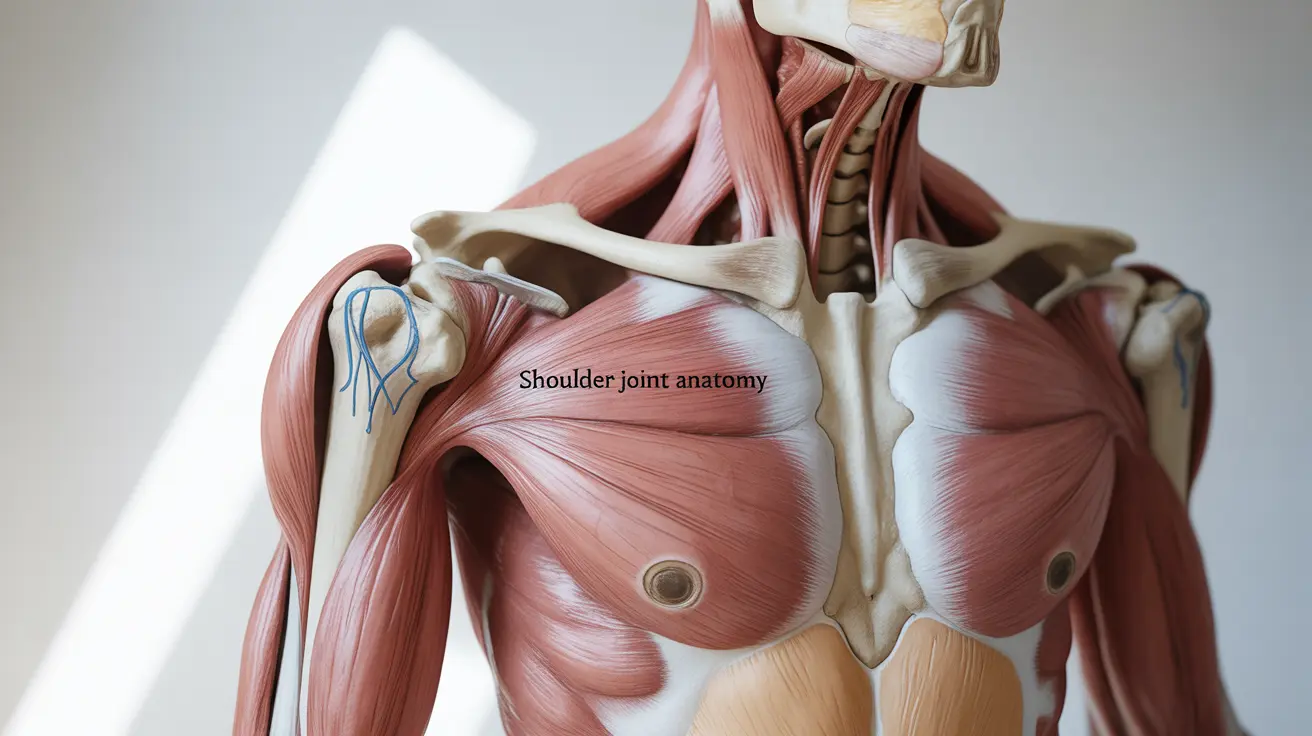
The shoulder is one of the most complex and versatile joints in the human body, capable of an impressive range of motion. Understanding the labeled shoulder anatomy is crucial for medical professionals, students, and anyone interested in musculoskeletal health. This comprehensive guide will break down the key components of shoulder anatomy and their functions.
Essential Bones and Joints of the Shoulder
The shoulder joint complex consists of three main bones that work together to enable movement:
- The clavicle (collarbone)
- The scapula (shoulder blade)
- The humerus (upper arm bone)
These bones form three important joints:
- The glenohumeral joint (main shoulder joint)
- The acromioclavicular (AC) joint
- The sternoclavicular joint
The Rotator Cuff Muscles and Their Functions
The rotator cuff comprises four essential muscles that stabilize and move the shoulder:
Supraspinatus
Located on top of the shoulder blade, this muscle helps lift the arm away from the body (abduction).
Infraspinatus
Positioned on the back of the shoulder blade, it assists in external rotation of the arm.
Teres Minor
Working alongside the infraspinatus, it aids in external rotation and arm stabilization.
Subscapularis
Found on the front of the shoulder blade, this muscle enables internal rotation of the arm.
Critical Ligaments and Soft Tissues
The shoulder's stability relies heavily on various ligaments and soft tissues:
- Glenohumeral ligaments
- Coracohumeral ligament
- Coracoacromial ligament
- Glenoid labrum
- Joint capsule
These structures work together to maintain joint integrity while allowing for extensive movement.
Common Injury Sites and Prevention
Several areas of the shoulder are particularly vulnerable to injury:
Rotator Cuff
The most frequently injured component, often due to overuse or acute trauma.
Labrum
Susceptible to tears, especially during repetitive overhead movements.
AC Joint
Commonly injured in contact sports or falls onto the shoulder.
Important Muscle Groups
Beyond the rotator cuff, other significant muscle groups include:
- Deltoid (anterior, middle, and posterior)
- Biceps brachii
- Triceps brachii
- Trapezius
- Latissimus dorsi
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main bones and joints labeled in the shoulder anatomy? The main bones are the clavicle, scapula, and humerus. The primary joints are the glenohumeral joint, acromioclavicular joint, and sternoclavicular joint.
Which muscles make up the rotator cuff, and what roles do they play in shoulder movement? The rotator cuff consists of the supraspinatus (arm lifting), infraspinatus (external rotation), teres minor (external rotation), and subscapularis (internal rotation). Together, they stabilize the shoulder joint and enable precise arm movements.
How do the ligaments and soft tissues contribute to shoulder joint stability? Ligaments and soft tissues form a network that holds the joint together while allowing movement. The glenohumeral ligaments, labrum, and joint capsule create a stable yet flexible environment for shoulder function.
What parts of the shoulder anatomy are most prone to injury and why? The rotator cuff, labrum, and AC joint are most susceptible to injury due to their extensive use in movement and their vulnerability to overuse, trauma, and degenerative conditions.
Where can I find detailed labeled diagrams of the shoulder bones, muscles, and joints for better understanding? Medical textbooks, anatomical atlases, and reputable medical websites like medical schools' educational resources often provide detailed, labeled shoulder anatomy diagrams. Professional medical associations also offer comprehensive anatomical resources.