Skin tuberculosis, also known as cutaneous TB, is a less common but significant form of tuberculosis that primarily affects the skin. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment is crucial for early detection and successful management of this condition.
While skin TB accounts for only a small percentage of all tuberculosis cases, recognizing its distinctive features can help ensure timely medical intervention and prevent complications. This comprehensive guide explores the key aspects of cutaneous tuberculosis that everyone should know.
Types and Manifestations of Skin TB
Cutaneous tuberculosis can present in various forms, each with distinct characteristics:
- Lupus vulgaris (most common in Europe)
- Scrofuloderma
- Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis
- Tuberculous chancre
- Miliary tuberculosis of the skin
Each type manifests differently, making recognition of specific skin TB symptoms essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Skin TB Symptoms to Watch For
The manifestation of skin tuberculosis varies depending on the type, but common symptoms include:
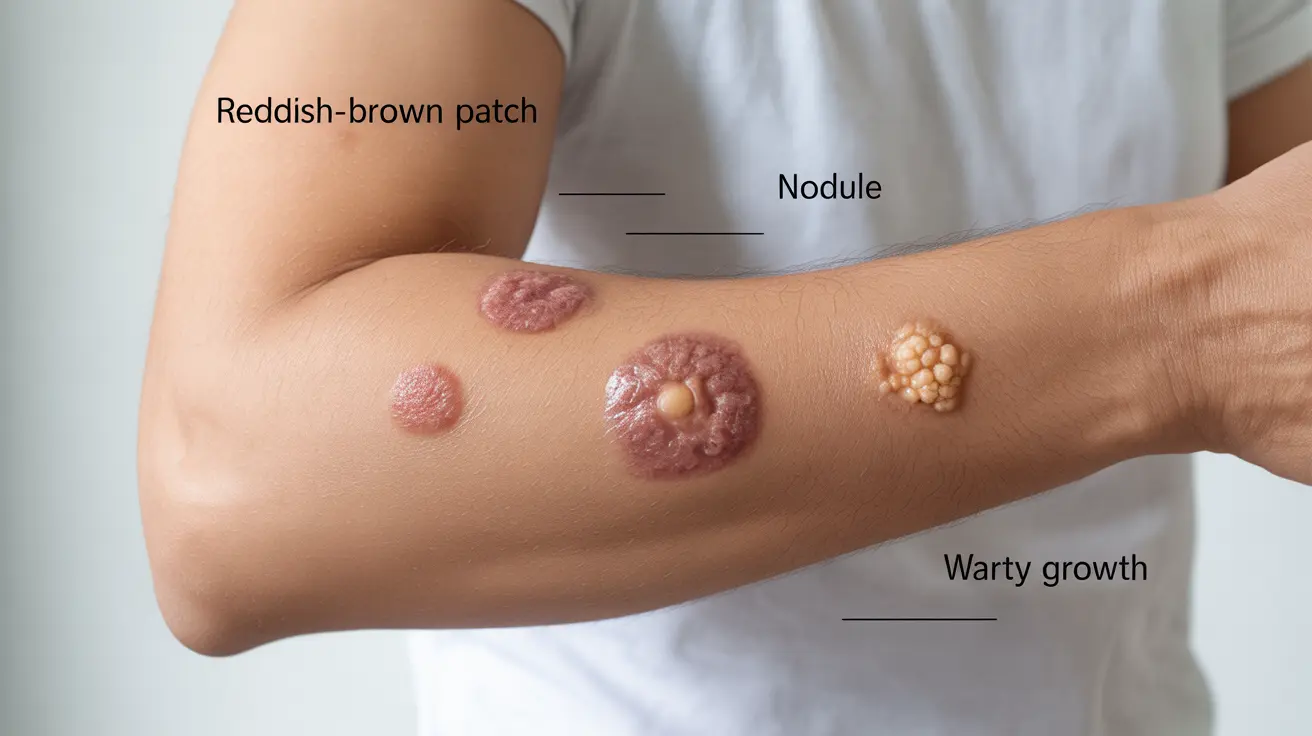
- Reddish-brown patches or plaques
- Nodules under the skin
- Ulcers that heal slowly
- Warty growths
- Painful abscesses
- Drainage from affected areas
These symptoms typically develop gradually and may persist for extended periods without proper treatment.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing skin tuberculosis:
- Direct inoculation of TB bacteria into the skin
- Spread from internal TB infection
- Weakened immune system
- Poor nutrition
- Overcrowded living conditions
- Limited access to healthcare
Diagnosis and Testing
Accurate diagnosis of skin TB requires a comprehensive approach:
Physical Examination
Doctors will carefully examine skin lesions and note their characteristics, distribution, and progression.
Laboratory Tests
- Skin biopsy
- Culture tests
- PCR testing
- Tuberculin skin test
- Interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs)
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for skin tuberculosis typically involves:
Medication Regimen
A combination of anti-tuberculosis drugs is usually prescribed for 6-12 months, including:
- Isoniazid
- Rifampin
- Pyrazinamide
- Ethambutol
Supportive Care
Additional measures may include wound care, nutritional support, and management of any underlying conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common skin symptoms and types of lesions seen in skin tuberculosis (TB)? Skin TB typically presents with reddish-brown patches, nodules, slow-healing ulcers, and warty growths. The most common types include lupus vulgaris, scrofuloderma, and tuberculosis verrucosa cutis.
How is skin tuberculosis diagnosed and what tests are used to confirm it? Diagnosis involves physical examination, skin biopsy, culture tests, PCR testing, tuberculin skin test, and IGRAs. Multiple tests are often needed for accurate diagnosis.
What causes skin tuberculosis and who is at higher risk of developing it? Skin TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. People with weakened immune systems, poor nutrition, or those living in overcrowded conditions are at higher risk.
How is skin tuberculosis treated and how long does the treatment usually last? Treatment typically involves a combination of anti-tuberculosis medications taken for 6-12 months. The exact duration depends on the severity and type of infection.
Can skin tuberculosis cause symptoms beyond the skin, and what systemic signs should I watch for? Yes, skin TB can be associated with fever, fatigue, weight loss, and night sweats. In some cases, it may indicate the presence of tuberculosis in other parts of the body.