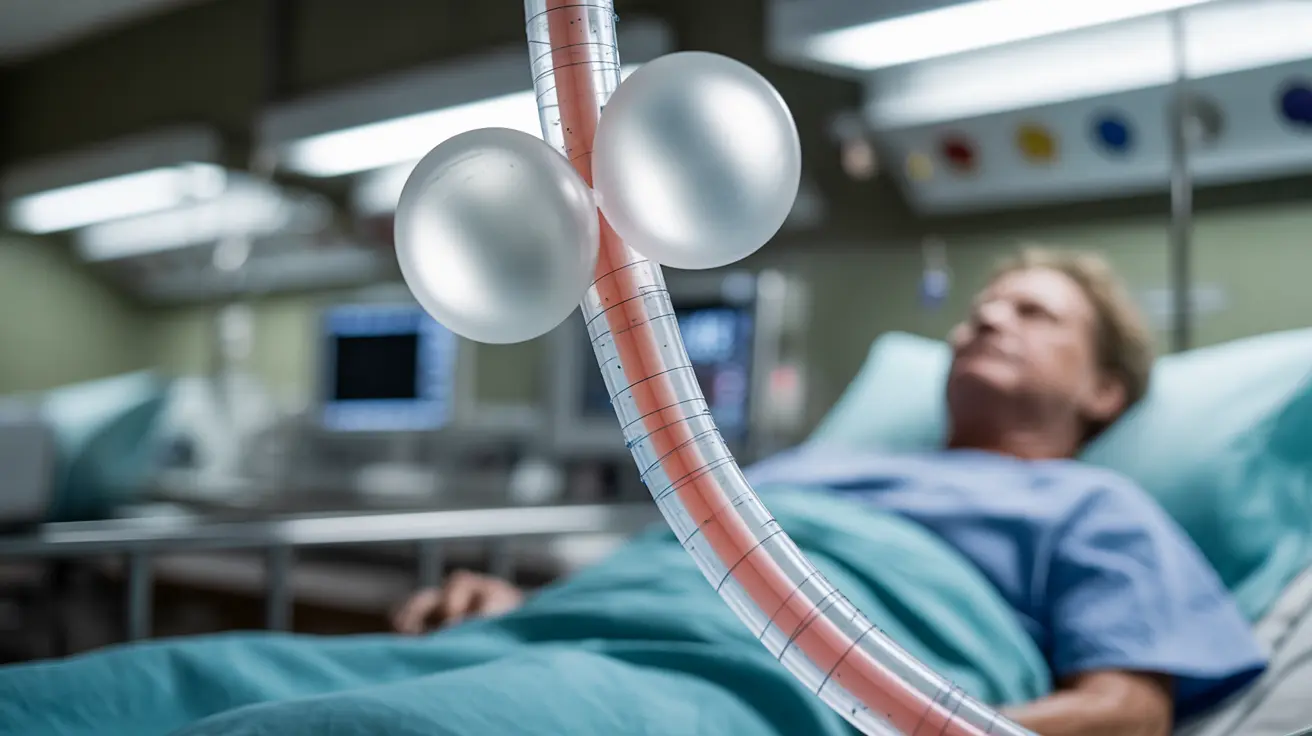
A Sengstaken-Blakemore tube is a specialized medical device used in emergency situations to control severe bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, particularly from esophageal varices. This life-saving intervention, while invasive, can be crucial when other treatment options have failed or aren't immediately available.
Understanding how this device works, when it's used, and its associated risks is essential for both healthcare providers and patients facing severe gastrointestinal bleeding emergencies. Let's explore the key aspects of this important medical tool.
What is a Sengstaken-Blakemore Tube?
A Sengstaken-Blakemore tube is a specialized multi-lumen tube featuring two inflatable balloons: an esophageal balloon and a gastric balloon. The device is inserted through the nose or mouth and passed down into the stomach. When properly positioned, these balloons can be inflated to apply pressure to bleeding sites in the esophagus and stomach.
The tube contains several channels that serve different purposes, including:
- Gastric aspiration port for removing stomach contents
- Esophageal aspiration port for drainage
- Inflation channels for both balloons
- A central lumen for gastric decompression
Medical Emergency Applications
This device is primarily used in critical situations involving severe upper gastrointestinal bleeding, particularly when other treatments have proven ineffective. The most common scenarios include:
- Bleeding from esophageal varices
- Severe portal hypertension
- Acute gastric bleeding
- Bridge therapy until definitive treatment can be initiated
Insertion and Management Procedure
The insertion of a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube requires careful attention to proper technique and positioning. Healthcare providers must follow specific steps:
- Confirm the need for tube placement
- Obtain necessary patient consent when possible
- Position the patient appropriately
- Insert the tube carefully through the nose or mouth
- Confirm proper placement through X-ray
- Monitor balloon pressures regularly
Potential Complications and Risks
While this device can be life-saving, it comes with significant risks that require careful monitoring:
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Esophageal perforation
- Airway obstruction
- Pressure necrosis
- Mucosal ulceration
- Discomfort and pain
Duration and Monitoring
The Sengstaken-Blakemore tube is typically a temporary measure, usually kept in place for 24-48 hours maximum. During this time, continuous monitoring is essential to:
- Check balloon pressures
- Monitor for complications
- Assess bleeding control
- Evaluate patient comfort and stability
Alternative Treatment Options
Several alternative treatments may be considered before or after using a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube:
- Endoscopic band ligation
- Sclerotherapy
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
- Pharmacological therapy
- Surgical interventions
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube work to stop bleeding in the esophagus or stomach?
The tube works through two inflatable balloons - one in the stomach and one in the esophagus. These balloons, when inflated, apply direct pressure to the bleeding sites, particularly in cases of esophageal varices. The pressure helps compress the blood vessels and stop the bleeding.
What are the common complications associated with using a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube?
Common complications include aspiration pneumonia, esophageal perforation, airway obstruction, pressure necrosis, and mucosal ulceration. These risks necessitate careful monitoring and proper management by healthcare professionals.
When is a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube typically used in medical emergencies?
The tube is typically used in cases of severe upper gastrointestinal bleeding, particularly from esophageal varices, when other treatment options have failed or aren't immediately available. It's considered a temporary, life-saving measure in emergency situations.
How long can a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube be safely left in place?
The tube should typically not remain in place for more than 24-48 hours due to the risk of complications. It's considered a temporary measure until more definitive treatment can be implemented.
What are the alternatives to using a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube for treating variceal bleeding?
Alternative treatments include endoscopic band ligation, sclerotherapy, TIPS procedure, pharmacological treatments (such as vasopressors), and various surgical interventions. The choice depends on the specific clinical situation and availability of resources.