When a child experiences a Salter-Harris type 2 fracture, understanding the recovery process is crucial for both parents and young patients. This growth plate injury, commonly occurring in children and adolescents, requires careful management to ensure proper healing and prevent potential complications. Let's explore the recovery timeline, treatment approaches, and essential care guidelines.
Understanding the Recovery Timeline
The typical recovery period for a Salter-Harris type 2 fracture varies depending on several factors, including the child's age, the affected bone, and the severity of the injury. Most children can expect a recovery period of 4-6 weeks, though some cases may require longer healing times.
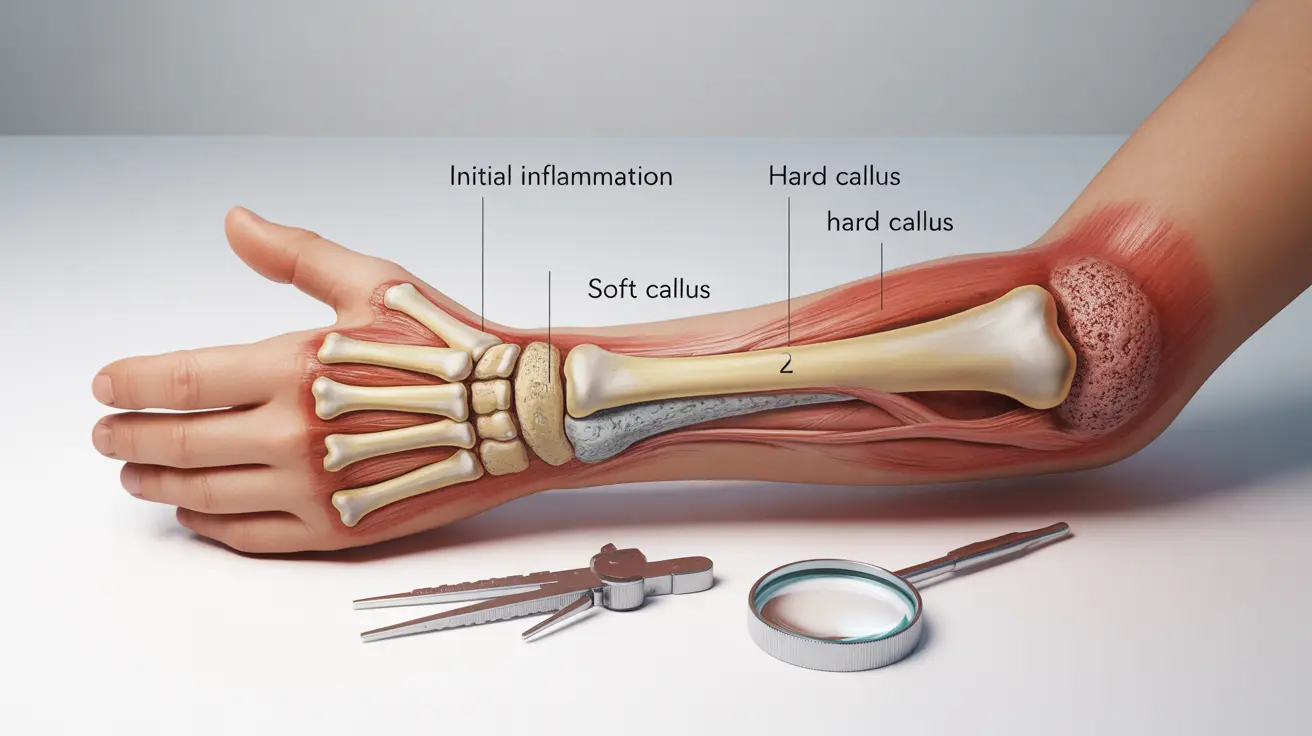
During this time, the healing process progresses through several stages:
- Initial inflammation (first few days)
- Soft callus formation (2-3 weeks)
- Hard callus development (3-6 weeks)
- Bone remodeling (continues for several months)
Treatment and Management Approaches
Initial Treatment Phase
The immediate treatment typically involves:
- Fracture reduction (realignment of the bone)
- Immobilization through casting or splinting
- Pain management as prescribed by healthcare providers
- Regular monitoring through X-rays
Ongoing Care and Monitoring
Healthcare providers will closely monitor the healing progress through regular check-ups and imaging studies. This surveillance is essential to ensure the growth plate heals properly and maintains its normal function.
Managing Potential Complications
While most Salter-Harris type 2 fractures heal well with proper treatment, monitoring for potential complications is crucial. Healthcare providers pay special attention to:
- Growth plate activity
- Bone alignment
- Joint function
- Signs of delayed healing
Activity Modifications During Recovery
Restricted Activities
During the healing period, certain activities should be avoided:
- High-impact sports
- Weight-bearing exercises (if the fracture is in a weight-bearing bone)
- Activities that risk re-injury
- Excessive movement of the affected area
Approved Activities
Gradually, as healing progresses, children can engage in:
- Gentle range-of-motion exercises (as directed by healthcare providers)
- Non-weight-bearing activities
- Physical therapy exercises
- Modified daily activities
Supporting Recovery Through Nutrition and Physical Therapy
Nutritional Support
Optimal nutrition can enhance healing through:
- Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake
- Protein-rich foods
- Balanced meals with plenty of fruits and vegetables
- Proper hydration
Physical Therapy Benefits
Physical therapy plays a vital role in recovery by:
- Maintaining joint mobility
- Preventing muscle atrophy
- Improving strength and flexibility
- Ensuring proper function post-healing
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical recovery time for a Salter-Harris type 2 fracture in children?
Most children recover within 4-6 weeks, though complete healing and bone remodeling may continue for several months. The exact timeline depends on factors such as age, location, and severity of the fracture.
How is a Salter-Harris type 2 fracture treated and managed to ensure proper healing?
Treatment typically involves fracture reduction, immobilization through casting or splinting, regular monitoring through X-rays, and gradual return to activities under medical supervision.
Can a Salter-Harris type 2 fracture cause growth problems or long-term complications?
While most cases heal without issues, there is a small risk of growth disturbances. Regular medical follow-up helps identify and address any potential complications early.
What activities should be avoided during the recovery period of a Salter-Harris type 2 fracture?
High-impact activities, sports, and excessive weight-bearing should be avoided until cleared by a healthcare provider. The specific restrictions depend on the fracture location and healing progress.
How can nutrition and physical therapy aid in the recovery from a Salter-Harris type 2 fracture?
Proper nutrition, especially adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, supports bone healing. Physical therapy helps maintain joint mobility, prevent muscle weakness, and ensure optimal recovery outcomes.