When experiencing persistent ringing in the ears (tinnitus) along with dizziness, it's natural to feel concerned about the underlying cause. While these symptoms can stem from various conditions, they may sometimes indicate the presence of a brain tumor. Understanding the relationship between these symptoms and brain tumors is crucial for early detection and appropriate medical intervention.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the connection between brain tumors and these concerning symptoms, helping you understand when to seek medical attention and what to expect during the diagnostic process.
Common Types of Brain Tumors Associated with Ear Ringing and Dizziness
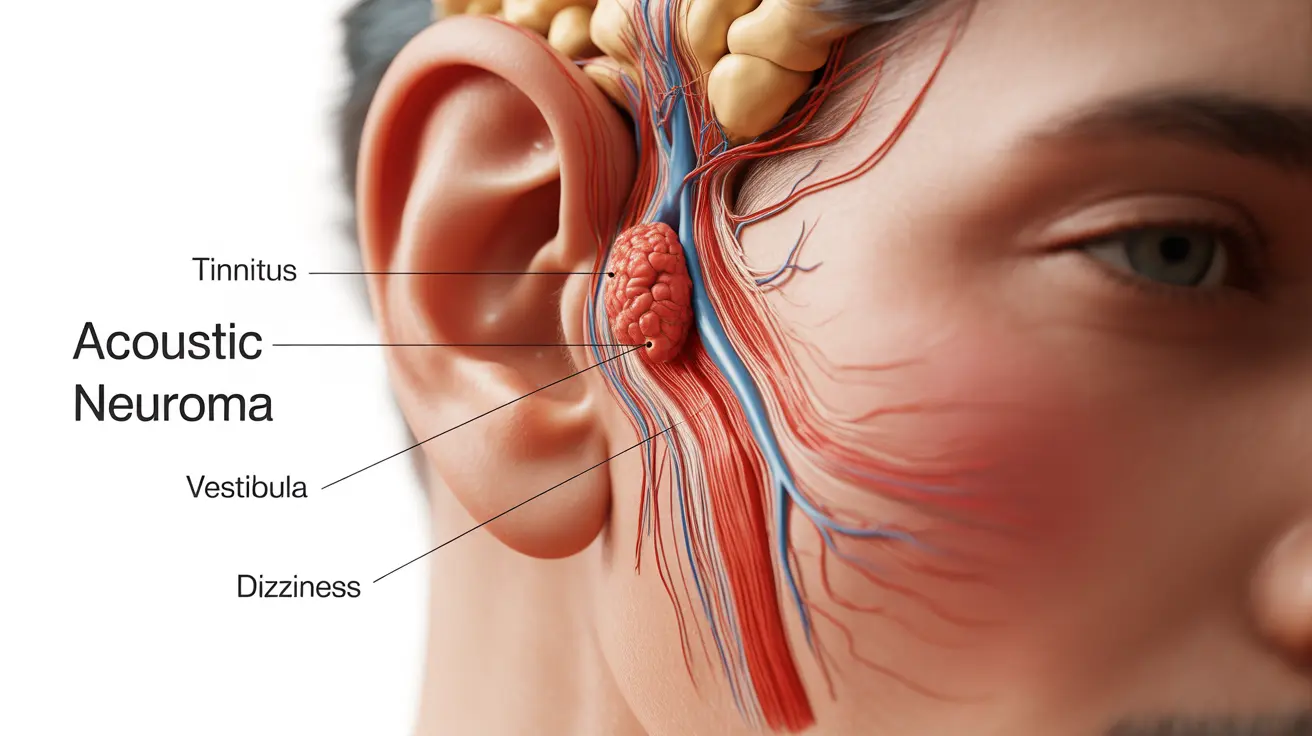
Several types of brain tumors can cause tinnitus and balance problems, with acoustic neuromas being the most common. These benign tumors develop on the vestibulocochlear nerve, which is responsible for hearing and balance.
Acoustic Neuroma
This slow-growing tumor typically affects one side of the head and can cause:
- Progressive hearing loss in one ear
- Unilateral tinnitus (ringing in one ear)
- Balance problems and dizziness
- Facial numbness or weakness
Other Relevant Tumor Types
Additional brain tumors that may cause similar symptoms include:
- Meningiomas near the inner ear
- Brainstem gliomas
- Temporal lobe tumors
Warning Signs and Symptoms
While tinnitus and dizziness alone don't necessarily indicate a brain tumor, certain patterns and additional symptoms warrant medical attention:
Key Indicators
Watch for:
- Persistent ringing in one ear
- Progressive hearing loss
- Worsening balance problems
- Headaches that increase in severity
- Changes in facial sensation
- Coordination difficulties
Diagnostic Process
If you're experiencing concerning symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend several diagnostic tests:
Initial Evaluation
The process typically begins with:
- Detailed medical history
- Physical examination
- Hearing tests
- Balance assessment
Advanced Imaging
Diagnostic imaging may include:
- MRI with contrast
- CT scan
- Specialized auditory testing
- Vestibular function tests
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options vary depending on the tumor type, size, and location. Common approaches include:
Conservative Management
For small, slow-growing tumors:
- Regular monitoring
- Hearing aids when necessary
- Balance therapy
- Symptom management
Active Treatment
More aggressive cases may require:
- Surgical removal
- Radiation therapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Combined treatment approaches
Frequently Asked Questions
Can ringing in the ears and dizziness be signs of a brain tumor? Yes, persistent ringing in the ears (tinnitus) and dizziness can be symptoms of certain brain tumors, particularly acoustic neuromas. However, these symptoms are more commonly caused by other conditions and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis.
What types of brain tumors commonly cause tinnitus and dizziness? Acoustic neuromas are the most common type of brain tumor associated with these symptoms. Other types include meningiomas near the inner ear, brainstem gliomas, and temporal lobe tumors that affect the hearing and balance centers of the brain.
How is an acoustic neuroma diagnosed if I have hearing loss and ringing in one ear? Diagnosis typically involves a combination of hearing tests, balance assessments, and imaging studies, particularly MRI with contrast. Your doctor will also perform a thorough neurological examination and may request additional specialized tests.
When should I see a doctor if I experience dizziness along with ear ringing? Seek medical attention if you experience persistent tinnitus in one ear, progressive hearing loss, worsening dizziness, or if these symptoms are accompanied by headaches, facial numbness, or coordination problems.
What treatment options are available for brain tumors causing hearing and balance problems? Treatment options range from watchful waiting with regular monitoring to surgical removal, radiation therapy, or stereotactic radiosurgery. The choice of treatment depends on the tumor's size, location, growth rate, and the patient's overall health and preferences.