When you experience pain after a physical injury or overexertion, determining whether you're dealing with a sprain or strain can be crucial for proper treatment. While these injuries may seem similar, they affect different parts of the body and require specific approaches to healing. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the key differences between sprains and strains, their treatments, and prevention strategies.
The Fundamental Differences Between Sprains and Strains
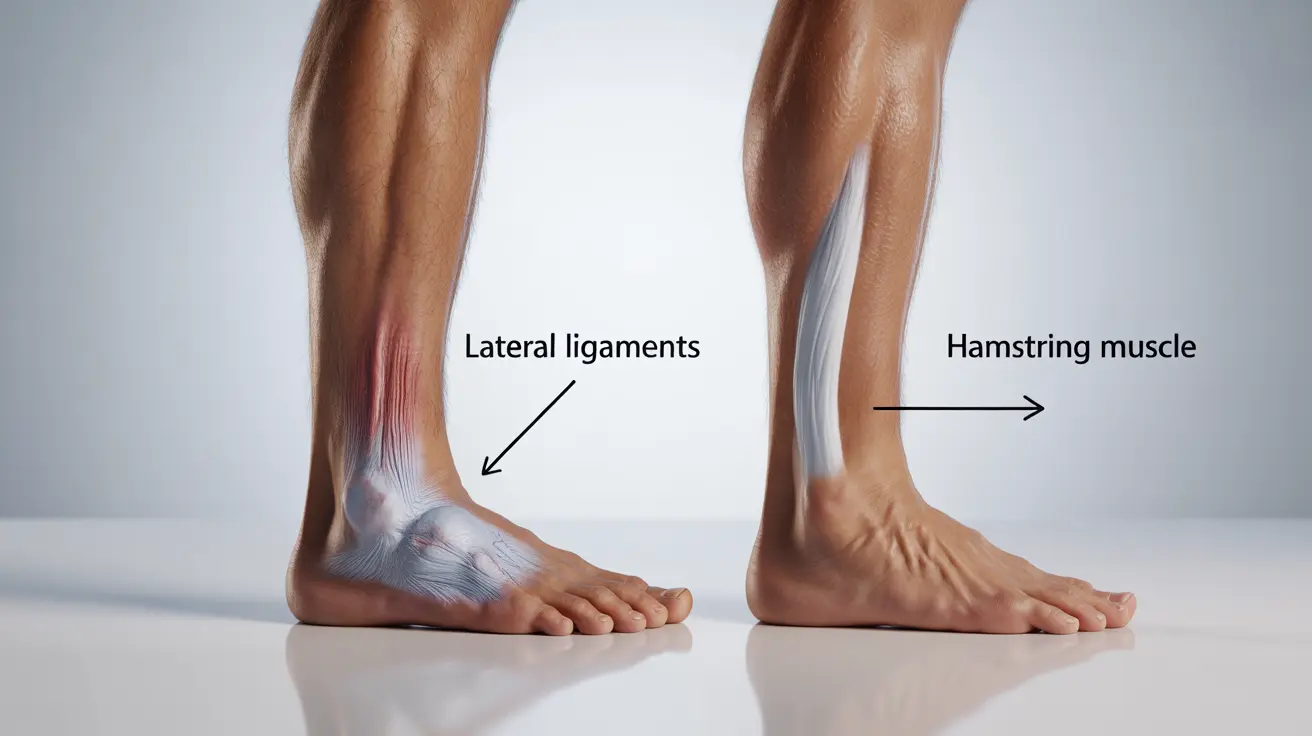
Sprains and strains are distinct injuries that affect different anatomical structures. A sprain occurs when ligaments - the tough bands connecting bones at joints - are stretched or torn. Common locations include ankles, wrists, and knees. Strains, on the other hand, involve injury to muscles or tendons, frequently affecting the back, hamstrings, or neck muscles.
Identifying Symptoms of Sprains
Sprains typically present with these characteristic signs:
- Pain and tenderness around the affected joint
- Swelling and bruising
- Limited joint mobility
- Possible popping sound at the time of injury
- Joint instability
Recognizing Strain Symptoms
Strain symptoms often include:
- Muscle pain and tenderness
- Muscle weakness and spasms
- Inflammation
- Limited range of motion
- Gradual onset in cases of chronic strains
Treatment Approaches for Both Injuries
While treatment strategies share some similarities, they may vary depending on the specific injury and its severity. The RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) forms the foundation of initial treatment for both conditions.
Managing Sprains
Sprain treatment typically involves:
- Immediate joint immobilization
- Ice therapy for the first 48-72 hours
- Compression with an elastic bandage
- Gradual return to movement through physical therapy
- Possible surgical intervention for severe cases
Treating Strains
For strains, treatment usually includes:
- Gentle stretching exercises
- Heat therapy after initial inflammation subsides
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Muscle strengthening exercises
- Physical therapy for severe cases
Prevention Strategies
Preventing both sprains and strains involves proper preparation and technique during physical activities:
- Regular stretching and warm-up exercises
- Proper form during exercise and sports
- Gradually increasing activity intensity
- Using appropriate equipment and footwear
- Maintaining overall physical fitness and flexibility
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
Recovery time varies significantly based on injury severity and location. Mild sprains and strains may heal within 2-4 weeks, while severe injuries can take several months. Factors affecting recovery include:
- Injury grade (mild, moderate, or severe)
- Individual healing capacity
- Adherence to treatment protocol
- Overall health and fitness level
- Previous injury history
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between a sprain and a strain, and how do you determine which one you have?
Sprains affect ligaments connecting bones at joints, while strains involve muscles or tendons. You can often determine which you have based on location and symptoms - sprains typically occur at joints with sudden pain and swelling, while strains usually affect muscles with gradual onset of pain and tightness.
How do you treat a sprain versus a strain at home, and what are the common signs that you need medical attention?
Both injuries initially benefit from RICE treatment. Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, inability to bear weight, significant swelling, or numbness/tingling. Additionally, if symptoms don't improve after several days of home treatment, consult a healthcare provider.
Can a sprain or strain be caused by overuse rather than a sudden injury, and what are common examples?
Yes, particularly strains can develop from overuse. Common examples include tennis elbow, runner's knee, and repetitive stress injuries from poor workplace ergonomics. Sprains are more commonly associated with sudden movements but can also develop from repeated stress on joints.
What are some effective ways to prevent sprains and strains, particularly in sports or regular physical activity?
Effective prevention includes proper warm-up routines, maintaining good flexibility and strength, using correct form during activities, wearing appropriate protective gear, and gradually increasing activity intensity. Regular rest periods and listening to your body's signals are also crucial.
How long does it typically take for a sprain or strain to heal, and what factors can influence recovery time?
Healing time varies from 2-8 weeks for mild injuries to several months for severe cases. Recovery is influenced by injury severity, location, adherence to treatment, age, overall health, and whether proper rest and rehabilitation protocols are followed.