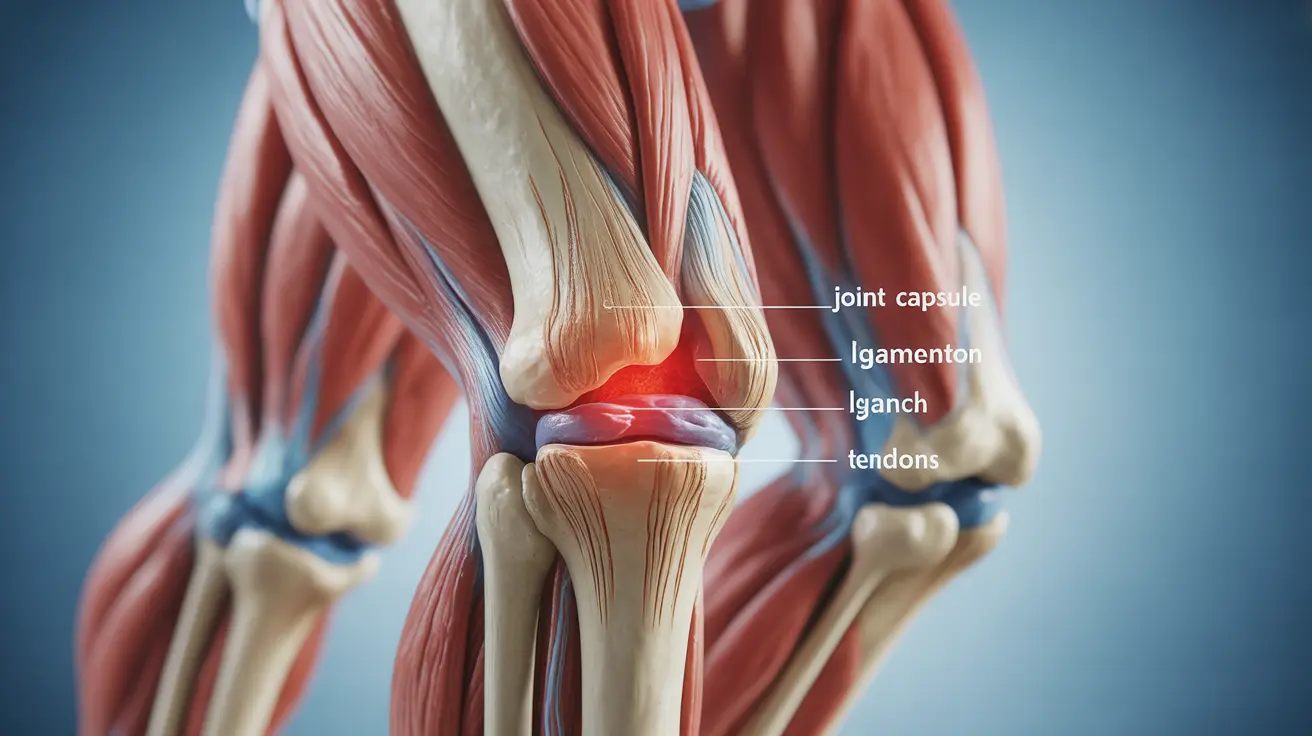
Rheumatism refers to a group of conditions causing chronic pain and inflammation in joints, muscles, and soft tissues. Unlike specific conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism is an umbrella term that encompasses multiple inflammatory and degenerative conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system.
Types of Rheumatic Conditions
Rheumatic conditions can be broadly categorized into several main types:
Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases
These conditions involve inflammation of joints and surrounding tissues, with rheumatoid arthritis being the most common example. They often affect multiple joints simultaneously and can cause systemic symptoms throughout the body.
Degenerative Rheumatic Conditions
These include conditions like osteoarthritis, where joint cartilage gradually wears down over time. While inflammation may be present, it's typically not the primary cause of symptoms.
Soft Tissue Rheumatism
This category includes conditions affecting muscles, tendons, and ligaments, such as fibromyalgia and myofascial pain syndrome.
Common Symptoms of Rheumatism
The symptoms of rheumatic conditions can vary significantly but often include:
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Muscle aches and weakness
- Swelling around joints
- Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Reduced range of motion
- Warmth and redness around affected areas
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosing rheumatic conditions typically involves:
- Physical examination
- Detailed medical history
- Blood tests for inflammatory markers
- Imaging studies (X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound)
- Specialized tests depending on suspected conditions
Treatment Approaches
Management of rheumatic conditions often requires a multi-faceted approach:
Medication Options
Various medications may be prescribed, including anti-inflammatory drugs, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and pain relievers, depending on the specific condition and symptoms.
Physical Therapy
Regular exercise and physical therapy can help maintain joint flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and improve overall function.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, following an anti-inflammatory diet, and managing stress, can help control symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What does rheumatism mean and how is it different from arthritis?
Rheumatism is a broader term encompassing various conditions affecting joints, muscles, and connective tissues, while arthritis specifically refers to joint inflammation. Arthritis is actually one type of rheumatic condition.
- What are the common symptoms of inflammatory rheumatism like rheumatoid arthritis?
Common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, morning stiffness, fatigue, and reduced range of motion. In rheumatoid arthritis specifically, symptoms often occur symmetrically on both sides of the body.
- What causes rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory rheumatic diseases?
These conditions are typically autoimmune in nature, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. Genetic factors, environmental triggers, and certain lifestyle factors can contribute to their development.
- How is inflammatory rheumatism diagnosed by doctors?
Doctors use a combination of physical examination, medical history, blood tests for inflammatory markers, and imaging studies like X-rays or MRI scans to diagnose rheumatic conditions.
- What treatment options are available to manage symptoms of inflammatory rheumatism?
Treatment options include medications (such as NSAIDs and DMARDs), physical therapy, exercise programs, and lifestyle modifications. The specific treatment plan depends on the type and severity of the condition.