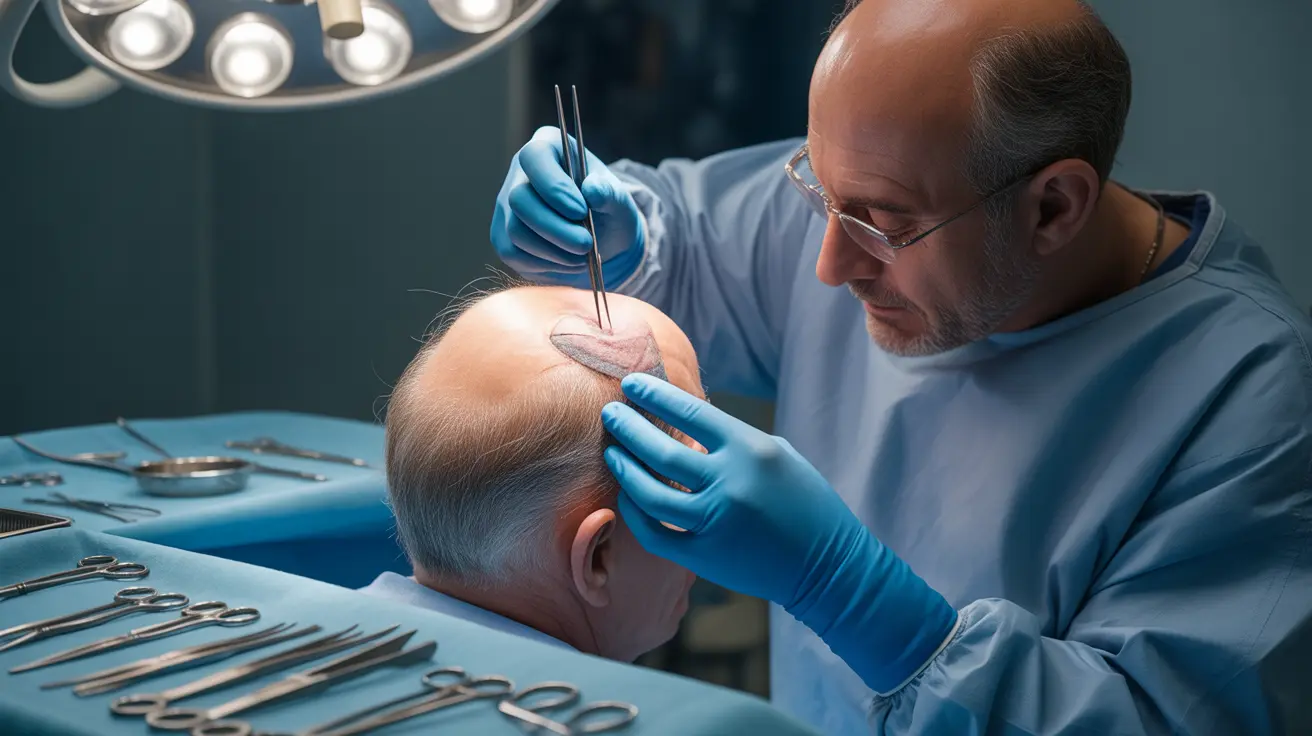
For individuals experiencing significant hair loss or baldness, scalp reduction surgery presents a surgical solution that can help restore a fuller head of hair. This procedure, while less common than other hair restoration methods, offers a unique approach by physically removing bald areas of the scalp rather than adding new hair.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore what scalp reduction surgery entails, its benefits and risks, and help you determine if this treatment might be right for you.
What Is Scalp Reduction Surgery?
Scalp reduction surgery, also known as alopecia reduction surgery, is a surgical procedure that involves removing areas of bald scalp and stretching the surrounding hair-bearing scalp to cover the removed section. This technique effectively reduces the size of the hairless area, creating the appearance of fuller hair coverage.
Candidacy for Scalp Reduction Surgery
Not everyone experiencing hair loss is an ideal candidate for this procedure. The best candidates typically have:
- Dense hair growth in the donor areas
- Good scalp flexibility
- Stable hair loss pattern
- Realistic expectations about results
- Good overall health
- Sufficient scalp laxity
The Surgical Procedure Process
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Before the procedure, patients undergo a thorough medical evaluation to ensure they're suitable candidates. The surgeon will discuss expectations, potential outcomes, and create a customized surgical plan.
During the Surgery
The procedure typically involves:
- Local anesthesia administration
- Removal of the bald scalp section
- Careful advancement of hair-bearing scalp
- Precise closure of the surgical site
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from scalp reduction surgery requires careful attention and following specific aftercare instructions:
- Keep the surgical site clean and dry
- Take prescribed medications as directed
- Avoid strenuous activities for several weeks
- Attend all follow-up appointments
- Monitor for signs of complications
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, scalp reduction surgery carries certain risks, including:
- Infection at the surgical site
- Scarring
- Bleeding
- Numbness or altered sensation
- Stretched scars
- Possible hair loss around the incision sites
Alternative Treatment Options
For those who may not be suitable candidates for scalp reduction surgery, several alternatives exist:
- Hair transplantation procedures
- Medication-based treatments (minoxidil, finasteride)
- Non-surgical hair replacement systems
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy
- Low-level laser therapy
Frequently Asked Questions
What is scalp reduction surgery and how does it help with baldness?
Scalp reduction surgery is a procedure that removes bald areas of the scalp and stretches hair-bearing scalp to cover the removed section. It helps with baldness by reducing the total area of bald scalp, creating an appearance of more complete hair coverage.
Who is a good candidate for scalp reduction surgery?
Good candidates are individuals with stable hair loss patterns, dense hair in donor areas, good scalp flexibility, and realistic expectations. They should be in good overall health and have sufficient scalp laxity for the procedure to be successful.
What are the risks and potential complications of scalp reduction surgery?
The main risks include infection, scarring, bleeding, numbness, stretched scars, and potential hair loss around incision sites. Some patients may also experience complications related to anesthesia or wound healing.
How long is the recovery time after scalp reduction surgery and what does aftercare involve?
Recovery typically takes several weeks. Aftercare involves keeping the surgical site clean, taking prescribed medications, avoiding strenuous activities, and attending follow-up appointments. Most patients can return to normal activities within 2-3 weeks.
What are the alternatives to scalp reduction surgery for hair loss treatment?
Alternatives include hair transplantation, medication-based treatments like minoxidil and finasteride, non-surgical hair replacement systems, PRP therapy, and low-level laser therapy. Each option has its own benefits and considerations.