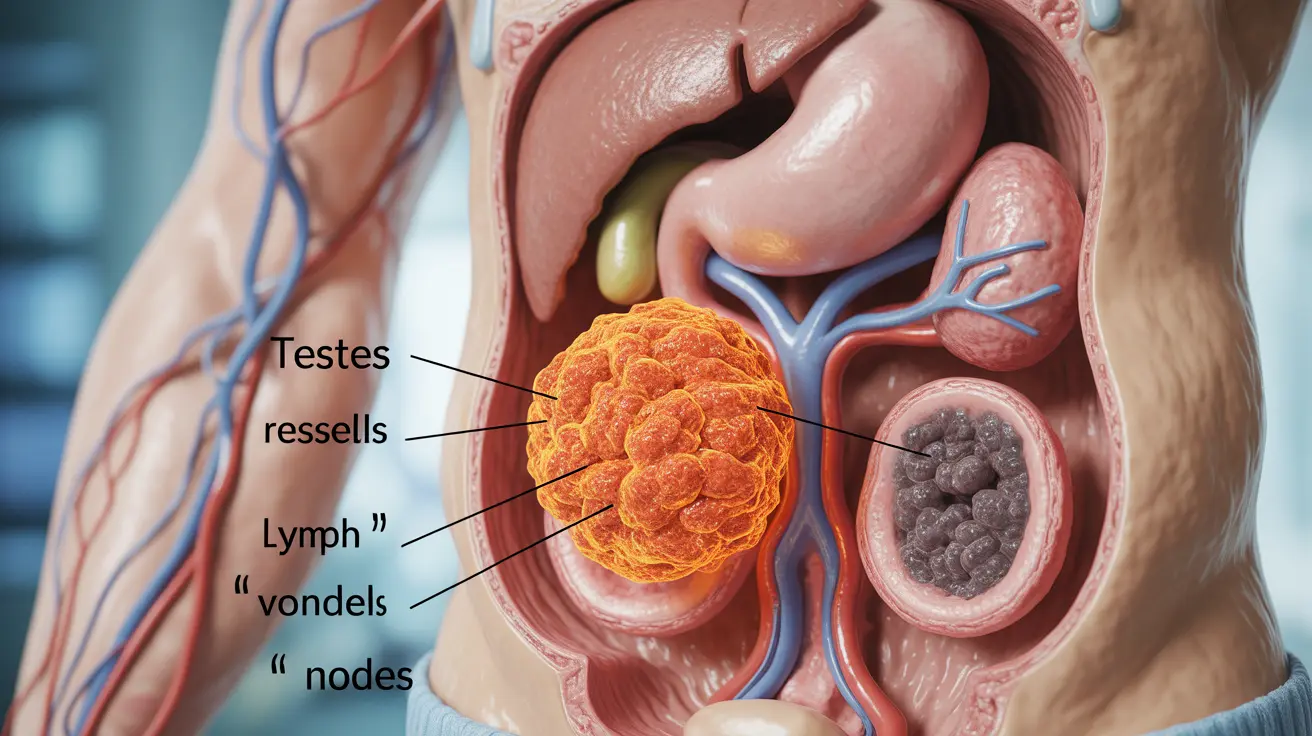
Understanding stage 2 testicular cancer is crucial for patients and their loved ones facing this diagnosis. This stage indicates that cancer has spread beyond the testicle but remains confined to lymph nodes below the diaphragm. While a cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, it's important to know that testicular cancer, even at stage 2, has excellent treatment outcomes with proper medical care.
Understanding Stage 2 Testicular Cancer
Stage 2 testicular cancer is characterized by cancer cells that have spread from the original tumor to nearby lymph nodes in the abdomen. This stage is further divided into substages (2A, 2B, and 2C) based on the size of lymph node involvement and specific tumor marker levels in the blood.
Survival Rates and Prognosis
The outlook for stage 2 testicular cancer is generally very positive. The five-year survival rate typically exceeds 95%, making it one of the most treatable forms of cancer. These high success rates are attributed to the effectiveness of modern treatment protocols and the tendency of testicular cancer to respond well to therapy.
Treatment Approaches
Surgery
The primary treatment usually begins with radical inguinal orchiectomy – surgical removal of the affected testicle. This procedure is typically followed by additional treatments to address any spread to the lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy
Most stage 2 patients receive chemotherapy after surgery. The standard protocol often includes BEP (Bleomycin, Etoposide, and Cisplatin) combination therapy, typically administered in three to four cycles.
Radiation Therapy
In some cases, particularly for seminoma-type tumors, radiation therapy might be recommended as an alternative to chemotherapy, targeting affected lymph nodes in the abdomen.
Post-Treatment Monitoring
After completing primary treatment, patients enter a structured follow-up program. This typically involves:
- Regular physical examinations
- Blood tests for tumor markers
- Chest X-rays and CT scans
- Scheduled follow-up appointments for at least 5 years
Signs and Symptoms
Early detection is crucial for optimal treatment outcomes. Key symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention include:
- A painless lump or swelling in either testicle
- Dull ache or heavy sensation in the lower abdomen or scrotum
- Back pain (which may indicate lymph node involvement)
- Unexplained fatigue or general illness
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the five-year survival rate for stage 2 testicular cancer?
The five-year survival rate for stage 2 testicular cancer typically exceeds 95%. With proper treatment and follow-up care, most patients achieve complete remission and long-term survival.
How is stage 2 testicular cancer typically treated and managed?
Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the affected testicle (radical orchiectomy) followed by chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The specific treatment plan depends on the cancer subtype and individual patient factors.
What are the chances of relapse after treatment for stage 2 testicular cancer?
The relapse rate for stage 2 testicular cancer is relatively low, typically less than 20%. Regular follow-up monitoring helps detect and address any potential recurrence early.
What symptoms should prompt early testing for stage 2 testicular cancer?
Key symptoms include a painless lump or swelling in the testicle, dull ache in the lower abdomen or scrotum, back pain, and unexplained fatigue. Any unusual changes should be evaluated by a healthcare provider promptly.
How long is follow-up monitoring needed after treatment for stage 2 testicular cancer?
Follow-up monitoring typically continues for at least 5 years after treatment completion, with more frequent visits in the first two years. Some patients may require longer monitoring based on individual risk factors.