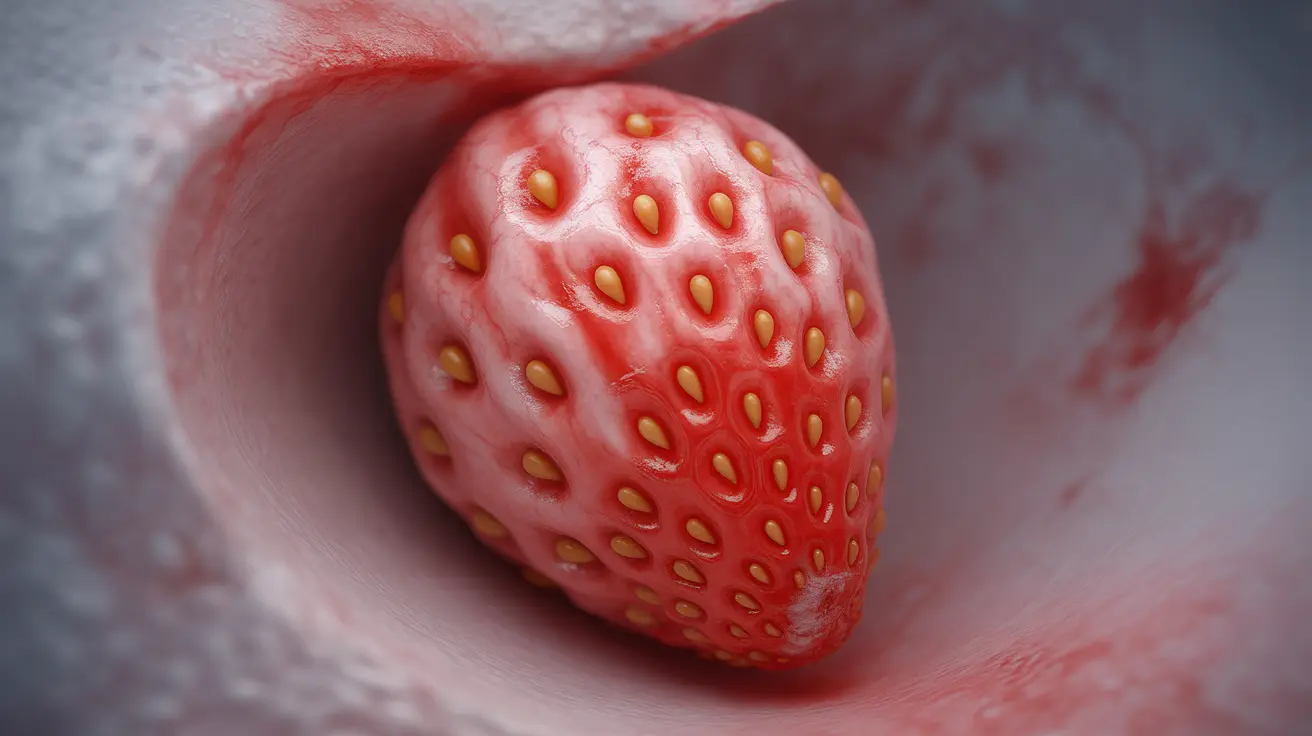
A strawberry cervix is a distinctive medical condition where the cervix develops a characteristic spotted appearance resembling the surface of a strawberry. This condition typically occurs as a result of a sexually transmitted infection called trichomoniasis. Understanding the signs, causes, and treatment options for this condition is crucial for women's health and early intervention.
While the name might sound benign, a strawberry cervix requires prompt medical attention as it indicates an active infection that needs treatment. This article will explore everything you need to know about this condition, from its appearance and causes to diagnosis and treatment options.
Understanding Strawberry Cervix and Its Appearance
A strawberry cervix, medically known as colpitis macularis, presents with a distinct appearance during medical examination. The cervix appears red and inflamed with small, punctate hemorrhagic spots that give it a strawberry-like appearance. This characteristic presentation is caused by dilated blood vessels and inflammation in response to the underlying infection.
The condition most commonly results from Trichomonas vaginalis, a parasitic infection. The organism causes an inflammatory response in the cervical tissue, leading to the distinctive appearance that medical professionals can identify during examination.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
While the strawberry appearance of the cervix is only visible during a medical examination, several other symptoms may indicate the presence of trichomoniasis:
- Unusual vaginal discharge that may be yellow, green, or gray
- Unpleasant vaginal odor
- Itching or irritation in the genital area
- Discomfort during urination
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Lower abdominal pain (in some cases)
It's important to note that some individuals may be asymptomatic, making regular gynecological check-ups essential for early detection and treatment.
Diagnosis Process
Healthcare providers typically diagnose a strawberry cervix through several methods:
- Visual examination during a pelvic exam
- Microscopic examination of vaginal secretions
- Laboratory testing of vaginal swabs
- Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs)
A comprehensive examination is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for strawberry cervix primarily focuses on addressing the underlying trichomoniasis infection. The standard treatment protocol includes:
- Prescription of antiprotozoal medications (typically metronidazole or tinidazole)
- Treatment of all sexual partners to prevent reinfection
- Temporary abstinence from sexual activity during treatment
- Follow-up testing to ensure the infection has cleared
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Several preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing a strawberry cervix:
- Practicing safe sex using barrier methods like condoms
- Regular STI screening
- Limiting sexual partners
- Open communication with sexual partners about STI status
- Maintaining regular gynecological check-ups
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a strawberry cervix look like and what causes it?
A strawberry cervix appears red and inflamed with small red spots, resembling the surface of a strawberry. It is primarily caused by trichomoniasis, a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis.
What are the common symptoms associated with strawberry cervix and trichomoniasis?
Common symptoms include unusual vaginal discharge, unpleasant odor, genital itching or irritation, discomfort during urination or intercourse, and sometimes lower abdominal pain. However, some people may be asymptomatic.
How is strawberry cervix diagnosed during a medical exam?
Diagnosis typically involves a pelvic examination where the healthcare provider can visually identify the characteristic strawberry-like appearance of the cervix. This is often confirmed through laboratory testing of vaginal swabs and microscopic examination of discharge.
What are the recommended treatments for trichomoniasis that causes strawberry cervix?
Treatment usually involves oral antiprotozoal medications such as metronidazole or tinidazole. It's essential that all sexual partners receive treatment simultaneously to prevent reinfection, and patients should abstain from sexual activity until treatment is complete.
Can strawberry cervix be prevented and how can I reduce my risk of trichomoniasis?
Strawberry cervix can be prevented by practicing safe sex, using condoms consistently, limiting sexual partners, and getting regular STI screenings. Regular gynecological check-ups can also help with early detection and treatment of any infections.