One of the most persistent myths in personal grooming is that shaving makes hair grow back thicker, darker, or faster. This belief has been passed down through generations, leading many people to avoid shaving certain areas or feel concerned about the long-term effects of their grooming habits. Understanding the science behind hair growth and how shaving actually affects your hair can help you make informed decisions about your personal care routine.
The short answer is no—shaving does not make hair grow back thicker, darker, or faster than it naturally would. This misconception stems from how freshly shaved hair appears and feels when it begins to regrow. Let's explore the scientific facts behind hair growth and examine why this myth continues to persist despite being thoroughly debunked by dermatologists and hair growth specialists.
The Science Behind Hair Growth and Structure
To understand why shaving doesn't affect hair thickness, it's essential to know how hair grows. Hair follicles are located beneath the skin's surface, and each follicle produces hair from its root. The thickness, color, and growth rate of your hair are determined by genetics, hormones, age, and overall health—not by what happens to the hair shaft above the skin.
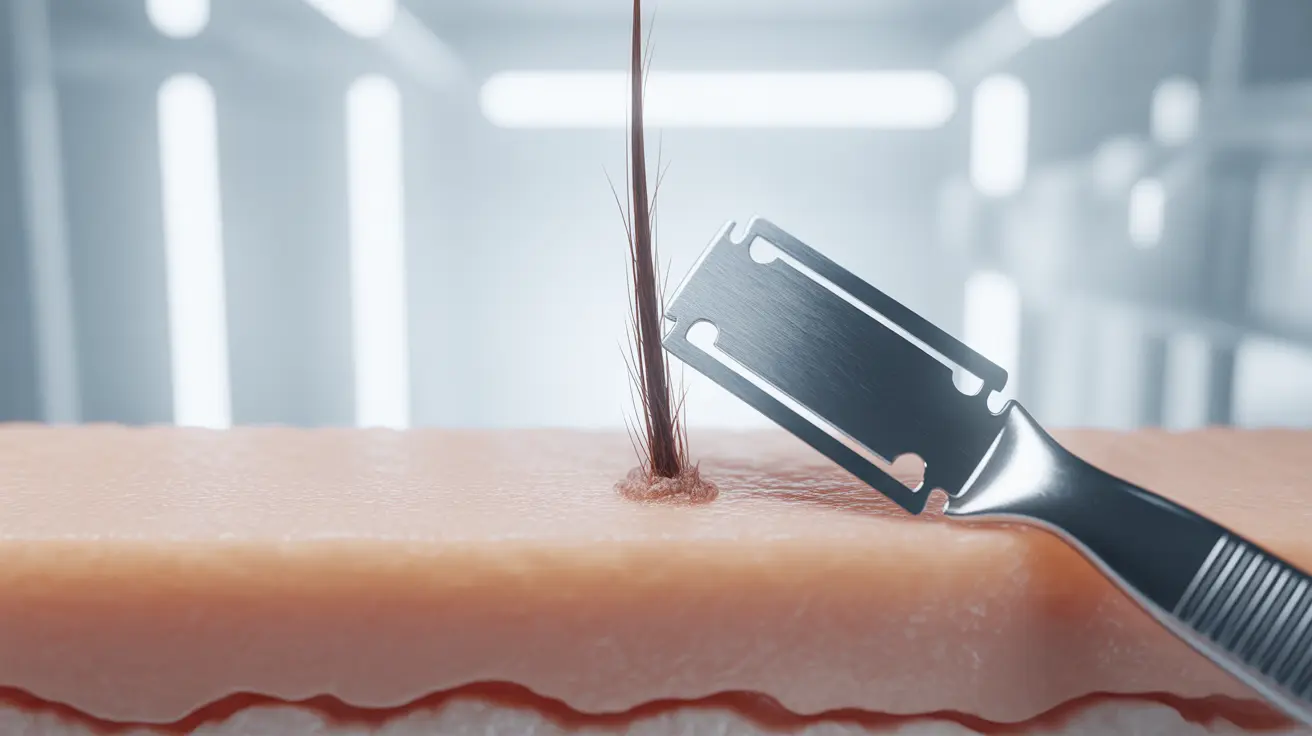
When you shave, you're only cutting the hair shaft at or slightly below the skin's surface. This process doesn't affect the hair follicle, the root, or the underlying structures that determine hair characteristics. Think of it like mowing grass—cutting the visible blades doesn't change the root system or make the grass grow back differently.
Hair naturally tapers to a fine point at its tip. When you shave, you create a blunt edge at the widest part of the hair shaft. As this blunt-edged hair emerges from the skin, it feels coarser and may appear darker because you're seeing the full diameter of the hair shaft rather than the naturally tapered end.
Why Shaved Hair Appears Different When Regrowing
The illusion that shaved hair grows back thicker occurs for several reasons related to hair structure and perception. Fresh hair growth after shaving has a blunt, straight-cut edge rather than the natural taper that develops over time through weathering and daily wear.
Additionally, shorter hair often appears darker because it hasn't been exposed to sun, styling products, and environmental factors that can lighten hair over time. The contrast between the darker, blunt-edged stubble and the surrounding skin can make the hair seem more prominent and thicker than it actually is.
The coarse feeling of regrown hair is simply due to the blunt cut created by the razor. As hair continues to grow and is exposed to environmental factors, the ends naturally become softer and more tapered, returning to their normal texture and appearance.
How Shaving Actually Affects Hair Follicles
Contrary to popular belief, shaving has no impact on the hair follicle's structure or function. The follicle remains unchanged because shaving occurs entirely above the skin's surface. Hair growth rate, thickness, and color are predetermined by factors deep within the follicle and surrounding tissues.
Research has consistently shown that the diameter of individual hair strands remains constant regardless of shaving frequency. A study published in dermatological journals measured hair thickness before and after shaving and found no significant changes in hair diameter or growth rate.
Some people may notice changes in their hair over time and mistakenly attribute these changes to shaving. However, natural variations in hair growth often result from hormonal changes, aging, stress, nutrition, or underlying health conditions—not from grooming practices.
Optimal Shaving Techniques for Healthy Skin
While shaving doesn't affect hair growth, proper technique can significantly impact your skin's health and appearance. Using a sharp, clean razor is essential for preventing irritation, cuts, and ingrown hairs. Dull blades require more pressure and multiple passes, increasing the risk of skin damage.
Preparation is key to a comfortable shave. Start with clean, warm skin to soften hair and open pores. Use a quality shaving cream or gel to create a protective barrier between the razor and your skin. Shave in the direction of hair growth to minimize irritation, and avoid applying excessive pressure.
After shaving, rinse with cool water to close pores and apply a gentle, alcohol-free moisturizer to soothe and hydrate the skin. Replace razor blades regularly, and consider using a single-blade razor if you experience frequent irritation or ingrown hairs with multi-blade options.
Comparing Hair Removal Methods and Regrowth Patterns
Different hair removal methods affect regrowth patterns in various ways, though none actually change the fundamental characteristics of your hair. Shaving cuts hair at the surface level, resulting in immediate regrowth visibility within a day or two.
Waxing and plucking remove hair from the root, which means regrowth takes longer—typically 3-6 weeks. However, the new hair that emerges has the same thickness and color as before. Some people believe waxed hair grows back finer, but this is usually due to hair becoming damaged over time from repeated removal, not from the waxing process itself changing hair structure.
Laser hair removal targets hair follicles with concentrated light energy, potentially reducing future growth. This method can decrease hair density and thickness over multiple sessions, but it works by damaging follicles rather than changing natural hair characteristics. The results vary based on hair color, skin type, and individual response to treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does shaving make hair grow back thicker, darker, or faster?
No, shaving does not make hair grow back thicker, darker, or faster. This is a persistent myth that has been scientifically disproven. Shaving only cuts the hair shaft at the surface level and doesn't affect the hair follicle, which determines hair thickness, color, and growth rate. The appearance of thicker, darker hair after shaving is due to the blunt edge created by cutting and the fact that new growth hasn't been exposed to environmental factors that naturally lighten and soften hair over time.
Why does shaved hair seem coarser or darker when it starts to grow back?
Shaved hair appears coarser and darker because the razor creates a blunt, straight-cut edge at the widest part of the hair shaft, rather than the naturally tapered end that develops over time. This blunt edge feels rougher against the skin and appears more prominent. Additionally, newly grown hair hasn't been exposed to sun, styling products, and environmental factors that gradually lighten and soften hair, making it appear darker than mature hair growth.
How does shaving affect the actual growth and structure of hair follicles?
Shaving has no effect on hair follicles or their structure. Since shaving occurs entirely above the skin's surface, it cannot reach or influence the follicle, which is located beneath the skin. Hair follicles determine all the characteristics of hair growth, including thickness, color, texture, and growth rate. These factors are controlled by genetics, hormones, and overall health—not by surface-level hair removal methods like shaving.
What are the best shaving practices to avoid skin irritation and ingrown hairs?
To minimize irritation and ingrown hairs, use a sharp, clean razor and replace blades regularly. Prepare your skin with warm water and use a quality shaving cream or gel. Shave in the direction of hair growth rather than against it, and avoid applying excessive pressure. After shaving, rinse with cool water and apply an alcohol-free moisturizer. If you're prone to ingrown hairs, consider using a single-blade razor and gently exfoliating the area regularly with a soft brush or cloth.
How does shaving compare to other hair removal methods like waxing or laser in terms of hair regrowth?
Different hair removal methods affect the timing and appearance of regrowth, but none change the fundamental characteristics of your hair. Shaving cuts hair at the surface, so regrowth is visible within days. Waxing and plucking remove hair from the root, delaying regrowth for 3-6 weeks, but the new hair maintains the same thickness and color. Laser hair removal can reduce hair density and thickness over multiple sessions by targeting follicles, but this works through follicle damage rather than changing natural hair properties. Each method has different duration and maintenance requirements, but your hair's genetic characteristics remain constant regardless of the removal method chosen.