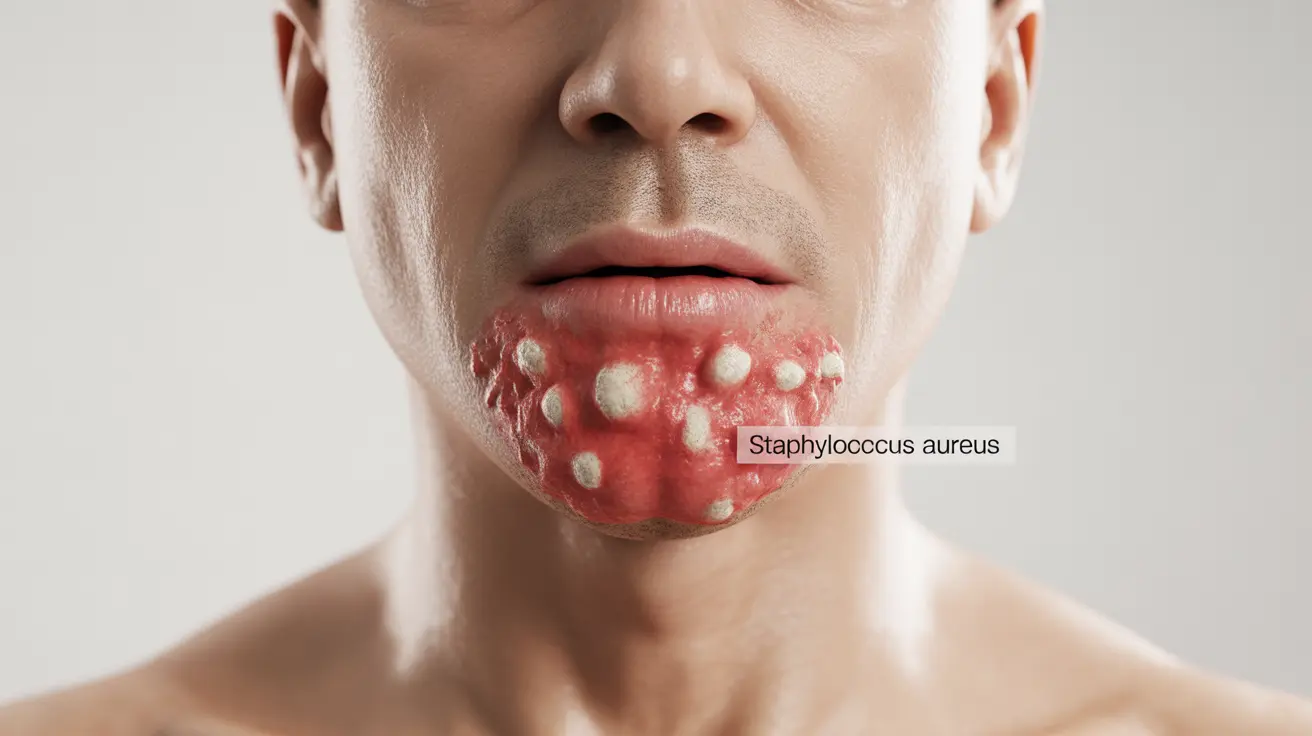
A staph infection in the throat, caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, can be a serious medical condition requiring prompt attention and treatment. While less common than strep throat, throat infections caused by staph bacteria can lead to significant complications if not properly diagnosed and treated. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about staph throat infections, from recognizing early warning signs to understanding treatment approaches and prevention strategies.
Identifying Symptoms of Staph Throat Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a staph infection in the throat is crucial for seeking timely medical attention. Common signs include:
- Severe throat pain and difficulty swallowing
- Swollen, red tonsils that may have white patches or pus
- Fever and chills
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Persistent cough
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- General fatigue and body aches
Unlike strep throat, staph throat infections may also present with:
- Yellow or white mucus discharge
- Persistent bad breath
- Small red spots on the roof of the mouth
- Symptoms that don't improve with typical strep throat treatments
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Healthcare providers use several methods to diagnose a staph infection in the throat accurately:
Physical Examination
During the initial evaluation, your doctor will examine your throat, check for swollen lymph nodes, and assess other physical symptoms.
Laboratory Testing
Specific tests may include:
- Throat culture
- Rapid antigen testing
- Blood tests to check for infection markers
- Culture sensitivity testing to determine effective antibiotics
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for staph throat infections typically involves a multi-faceted approach:
Antibiotic Therapy
The primary treatment usually includes:
- Prescribed antibiotics specific to staph bacteria
- Complete course of medication as directed
- Regular follow-up to ensure treatment effectiveness
Supportive Care
Additional measures to manage symptoms include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Throat lozenges or sprays
- Warm salt water gargles
- Plenty of rest and hydration
Prevention Strategies
Preventing staph throat infections involves several key practices:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals
- Not sharing personal items like towels or drinking vessels
- Maintaining good oral hygiene
- Strengthening immune system through proper nutrition and rest
Potential Complications
If left untreated, staph throat infections can lead to serious complications:
- Abscess formation in the throat or tonsils
- Spread of infection to nearby tissues
- Systemic infection or sepsis
- Toxic shock syndrome in severe cases
- Long-term throat damage or scarring
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a staph infection in the throat?
Common symptoms include severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, fever, swollen tonsils with white patches or pus, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck. You may also notice yellow or white mucus discharge and persistent bad breath.
How is a staph infection in the throat diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, throat culture, and possibly blood tests. Treatment usually consists of specific antibiotics targeted at staph bacteria, along with supportive care measures like pain relief and rest.
Can a staph throat infection be mistaken for strep throat or other throat infections?
Yes, staph throat infections can present similarly to strep throat and other throat infections. However, staph infections may not respond to treatments typically used for strep throat, and laboratory testing is necessary for accurate diagnosis.
What are the risks and complications if a staph infection in the throat is left untreated?
Untreated staph throat infections can lead to serious complications including throat abscesses, spread of infection to surrounding tissues, systemic infection, and in severe cases, toxic shock syndrome.
How can I prevent getting or spreading a staph infection in the throat?
Prevention involves regular handwashing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, not sharing personal items, maintaining good oral hygiene, and supporting your immune system through proper nutrition and rest.