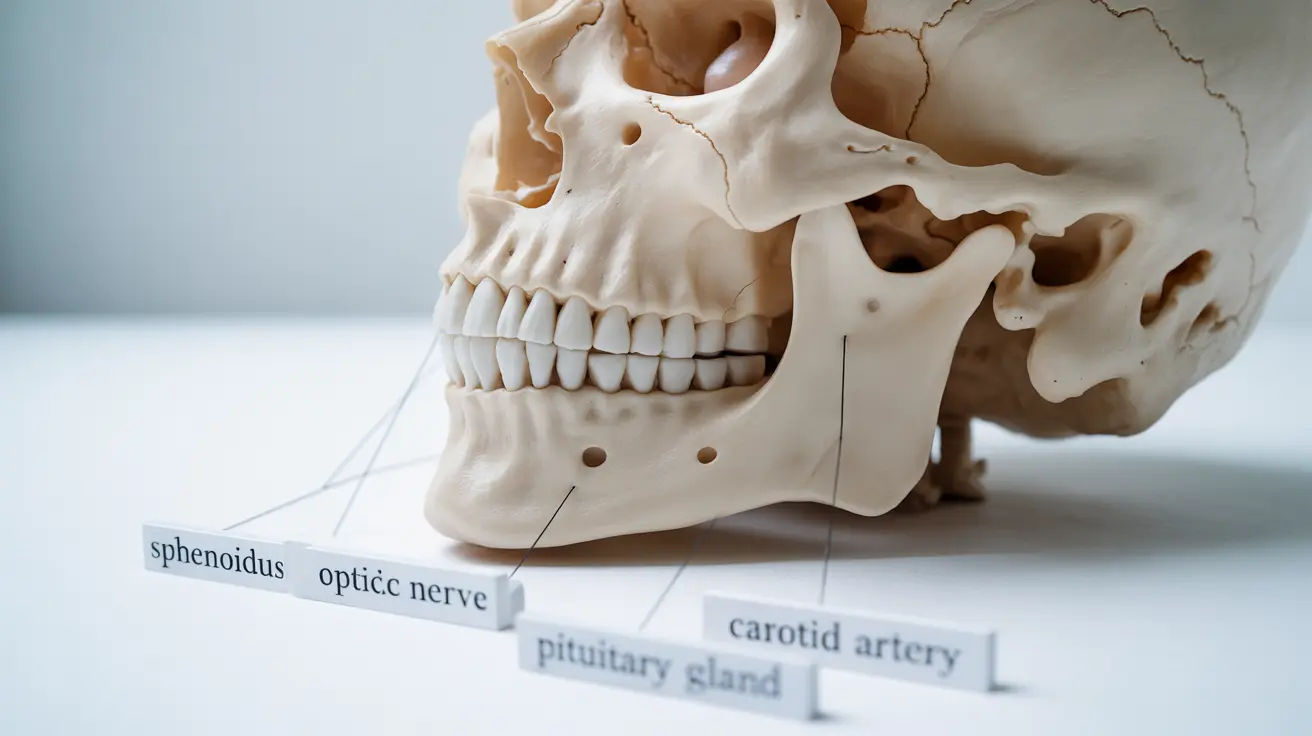
The sphenoid sinus is a crucial yet often overlooked part of your skull's anatomy, playing important roles in breathing, voice production, and overall sinus health. Located deep within the skull behind your nose, this air-filled cavity requires special attention when problems arise due to its proximity to vital structures like the optic nerve and pituitary gland.
Understanding the sphenoid sinus and its potential issues is essential for recognizing when to seek medical attention and maintaining optimal sinus health. Let's explore this important anatomical structure in detail.
Anatomy and Location of the Sphenoid Sinus
The sphenoid sinus is one of four paired paranasal sinuses, situated in the sphenoid bone at the base of your skull. Unlike other sinuses that are more readily accessible, the sphenoid sinus lies in a deeper, more central location, making it particularly challenging to examine and treat when problems occur.
This unique positioning means the sphenoid sinus is surrounded by several critical structures:
- The optic nerve (responsible for vision)
- The carotid arteries (main blood supply to the brain)
- The pituitary gland (master hormone control)
- Various cranial nerves
Functions and Importance
Your sphenoid sinus serves several vital functions:
- Helps humidify and filter the air you breathe
- Contributes to voice resonance
- Reduces the weight of the skull
- Provides protection to surrounding structures
These air-filled cavities also help regulate the temperature of the air you breathe and produce mucus that helps trap harmful particles.
Common Problems and Conditions
Sphenoid Sinusitis
The most common condition affecting the sphenoid sinus is sinusitis, an inflammation or infection of the sinus cavity. This condition can present unique challenges due to the sinus's deep location and can cause symptoms such as:
- Severe headache, particularly behind the eyes
- Visual disturbances
- Post-nasal drip
- Facial pain or pressure
- Reduced sense of smell
Structural Abnormalities
Some people may have structural issues affecting their sphenoid sinus, including:
- Deviated septum affecting sinus drainage
- Bone spurs or other growth abnormalities
- Congenital variations in sinus size or shape
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing sphenoid sinus problems requires specialized imaging and examination techniques due to the sinus's deep location. Common diagnostic tools include:
- CT scans of the sinuses
- MRI imaging
- Nasal endoscopy
- Specialized X-rays
Treatment Options
Treatment for sphenoid sinus conditions varies depending on the specific issue but may include:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Nasal corticosteroids
- Decongestants
- Saline nasal irrigation
- Surgical intervention in severe cases
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common symptoms of sphenoid sinus infection or inflammation?
Common symptoms include severe headache behind the eyes, visual disturbances, post-nasal drip, facial pressure, and reduced sense of smell. The pain may be worse when bending forward or lying down.
- How is sphenoid sinusitis diagnosed and what imaging tests are used?
Diagnosis typically involves CT scans, MRI imaging, and nasal endoscopy. These tests help visualize the deep-seated sinus and identify any inflammation, infection, or structural abnormalities.
- What treatments are available for sphenoid sinusitis, including medications and surgery?
Treatment options range from medications like antibiotics, nasal corticosteroids, and decongestants to surgical procedures in severe cases. Saline irrigation can help maintain sinus health and manage symptoms.
- Can problems in the sphenoid sinus affect nearby structures like the optic nerve or pituitary gland?
Yes, due to its location, sphenoid sinus problems can affect nearby structures. Inflammation or infection can potentially impact vision (via the optic nerve) or hormone function (via the pituitary gland), making prompt treatment essential.
- How does the sphenoid sinus contribute to breathing and voice resonance?
The sphenoid sinus helps humidify and warm inhaled air while also acting as a resonating chamber for speech. It contributes to voice quality and helps regulate the temperature and moisture content of breathed air.