Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) poses significant health risks, particularly for infants, young children, and immunocompromised individuals. Understanding how long RSV can survive on various surfaces is crucial for preventing its spread and protecting vulnerable populations. This comprehensive guide explores RSV surface survival times and effective prevention strategies.
Understanding RSV Surface Transmission
RSV spreads primarily through respiratory droplets, but it can also transmit through contact with contaminated surfaces. The virus can remain viable on surfaces for several hours to days, depending on environmental conditions and surface type. This makes surface contamination a significant concern in homes, healthcare settings, and childcare facilities.
RSV Survival Times on Different Surfaces
Hard Surfaces
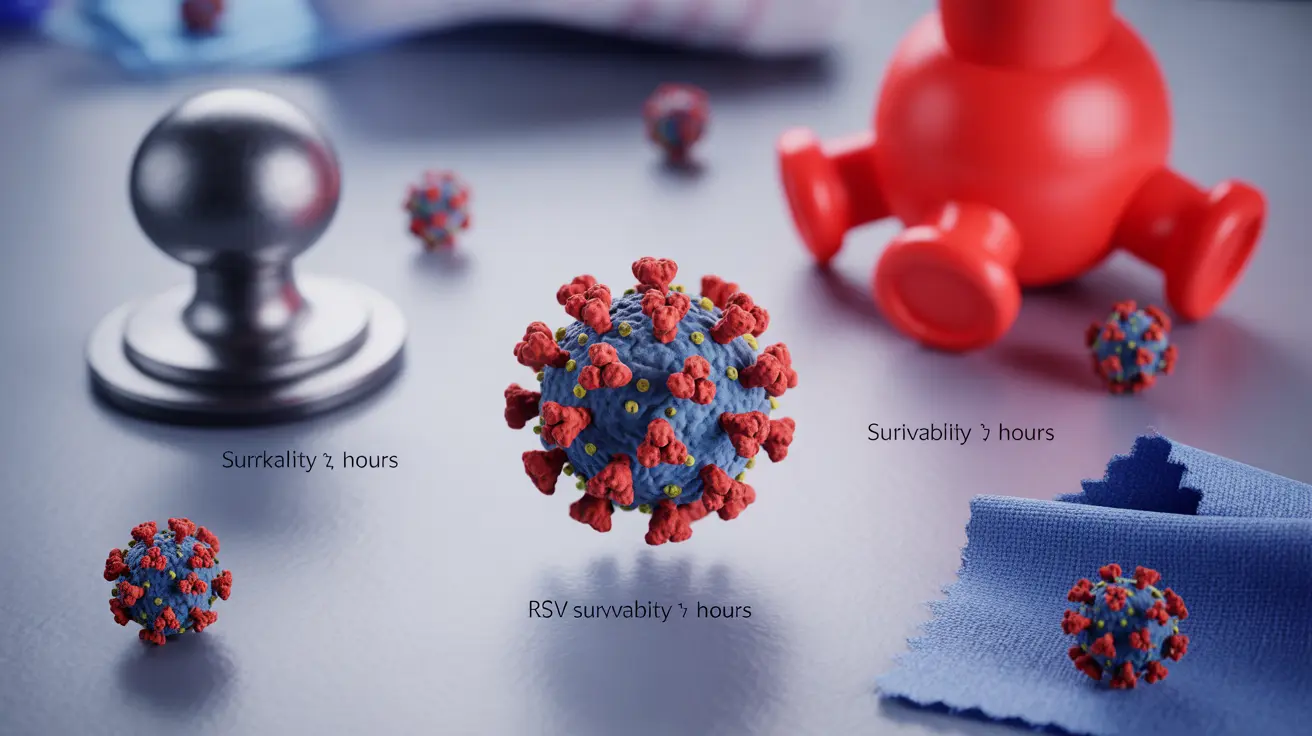
On hard, non-porous surfaces such as doorknobs, countertops, and plastic toys, RSV can survive for:
- Up to 6-12 hours on stainless steel and plastic
- 24 hours or more on hard surfaces in optimal conditions (cool, humid environments)
- Several hours on frequently touched surfaces like light switches and remote controls
Soft Surfaces
On soft, porous surfaces, RSV survival times typically vary:
- 30 minutes to 1 hour on hands
- Up to 2 hours on clothing and fabric
- Several hours on tissues and paper products
Factors Affecting RSV Surface Survival
Several environmental factors influence how long RSV remains infectious on surfaces:
- Temperature (survives longer in cooler conditions)
- Humidity levels (higher humidity extends survival)
- Amount of organic material present
- Surface type and porosity
- Exposure to direct sunlight or UV light
Prevention and Surface Disinfection
Effective Cleaning Methods
To minimize RSV transmission through surface contact:
- Use EPA-registered disinfectants effective against RSV
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces regularly
- Pay special attention to shared toys and equipment
- Allow proper contact time for disinfectants to work effectively
Hand Hygiene
Proper hand hygiene is crucial in preventing RSV transmission:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds
- Use alcohol-based hand sanitizers when soap isn't available
- Clean hands before touching face or handling food
- Wash hands after contact with potentially contaminated surfaces
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) live on hard and soft surfaces?
RSV can survive up to 24 hours on hard surfaces and between 30 minutes to 2 hours on soft surfaces, depending on environmental conditions and surface type.
What is the risk of catching RSV from touching contaminated surfaces like doorknobs or toys?
The risk of RSV transmission from contaminated surfaces is significant, especially if you touch the surface and then your face before washing your hands. This risk is higher in settings with infected individuals and during peak RSV season.
How effective is handwashing in preventing RSV spread from surfaces to people?
Proper handwashing is highly effective in preventing RSV transmission from surfaces. Regular handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
What are the best ways to disinfect surfaces to reduce RSV transmission in homes and childcare settings?
The most effective ways include using EPA-registered disinfectants, regularly cleaning frequently touched surfaces, ensuring proper contact time for disinfectants, and maintaining good ventilation during cleaning.
How long does RSV remain contagious in infants and people with weakened immune systems?
Infants and immunocompromised individuals can shed and spread RSV for up to 3-8 weeks, even after symptoms improve. This extended period of contagiousness makes proper surface cleaning and hygiene particularly important.