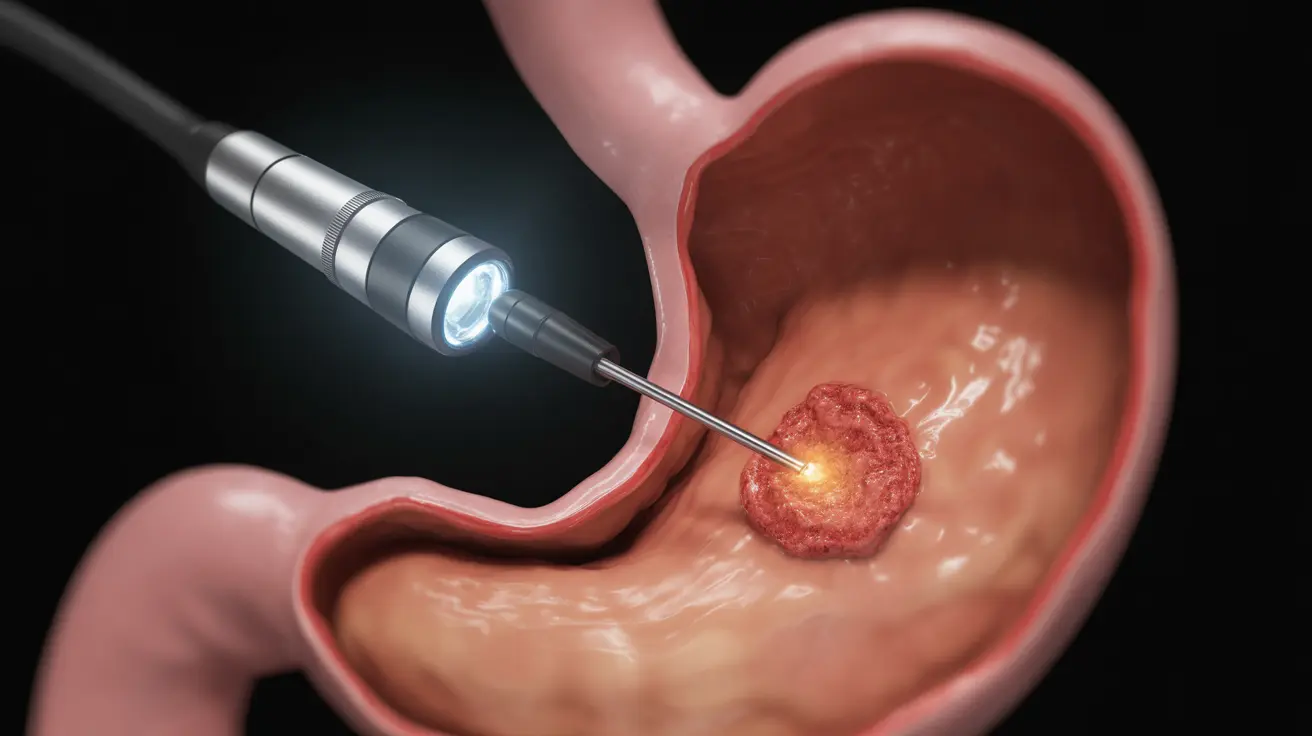
If you've been diagnosed with a stomach ulcer, your healthcare provider may recommend a therapeutic endoscopy procedure. This advanced medical technique allows doctors to both diagnose and treat ulcers directly, offering an effective solution for many patients. Understanding what to expect can help ease any concerns about the procedure.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the therapeutic endoscopy process for stomach ulcers, including preparation requirements, what happens during the procedure, and what to expect during recovery.
Understanding Therapeutic Endoscopy for Stomach Ulcers
Therapeutic endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a flexible tube with a camera and specialized tools to examine and treat problems in your digestive tract. Unlike diagnostic endoscopy, which only looks for issues, therapeutic endoscopy allows doctors to perform treatments during the same procedure.
Preparing for Your Therapeutic Endoscopy
Proper preparation is crucial for a successful therapeutic endoscopy procedure. Your doctor will provide specific instructions, but generally, you should:
- Fast for 6-8 hours before the procedure
- Stop taking certain medications as directed
- Arrange for someone to drive you home
- Inform your doctor about any medical conditions or allergies
You may need to temporarily adjust or stop taking blood thinners or other medications that could increase bleeding risk during the procedure.
The Therapeutic Endoscopy Procedure
During the procedure, you will receive sedation to ensure your comfort. The endoscope is carefully inserted through your mouth and guided down to your stomach. Your doctor can then:
- Visualize the ulcer directly
- Stop any active bleeding
- Apply medications directly to the ulcer site
- Take tissue samples if needed
- Perform other necessary treatments
The entire procedure typically takes 15-45 minutes, depending on the specific treatment needed.
Treatment Options During Endoscopy
Therapeutic endoscopy offers several treatment options for stomach ulcers, including:
- Injection therapy to stop bleeding
- Cauterization of bleeding vessels
- Application of clips to close bleeding sites
- Direct delivery of medications
- Removal of damaged tissue
Recovery and Aftercare
Most patients can return home the same day after the procedure. You may experience:
- Mild throat soreness
- Slight bloating
- Temporary grogginess from sedation
Full recovery typically occurs within 24-48 hours, though your doctor will provide specific aftercare instructions based on your treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I expect during a therapeutic endoscopy for a stomach ulcer?
During the procedure, you'll be sedated for comfort while the doctor inserts an endoscope through your mouth to access your stomach. The procedure allows for both examination and treatment of the ulcer, typically lasting 15-45 minutes. You may experience mild discomfort afterward, but the procedure itself shouldn't be painful.
How do doctors treat bleeding stomach ulcers using endoscopy?
Doctors can use several techniques during endoscopy to treat bleeding ulcers, including injection therapy, applying clips to bleeding vessels, cauterization, or a combination of these methods. The specific treatment chosen depends on the ulcer's location and severity of bleeding.
How should I prepare for an endoscopy to diagnose or treat a stomach ulcer?
You'll need to fast for 6-8 hours before the procedure, stop taking certain medications as directed by your doctor, and arrange for someone to drive you home afterward. Be sure to provide your medical history and list of current medications to your healthcare team.
What are the risks and recovery time after undergoing endoscopy for stomach ulcers?
While therapeutic endoscopy is generally safe, risks include bleeding, infection, or reaction to sedation. Recovery typically takes 24-48 hours, during which you may experience mild throat soreness and bloating. Most patients can return to normal activities the next day.
Why is a biopsy taken during an endoscopy for stomach ulcers and what does it test for?
Biopsies during endoscopy help determine the underlying cause of the ulcer, test for H. pylori infection, and rule out more serious conditions like cancer. The tissue samples are examined under a microscope to provide accurate diagnosis and guide treatment decisions.