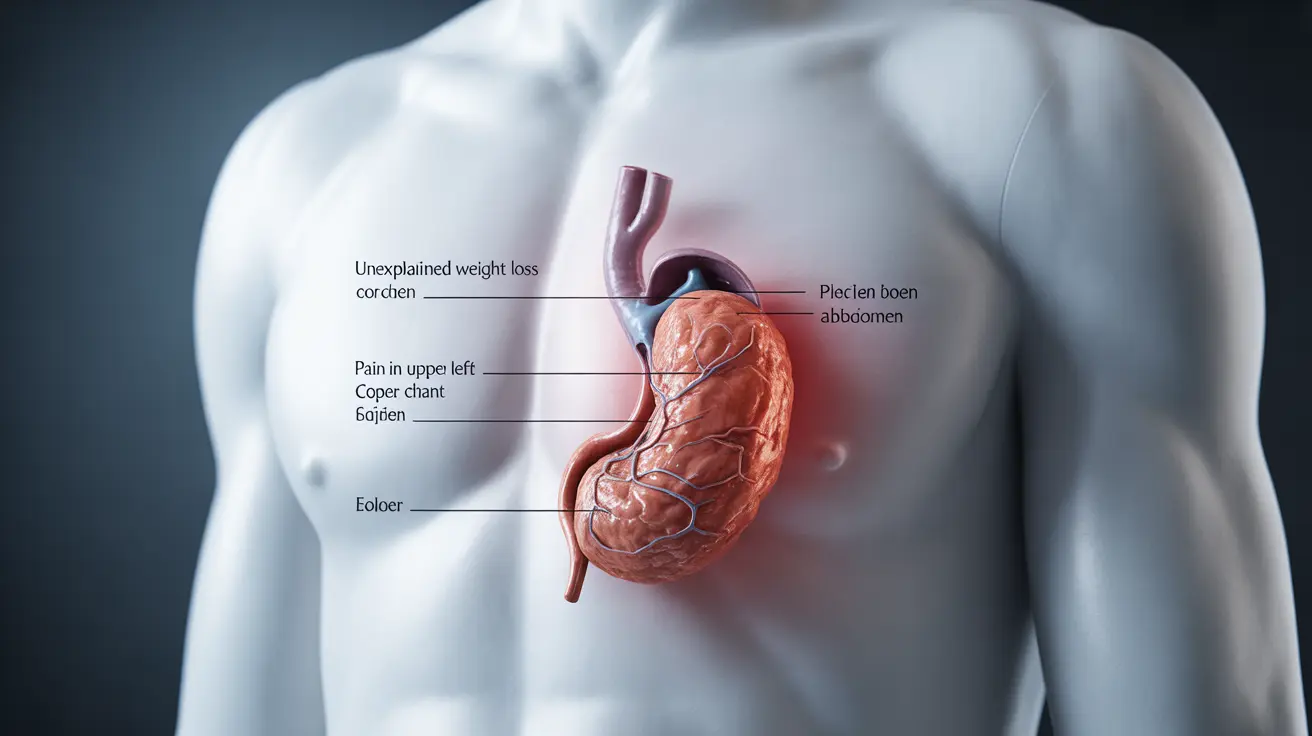
Spleen cancer is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and proper medical care. While relatively rare compared to other types of cancer, understanding its symptoms, diagnosis methods, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and improved outcomes. This comprehensive guide will help you learn about this condition and know when to seek medical attention.
What is Spleen Cancer?
Spleen cancer occurs when abnormal cells begin to grow uncontrollably in the spleen, an organ that plays a vital role in your immune system and blood filtering. While primary spleen cancer (cancer that originates in the spleen) is uncommon, secondary spleen cancer (cancer that spreads from other parts of the body) occurs more frequently.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of spleen cancer early can lead to better treatment outcomes. Common indicators include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pain or fullness in the upper left abdomen
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Night sweats
- Persistent fever
These symptoms can vary in severity and may also indicate other health conditions, making professional medical evaluation essential for accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Process and Testing
Diagnosing spleen cancer typically involves several steps and testing methods:
Physical Examination
Your doctor will perform a thorough physical exam, paying special attention to your abdomen to check for spleen enlargement or tenderness.
Imaging Tests
Various imaging techniques may be used, including:
- CT scans
- MRI scans
- Ultrasound
- PET scans
Blood Tests
Comprehensive blood work helps evaluate overall health and can indicate potential cancer markers or related conditions.
Biopsy
A tissue sample may be taken from the spleen for detailed laboratory analysis to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of cancer present.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment options for spleen cancer vary depending on several factors, including the type of cancer, its stage, and the patient's overall health. Common treatment approaches include:
Splenectomy
Surgical removal of the spleen is often the primary treatment option, especially for isolated spleen tumors.
Chemotherapy
Systematic treatment using cancer-fighting drugs may be necessary, particularly if the cancer has spread beyond the spleen.
Targeted Therapy
Newer treatments that target specific cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue may be appropriate in certain cases.
Risk Factors and Prevention
While the exact causes of spleen cancer aren't always clear, certain factors may increase risk:
- Previous cancer diagnosis
- Weakened immune system
- Certain viral infections
- Exposure to specific chemicals or radiation
- Family history of blood cancers
When to Seek Emergency Care
Some symptoms require immediate medical attention, including:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Sudden weakness or dizziness
- Signs of internal bleeding
- Rapid heart rate
- Difficulty breathing
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms that might indicate spleen cancer? Common symptoms include unexplained weight loss, pain in the upper left abdomen, fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, night sweats, and persistent fever.
How is spleen cancer diagnosed and what tests are usually performed? Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, imaging tests (CT, MRI, ultrasound, PET scans), blood tests, and possibly a biopsy to confirm the presence and type of cancer.
What treatment options are available for different types of spleen cancer? Treatment options include splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen), chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. The specific approach depends on the cancer type, stage, and overall patient health.
What are the main causes and risk factors for developing spleen cancer? Risk factors include previous cancer diagnosis, weakened immune system, certain viral infections, exposure to specific chemicals or radiation, and family history of blood cancers.
When should I seek emergency care for symptoms related to spleen cancer? Seek immediate medical attention for severe abdominal pain, sudden weakness or dizziness, signs of internal bleeding, rapid heart rate, or difficulty breathing.