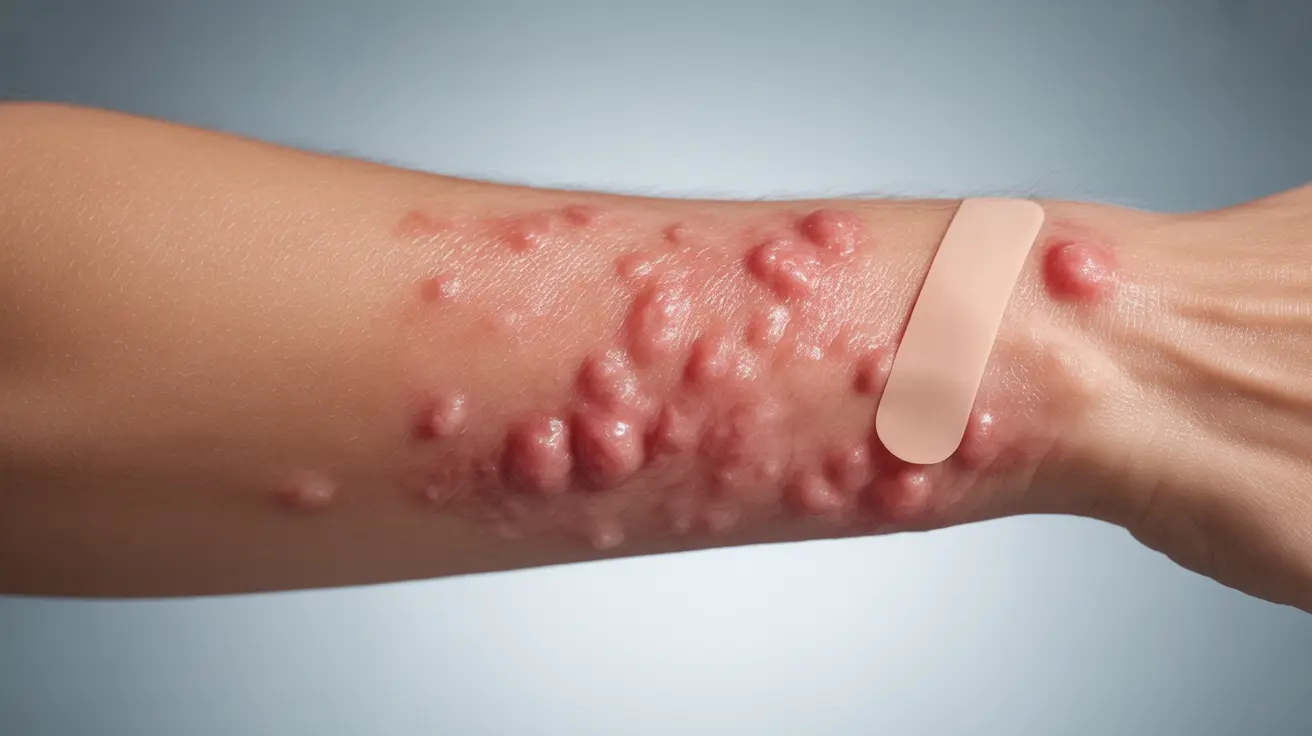
If you've ever experienced sudden, itchy welts on your skin during periods of high stress, you might be dealing with stress-induced urticaria. This condition, characterized by the appearance of hives triggered by psychological stress, can be both uncomfortable and concerning for those affected. Understanding the connection between stress and urticaria is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
While the relationship between stress and skin reactions has long been recognized by medical professionals, the exact mechanisms behind stress-induced urticaria are complex and involve multiple body systems. Let's explore what causes this condition, how to recognize it, and most importantly, what you can do to manage it.
Understanding the Stress-Urticaria Connection
Stress triggers a cascade of physiological responses in your body, including the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can affect your immune system and trigger inflammatory responses, potentially leading to urticaria outbreaks. The skin's mast cells, which play a crucial role in allergic responses, may become more reactive during periods of stress, releasing histamine and other inflammatory substances that cause hives.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Stress-induced urticaria typically presents with several distinctive characteristics:
- Raised, red welts on the skin
- Intense itching or burning sensation
- Swelling of affected areas
- Hives that appear suddenly during or after stressful events
- Welts that may change shape or move around the body
- Symptoms that can last from minutes to hours
Treatment Approaches for Stress-Induced Urticaria
Medical Interventions
Several medical treatments can help manage stress-induced urticaria:
- Antihistamines to reduce itching and inflammation
- Oral corticosteroids for severe outbreaks
- Anti-anxiety medications in some cases
- Topical treatments to soothe affected skin
Stress Management Techniques
Managing stress is crucial for preventing and reducing urticaria outbreaks. Effective strategies include:
- Regular exercise and physical activity
- Mindfulness meditation and deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Regular sleep schedule
- Time management and organization
- Professional counseling or therapy when needed
Prevention Strategies
Taking proactive steps to prevent stress-induced urticaria can significantly improve your quality of life:
- Identify and avoid personal stress triggers
- Maintain a consistent self-care routine
- Practice stress-reduction techniques regularly
- Keep a symptom diary to track triggers and patterns
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet
When to Seek Medical Help
While many cases of stress-induced urticaria can be managed at home, certain situations require professional medical attention:
- Hives that persist for more than six weeks
- Severe swelling, especially around the face or throat
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Symptoms that significantly impact daily life
- Hives accompanied by other concerning symptoms
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common symptoms of stress-induced urticaria and how can I recognize them?
Common symptoms include raised, red welts on the skin, intense itching, and swelling. These symptoms typically appear during or shortly after stressful events and may move around the body. The welts can vary in size and usually last for several hours before fading.
- How does stress trigger or worsen chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU)?
Stress activates the body's fight-or-flight response, releasing hormones that can trigger inflammatory responses. This can cause mast cells to release histamine and other chemicals, leading to hives. In CSU, stress can exacerbate existing symptoms or trigger new outbreaks.
- What treatments are effective for managing stress-related hives and urticaria outbreaks?
Effective treatments include antihistamines, corticosteroids for severe cases, and stress management techniques. Combining medical treatments with stress reduction strategies often provides the best results.
- Can lifestyle changes or stress reduction techniques help prevent or reduce stress-induced urticaria?
Yes, lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, meditation, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of urticaria outbreaks. Maintaining a healthy work-life balance and practicing relaxation techniques are particularly beneficial.
- When should I see a doctor for chronic or severe stress-induced hives?
Seek medical attention if hives persist for more than six weeks, cause severe swelling, affect breathing or swallowing, or significantly impact your daily life. Also consult a healthcare provider if your symptoms don't improve with over-the-counter treatments.