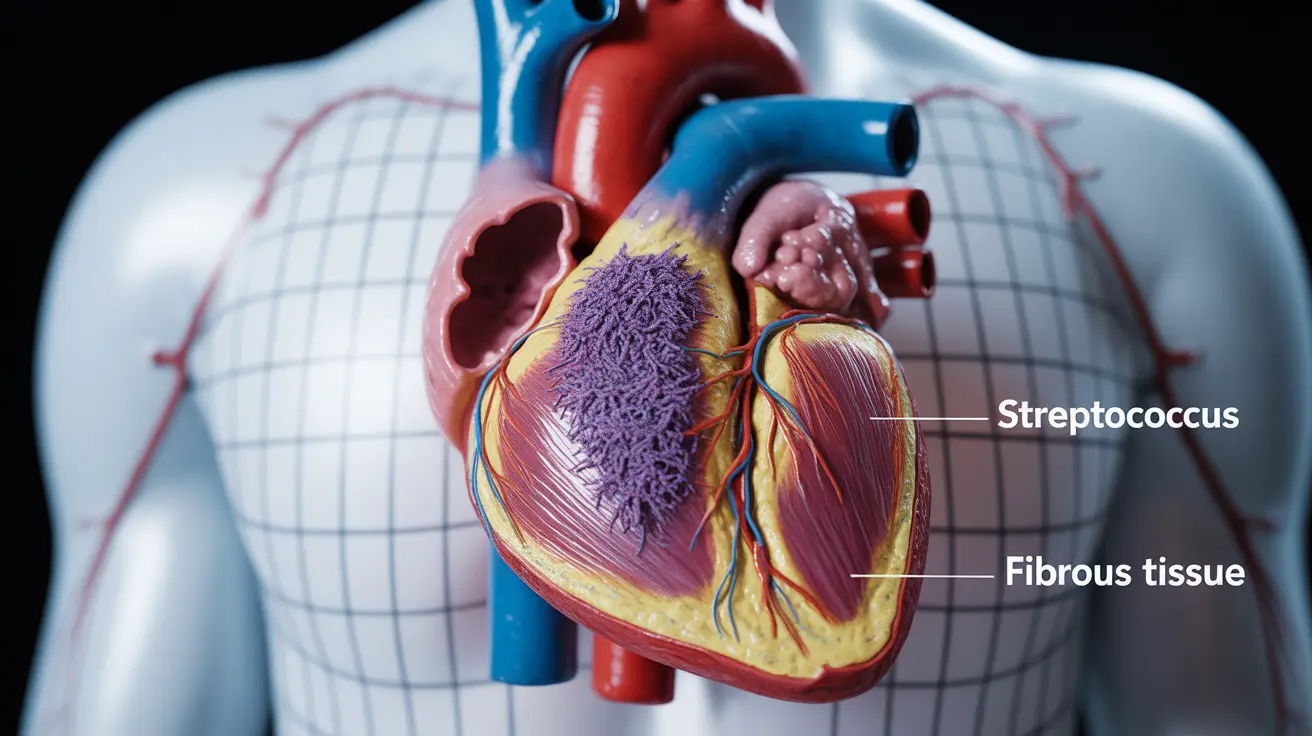
Subacute bacterial endocarditis (SBE) is a serious heart infection that develops gradually over weeks or months. This condition occurs when bacteria slowly accumulate on the heart valves or the inner lining of the heart chambers, leading to potentially severe complications if left untreated. Understanding SBE is crucial for early detection and proper medical intervention.
While less aggressive than acute bacterial endocarditis, SBE requires prompt medical attention and can have significant health implications. This article will explore the essential aspects of SBE, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Understanding Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis
SBE develops when bacteria enter the bloodstream and attach to damaged or abnormal heart valves, artificial heart valves, or other cardiac tissues. Unlike acute endocarditis, which progresses rapidly, SBE typically develops more slowly, allowing for a better prognosis when caught early.
The most common bacteria responsible for SBE include various strains of streptococci, particularly viridans streptococci. These organisms are typically less virulent than those causing acute endocarditis, which explains the more gradual onset of symptoms.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can increase your risk of developing SBE:
- Previous heart valve disease or damaged heart valves
- Artificial heart valves
- Congenital heart defects
- History of intravenous drug use
- Recent dental procedures or oral surgery
- Compromised immune system
Common Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of SBE often develop gradually and may include:
- Persistent low-grade fever
- Unexplained fatigue and weakness
- Night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Joint and muscle pain
- Small, dark spots under fingernails (splinter hemorrhages)
- Tender nodules on fingers and toes (Osler's nodes)
- Heart murmur
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing SBE requires a comprehensive medical evaluation, including:
- Blood cultures to identify the specific bacteria
- Echocardiogram (both transthoracic and transesophageal)
- Complete blood count
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- C-reactive protein (CRP) levels
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for SBE typically involves:
- Long-term intravenous antibiotics (usually 4-6 weeks)
- Regular monitoring of blood cultures
- Heart valve surgery in severe cases
- Management of any complications
- Close medical supervision throughout treatment
Prevention Strategies
Preventing SBE is crucial, especially for high-risk individuals. Key preventive measures include:
- Proper dental hygiene
- Antibiotic prophylaxis before certain dental or surgical procedures
- Regular medical check-ups for those with heart conditions
- Prompt treatment of any bacterial infections
- Maintaining good overall health
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the medical abbreviation SBE stand for and what is subacute bacterial endocarditis?
SBE stands for Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis, a gradually developing infection of the heart's inner lining or valves caused by bacteria. It's characterized by a slower onset compared to acute endocarditis and typically develops over weeks to months.
What are the common symptoms and signs of subacute bacterial endocarditis (SBE)?
Common symptoms include persistent low-grade fever, fatigue, night sweats, weight loss, joint pain, and characteristic skin findings such as splinter hemorrhages and Osler's nodes. A heart murmur may also be present.
How is subacute bacterial endocarditis diagnosed and what tests are used?
Diagnosis involves multiple blood cultures, echocardiography (both types), blood tests including complete blood count, ESR, and CRP levels. An ECG may also be performed to assess heart function.
What treatments are available for SBE and how long does antibiotic therapy usually last?
Treatment primarily consists of intravenous antibiotics administered for 4-6 weeks. Some cases may require heart valve surgery. The specific antibiotic regimen depends on the identified bacteria and their sensitivity patterns.
How can subacute bacterial endocarditis be prevented, especially in people with heart conditions?
Prevention focuses on maintaining good dental hygiene, taking antibiotic prophylaxis before certain procedures when recommended, regular medical check-ups, and prompt treatment of any bacterial infections. People with heart conditions should be particularly vigilant about following preventive measures.