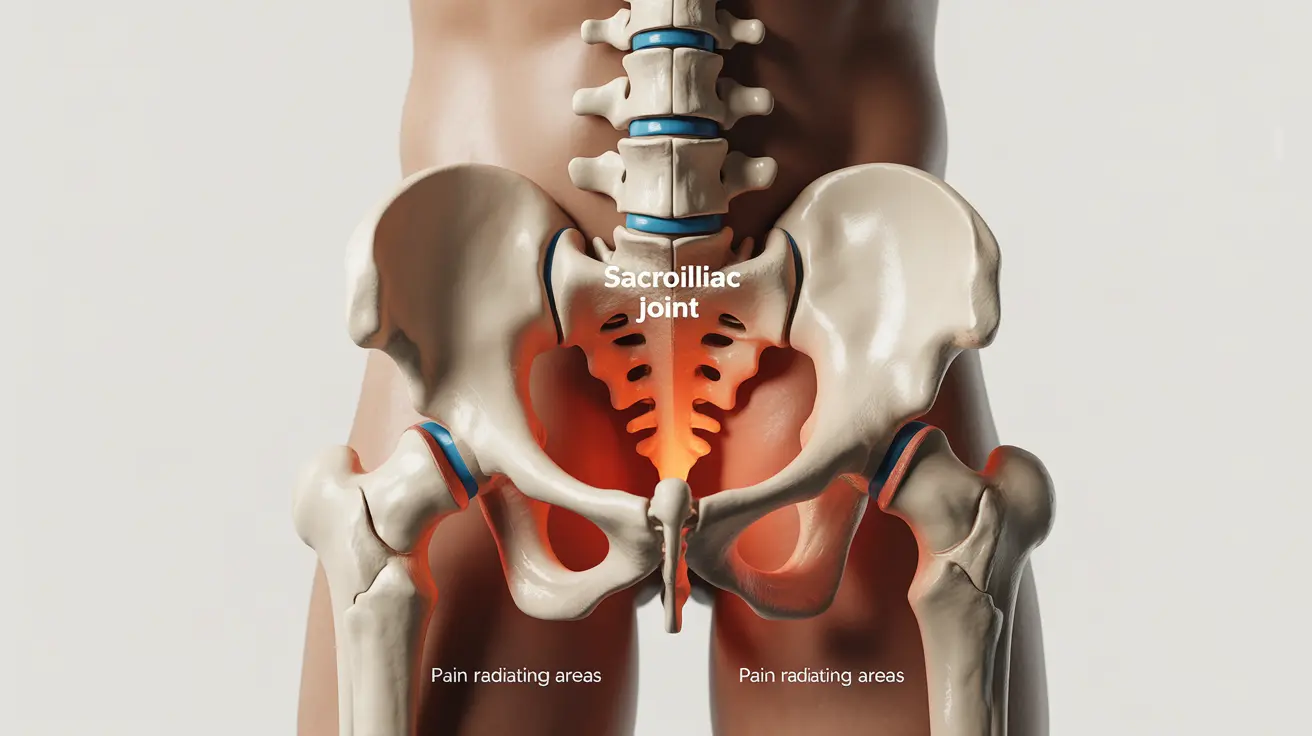
Sacroiliac joint pain can significantly impact your daily life, affecting everything from walking to sitting comfortably. This condition, which involves the joints connecting your pelvis to your lower spine, affects millions of Americans and often goes undiagnosed or misdiagnosed as general lower back pain. Understanding the symptoms and available treatments is crucial for managing this challenging condition effectively.
Whether you're experiencing discomfort for the first time or seeking better ways to manage chronic sacroiliac joint pain, this comprehensive guide will help you recognize the symptoms, understand diagnostic procedures, and explore various treatment options.
Common Symptoms and Recognition
Recognizing sacroiliac joint pain symptoms is the first step toward proper treatment. The most common indicators include:
- Lower back pain that may radiate to the buttocks and hips
- Pain that worsens when sitting for long periods
- Discomfort when climbing stairs or walking
- Sharp, stabbing pain on one side of the lower back
- Stiffness in the pelvis and lower back
- Pain that intensifies with certain movements or positions
These symptoms may vary in intensity throughout the day and can be affected by different activities or positions. Many people report that their pain is worst in the morning or after long periods of inactivity.
Diagnostic Process and Testing
Diagnosing sacroiliac joint pain typically involves a comprehensive approach that includes:
Physical Examination
Your healthcare provider will perform specific movement tests to assess your pain response and joint mobility. These may include various pressure points and movement patterns to identify the source of your discomfort.
Imaging Studies
Diagnostic imaging often includes:
- X-rays to check joint alignment
- MRI scans to evaluate soft tissue damage
- CT scans for detailed bone imaging
- Bone scans to identify areas of inflammation
Diagnostic Injections
A diagnostic injection into the sacroiliac joint can help confirm the diagnosis. If the injection provides temporary pain relief, it typically confirms that the sacroiliac joint is the source of the pain.
Treatment Approaches
Conservative Management
Initial treatment usually begins with non-invasive approaches:
- Physical therapy exercises
- Manual therapy techniques
- Heat and ice therapy
- Activity modification
- Proper posture education
Medical Interventions
When conservative treatments aren't sufficient, medical interventions may include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Corticosteroid injections
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Regenerative medicine treatments
Special Considerations
Pregnancy-Related SI Joint Pain
Pregnancy can significantly impact sacroiliac joint stability due to hormonal changes and increased weight. Management during pregnancy often focuses on safe exercises, proper body mechanics, and supportive devices like pregnancy belts.
Physical Activity Modifications
Maintaining an active lifestyle while managing sacroiliac joint pain requires careful attention to:
- Proper exercise form
- Activity pacing
- Appropriate workout modifications
- Strengthening core muscles
- Regular stretching routines
Surgical Options
When conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical intervention may be considered. Modern surgical approaches include minimally invasive techniques that can stabilize the joint while maintaining natural movement patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common symptoms of sacroiliac joint pain and how can I recognize them? The most common symptoms include lower back pain that may extend to the buttocks, hips, and groin, pain that worsens with sitting or standing for long periods, and difficulty with certain movements like climbing stairs or getting up from a seated position.
How is sacroiliac joint pain diagnosed and what tests are usually performed? Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies (X-rays, MRI, CT scans), and diagnostic injections to confirm the source of pain. Your healthcare provider will also review your medical history and perform specific movement tests.
What treatment options are available for sacroiliac joint pain, from home remedies to medical interventions? Treatment options range from conservative approaches like physical therapy, heat/ice therapy, and exercise, to medical interventions including medications, injections, and in severe cases, surgery. The treatment plan is typically tailored to the individual's specific condition and needs.
Can pregnancy or physical activities cause sacroiliac joint pain and how can it be managed during these conditions? Yes, both pregnancy and certain physical activities can cause or exacerbate sacroiliac joint pain. Management during pregnancy often includes specific exercises, proper body mechanics, and supportive devices. For physical activities, proper form, activity modification, and appropriate strengthening exercises are key.
When should someone consider surgery for sacroiliac joint dysfunction and what does the procedure involve? Surgery should be considered when conservative treatments have failed to provide adequate relief after several months, and the pain significantly impacts daily life. Modern surgical procedures often involve minimally invasive techniques to stabilize the joint, with the specific approach determined by individual factors and surgical assessment.