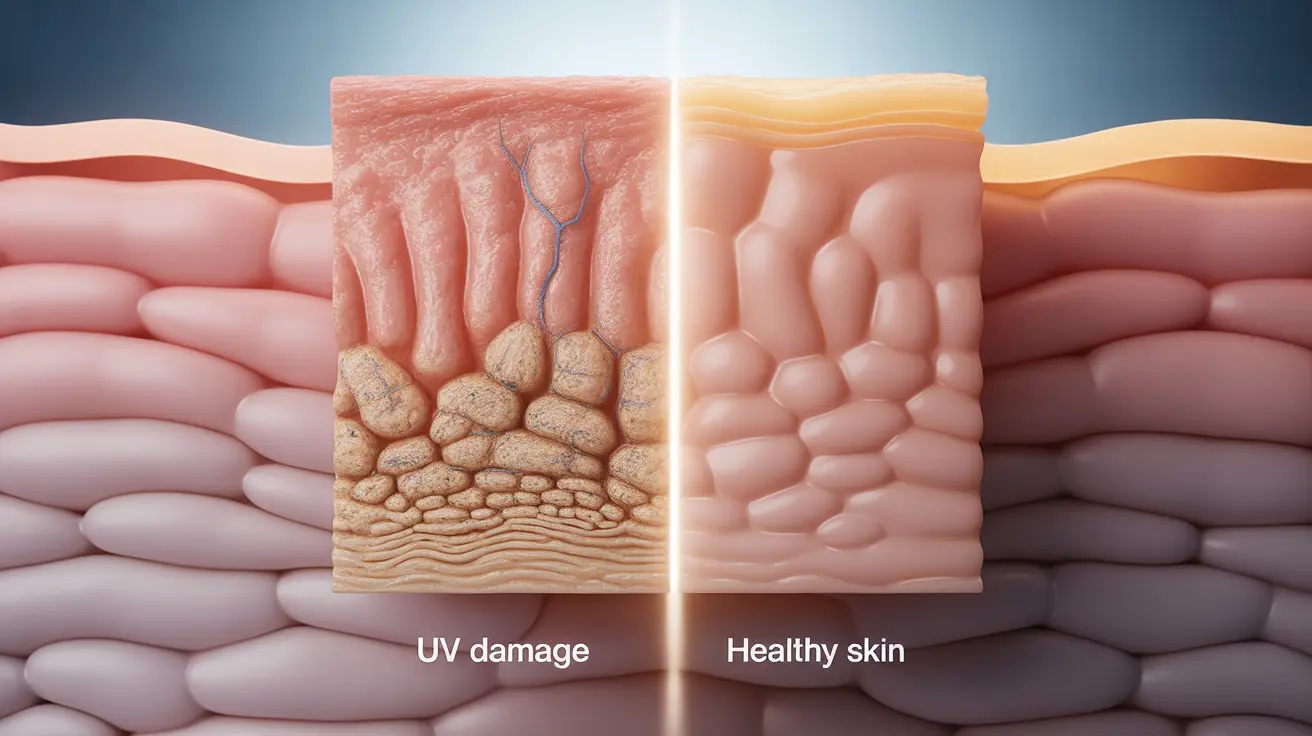
The impact of long-term tanning on your skin extends far beyond the temporary golden glow. Years of UV exposure, whether from outdoor sun exposure or indoor tanning beds, can lead to significant changes in your skin's health, appearance, and overall function. Understanding these effects is crucial for anyone who has spent considerable time tanning and wants to protect their skin moving forward.
If you've spent years tanning, it's important to know that while some damage can't be completely reversed, there are effective ways to improve your skin's health and prevent further deterioration. This comprehensive guide will explore the long-term effects of tanning and provide actionable steps for skin recovery and protection.
The Long-Term Impact of Chronic Tanning
Years of tanning can cause numerous changes to your skin's structure and appearance. These effects often become more visible as you age:
- Premature aging and wrinkles
- Uneven skin tone and dark spots
- Leather-like skin texture
- Enlarged pores
- Loss of elasticity
- Dry, rough patches
At a deeper level, UV exposure damages your skin's DNA and collagen production, leading to lasting structural changes that can take years to become visible.
Understanding UV-Related Skin Damage
Cellular Changes
Prolonged UV exposure affects your skin at the cellular level, causing:
- DNA mutations in skin cells
- Breakdown of collagen and elastin
- Compromised skin barrier function
- Increased melanin production
- Cellular inflammation
Cancer Risk Factors
One of the most serious consequences of long-term tanning is the increased risk of skin cancer. Regular tanning can lead to:
- Higher likelihood of developing melanoma
- Increased risk of basal cell carcinoma
- Greater chance of squamous cell carcinoma
- More frequent precancerous lesions
Healing and Recovery After Quitting Tanning
When you stop tanning, your skin begins a natural healing process. While some damage may be permanent, many aspects of skin health can improve:
Immediate Benefits
- Reduced inflammation
- Decreased risk of sunburn
- Improved hydration levels
- Better cellular turnover
Long-Term Improvements
Over time, consistent skin protection and proper care can lead to:
- More even skin tone
- Improved texture
- Better moisture retention
- Slower aging progression
- Reduced risk of new damage
Essential Skin Care Treatments for Recovery
Several treatments can help repair and protect skin after years of tanning:
Topical Treatments
- Retinoids for cell turnover
- Vitamin C for antioxidant protection
- Peptides for collagen production
- Niacinamide for barrier repair
- Hyaluronic acid for hydration
Professional Treatments
Consider these medical-grade options for enhanced results:
- Chemical peels
- Laser therapy
- Microdermabrasion
- LED light therapy
- Photodynamic therapy
Prevention Strategies Moving Forward
Protecting your skin from further damage is crucial. Implement these essential steps:
- Use broad-spectrum SPF 30+ daily
- Wear protective clothing and hats
- Seek shade during peak UV hours
- Regular skin cancer screenings
- Maintain a proper skincare routine
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the long-term effects of years of tanning on skin appearance and health?
Long-term tanning leads to premature aging, wrinkles, uneven pigmentation, reduced elasticity, and increased risk of skin cancer. It can also cause permanent DNA damage to skin cells and compromise the skin's natural barrier function.
How does quitting tanning improve skin damage caused by chronic UV exposure?
Quitting tanning allows your skin to begin natural repair processes, reducing inflammation and preventing new damage. While some effects are permanent, the skin can show improvements in texture, tone, and overall health when protected from further UV exposure.
What skin care treatments can help repair damage from years of tanning?
Effective treatments include retinoids, vitamin C serums, peptides, and professional procedures like chemical peels and laser therapy. Consistent use of these treatments, combined with proper sun protection, can help improve skin appearance and health.
How does tanning increase the risk of developing skin cancer over time?
Regular tanning causes cumulative DNA damage to skin cells, leading to mutations that can develop into skin cancer. This risk increases with each tanning session and continues to build over years of exposure.
What steps can I take to protect my skin and prevent further damage after years of tanning?
Key steps include daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, avoiding peak UV hours, getting regular skin checks, and maintaining a consistent skincare routine with protective and reparative ingredients.