The connection between stress and heart disease is a critical health concern that affects millions of Americans. While some stress is a normal part of life, chronic stress can significantly impact your cardiovascular health through various biological and behavioral mechanisms. Understanding this relationship is crucial for protecting your heart health and developing effective stress management strategies.
This comprehensive guide explores how stress contributes to heart disease risk, identifies warning signs, and provides practical solutions for managing stress to protect your cardiovascular health.
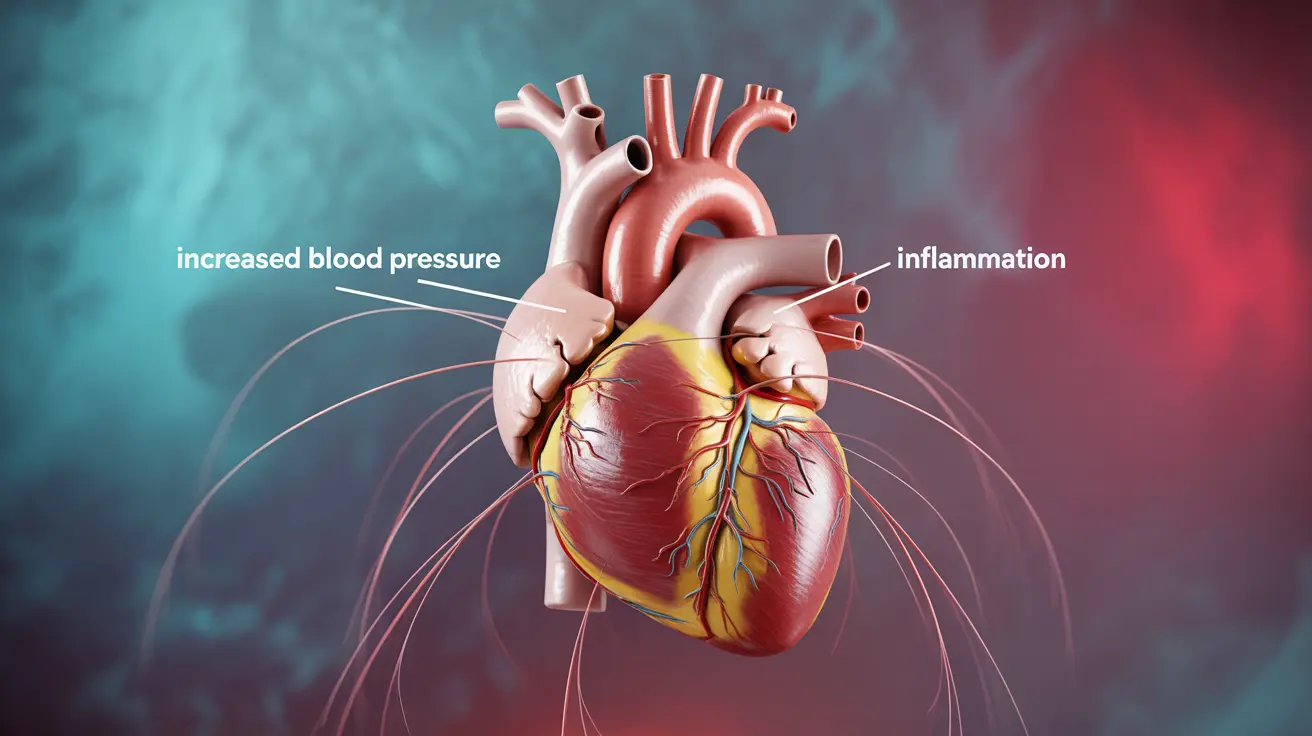
How Stress Affects Your Heart Health
When you experience stress, your body initiates a complex cascade of physiological responses. Your nervous system releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can temporarily increase blood pressure and heart rate. While this "fight or flight" response is natural, prolonged activation can lead to inflammation and damage to your cardiovascular system.
These stress-induced changes can affect your heart health in several ways:
- Increased blood pressure
- Elevated heart rate
- Higher levels of inflammation
- Blood vessel constriction
- Irregular heart rhythms
- Enhanced blood clotting
Recognizing Stress-Related Heart Problems
Identifying stress-related cardiovascular symptoms early is crucial for prevention and treatment. Common warning signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Irregular heartbeat or palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Unusual fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Sleep disturbances
The Impact of Stress-Related Behaviors on Heart Health
Chronic stress often leads to harmful coping behaviors that can further increase heart disease risk. These may include:
- Emotional eating and poor dietary choices
- Increased alcohol consumption
- Smoking or difficulty quitting
- Physical inactivity
- Poor sleep habits
- Social isolation
Effective Strategies for Managing Stress and Protecting Your Heart
Implementing stress management techniques is essential for reducing your heart disease risk. Consider these evidence-based approaches:
Physical Activity
Regular exercise helps reduce stress hormones and strengthens your cardiovascular system. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly.
Mindfulness and Relaxation
Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help lower blood pressure and reduce stress levels.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making positive changes to your daily routine can significantly impact both stress levels and heart health:
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Establishing regular sleep patterns
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol
- Creating boundaries between work and personal life
- Building strong social connections
Frequently Asked Questions
How does stress actually raise my risk of heart disease, and what changes happen in my body when I'm stressed?
Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which increase blood pressure and heart rate. Chronic stress leads to persistent inflammation and may damage blood vessels, contributing to atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular problems.
What are the most common symptoms of stress-related heart problems that I should watch out for?
Key symptoms include chest pain, irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, unusual fatigue, and anxiety-related heart palpitations. If you experience these symptoms, especially chest pain, seek immediate medical attention.
What are the best ways to reduce stress and lower my risk of heart disease?
Effective strategies include regular exercise, mindfulness practices, adequate sleep, maintaining social connections, and seeking professional help when needed. Creating a balanced lifestyle and developing healthy coping mechanisms are essential.
Can stress cause a heart attack, and what should people with heart disease know about stress?
While stress alone rarely causes a heart attack, it can trigger one in people with underlying heart disease. Those with heart conditions should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop appropriate stress management strategies and monitor their symptoms carefully.
How do unhealthy habits caused by stress contribute to heart disease?
Stress often leads to harmful coping behaviors like overeating, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and physical inactivity. These habits can increase blood pressure, contribute to obesity, and directly damage the cardiovascular system, significantly raising heart disease risk.