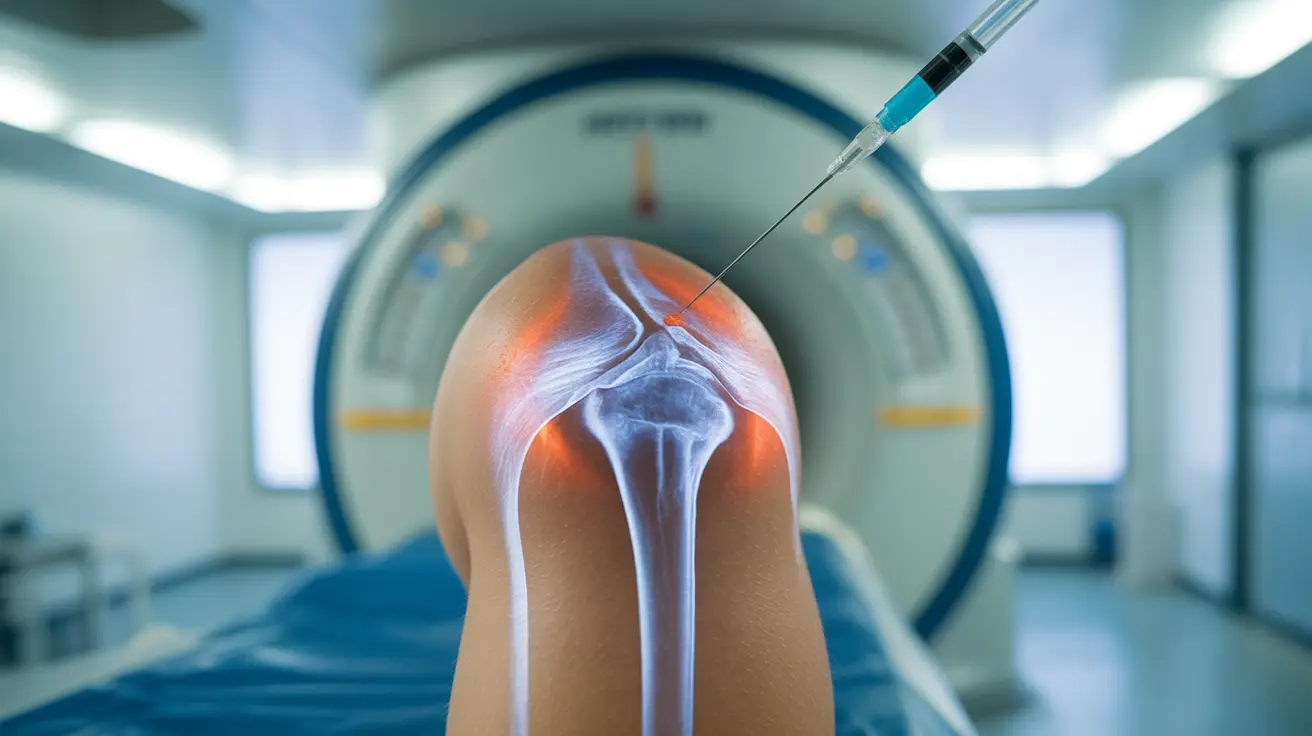
A shoulder arthrogram is a specialized diagnostic imaging procedure that helps doctors clearly visualize the internal structures of your shoulder joint. This detailed examination combines contrast material with imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans to provide precise images of your shoulder's soft tissues, including the rotator cuff, labrum, and joint capsule.
Understanding what a shoulder arthrogram involves and why it might be necessary can help you feel more confident about the procedure. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about shoulder arthrograms, from preparation to recovery.
Understanding Shoulder Arthrogram Basics
A shoulder arthrogram involves injecting a contrast material directly into your shoulder joint before taking detailed images. The contrast material helps highlight specific structures within the joint, making them more visible on imaging studies. This enhanced visibility helps doctors identify injuries or conditions that might not be apparent on standard X-rays or scans.
When Is a Shoulder Arthrogram Needed?
Doctors typically recommend a shoulder arthrogram when they need to:
- Evaluate persistent shoulder pain
- Assess suspected rotator cuff tears
- Investigate shoulder instability
- Diagnose labral tears
- Examine unexplained shoulder stiffness
- Plan for potential shoulder surgery
The Shoulder Arthrogram Procedure
The procedure typically involves two main phases: the contrast injection and the imaging study. During the first phase, your doctor will:
- Clean and numb the injection site
- Use fluoroscopy (real-time X-ray) to guide the needle placement
- Inject the contrast material into your shoulder joint
- Gently move your shoulder to distribute the contrast material
Following the injection, you'll undergo either an MRI, CT scan, or X-ray to capture detailed images of your shoulder structures.
Benefits of Shoulder Arthrography
This specialized imaging technique offers several advantages:
- Provides highly detailed images of shoulder structures
- Helps identify subtle injuries that might be missed on standard imaging
- Assists in surgical planning
- Can help determine the most effective treatment approach
- Allows for accurate diagnosis of complex shoulder conditions
Potential Risks and Considerations
While shoulder arthrograms are generally safe, you should be aware of potential risks:
- Temporary pain or discomfort at the injection site
- Infection (rare)
- Allergic reaction to contrast material
- Temporary shoulder stiffness
- Minor bleeding or bruising
Post-Procedure Care
After your shoulder arthrogram, following proper care instructions is essential for a smooth recovery:
- Rest your shoulder for 24 hours
- Apply ice if you experience discomfort
- Avoid strenuous activities for 1-2 days
- Keep the injection site clean and dry
- Monitor for signs of infection or unusual reactions
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a shoulder arthrogram and why is it performed?
A shoulder arthrogram is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses contrast material and imaging technology to examine the internal structures of your shoulder joint. It's performed to diagnose specific shoulder conditions, assess injuries, and guide treatment decisions when standard imaging isn't sufficient.
How is the shoulder arthrogram procedure done and what can I expect during it?
The procedure involves two steps: first, a contrast material is injected into your shoulder joint under fluoroscopic guidance after the area is cleaned and numbed. Then, imaging studies (MRI, CT, or X-ray) are performed to capture detailed images of your shoulder structures. The entire process typically takes 30-60 minutes.
What shoulder conditions or injuries can a shoulder arthrogram detect?
A shoulder arthrogram can detect various conditions including rotator cuff tears, labral tears, shoulder joint instability, capsular abnormalities, and other soft tissue injuries that might not be visible on standard imaging tests.
What are the risks and benefits of having a shoulder arthrogram?
Benefits include detailed imaging of shoulder structures and accurate diagnosis of complex conditions. Risks are minimal but may include temporary pain, infection risk, allergic reactions to contrast material, and brief shoulder stiffness.
How should I care for my shoulder and what precautions should I take after a shoulder arthrogram?
After the procedure, rest your shoulder for 24 hours, avoid strenuous activities for 1-2 days, apply ice if needed for discomfort, and keep the injection site clean. Monitor for signs of infection and follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider.