Have you ever experienced a strange rumbling sound in your ear, similar to distant thunder or the roar of ocean waves? This sensation, known as ear rumbling, is a relatively common occurrence that can have various causes, ranging from normal physiological responses to potential medical conditions. Understanding what causes this phenomenon and knowing when it might signal a health concern is essential for maintaining your ear health.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the different causes of ear rumbling, its potential implications for your health, and when you should consider seeking medical attention.
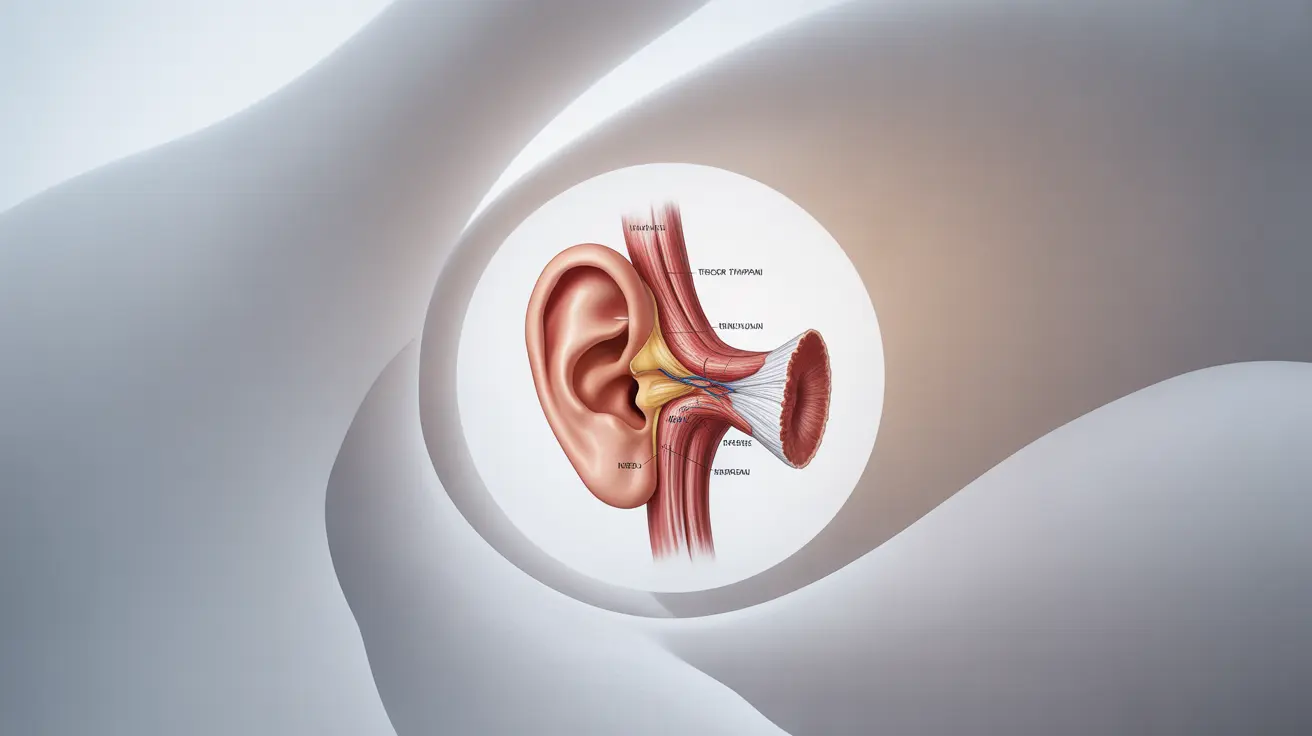
The Science Behind Ear Rumbling
Ear rumbling often occurs due to the movement or contraction of tiny muscles within your ear, particularly the tensor tympani muscle. This muscle plays a crucial role in protecting your inner ear from loud noises and helping to regulate pressure within the middle ear.
When this muscle contracts, either voluntarily or involuntarily, it can create a rumbling or thundering sensation that only you can hear. This is because the movement creates vibrations that are transmitted through the structures of your middle and inner ear.
Common Causes of Ear Rumbling
Natural Protective Responses
Your ears have built-in protective mechanisms that can trigger rumbling sounds. These typically occur in response to:
- Loud noises
- Yawning
- Swallowing
- Chewing
- Speaking loudly
Muscle Contractions
Sometimes, the muscles in and around your ear can experience involuntary contractions or spasms, leading to rumbling sounds. These contractions might be triggered by:
- Stress
- Fatigue
- Certain medications
- Muscle tension
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
Medical Conditions Associated with Ear Rumbling
Middle Ear Problems
Several middle ear conditions can cause rumbling sensations:
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Middle ear infections
- Fluid buildup
- Changes in air pressure
Neurological Conditions
In some cases, ear rumbling might be related to:
- Tinnitus
- Meniere's disease
- Acoustic neuroma
- Multiple sclerosis
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional ear rumbling is usually harmless, you should consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent rumbling that lasts for extended periods
- Accompanying symptoms like dizziness or hearing loss
- Pain or discomfort
- Changes in balance
- Frequent headaches
Treatment Options and Management
Treatment for ear rumbling depends on its underlying cause. Common approaches include:
- Addressing underlying medical conditions
- Stress management techniques
- Muscle relaxation exercises
- Medications (when appropriate)
- Lifestyle modifications
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a rumbling sound in my ear, and is it always a sign of a health problem?
The rumbling sound in your ear can be caused by muscle contractions, pressure changes, or various medical conditions. While it's often normal and harmless, persistent or severe symptoms may indicate an underlying health issue.
Can muscle spasms in the ear cause vibrations or rumbling, and how do I know if it's normal?
Yes, muscle spasms, particularly of the tensor tympani muscle, can cause rumbling sensations. Occasional, brief episodes are usually normal, especially during yawning or swallowing. However, frequent or prolonged spasms may require medical evaluation.
What are the main medical conditions linked to ear rumbling, like infections or Meniere's disease, and what symptoms should I watch for?
Common medical conditions include middle ear infections, Eustachian tube dysfunction, and Meniere's disease. Watch for additional symptoms like dizziness, hearing changes, ear pain, or balance problems.
Is the rumbling in my ear a protective response, and does it help prevent hearing damage?
Yes, in many cases, ear rumbling is a protective response. The tensor tympani muscle contracts to dampen very loud sounds and protect the inner ear from potential damage.
When should I see a doctor for rumbling in my ear, and what treatments are available if it's a sign of something serious?
Seek medical attention if the rumbling is persistent, accompanied by other symptoms, or affects your daily life. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and may include medications, physical therapy, or other interventions as determined by your healthcare provider.