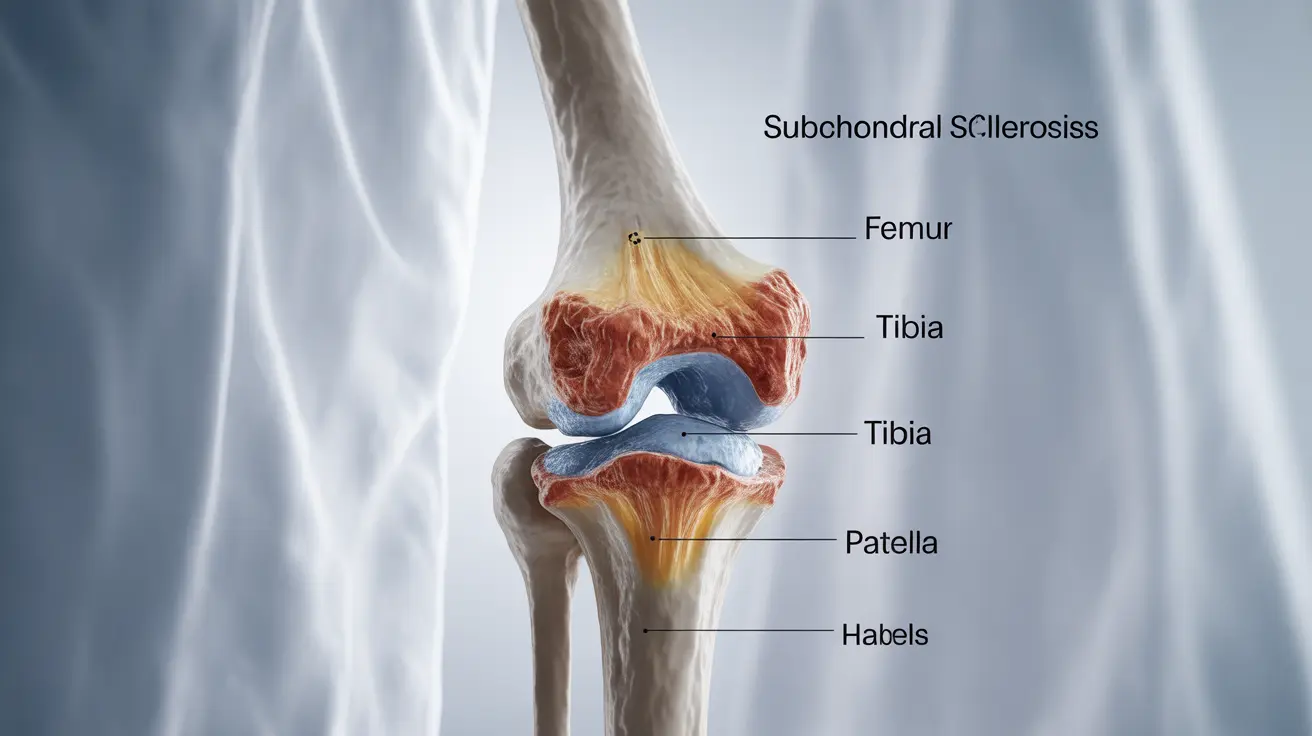
Subchondral sclerosis is a condition that affects the bone beneath joint cartilage, causing it to become denser and harder than normal. This change in bone structure often occurs as part of the osteoarthritis process and can significantly impact joint health and mobility. Understanding this condition is crucial for proper diagnosis and management of joint-related problems.
While subchondral sclerosis primarily affects weight-bearing joints like knees and hips, it can develop in any joint experiencing repeated stress or trauma. The condition represents an important marker in the progression of joint disease and requires careful medical attention for optimal outcomes.
What is Subchondral Sclerosis?
Subchondral sclerosis occurs when the bone layer directly beneath the cartilage (subchondral bone) becomes thicker and more dense. This process typically develops as a response to increased pressure or stress on the joint, leading to changes in bone architecture and strength. The affected bone appears whiter and more prominent on X-rays, making it a key diagnostic indicator for healthcare providers.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of subchondral sclerosis:
- Osteoarthritis progression
- Repetitive joint stress
- Previous joint injuries
- Obesity or excess weight
- Athletic activities with high impact
- Age-related joint wear and tear
Understanding these risk factors is essential for both prevention and management of the condition. Many of these factors are interrelated, often working together to accelerate joint deterioration.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of subchondral sclerosis can vary but typically include:
- Joint pain that worsens with activity
- Stiffness, especially after periods of rest
- Reduced range of motion
- Swelling around the affected joint
- Clicking or grinding sensations during movement
These symptoms often develop gradually and may become more pronounced over time, particularly if the underlying causes aren't addressed.
Diagnosis Methods
Healthcare providers use various imaging techniques to diagnose subchondral sclerosis:
X-ray Imaging
X-rays are typically the first-line diagnostic tool, showing increased bone density beneath the cartilage. The affected areas appear whiter and more prominent compared to normal bone tissue.
MRI Scans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides detailed views of both bone and soft tissue, helping doctors assess the extent of joint damage and associated conditions.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for subchondral sclerosis focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further joint damage. Options include:
Conservative Management
- Physical therapy exercises
- Weight management programs
- Activity modification
- Joint protection techniques
Medical Interventions
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Pain management strategies
- Corticosteroid injections
- Viscosupplementation
Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. This could include procedures such as joint replacement or corrective osteotomy, depending on the affected joint and extent of damage.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making appropriate lifestyle changes can significantly impact the progression of subchondral sclerosis:
- Regular low-impact exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Using proper body mechanics
- Avoiding activities that stress joints
- Following an anti-inflammatory diet
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes subchondral sclerosis and how is it related to osteoarthritis? Subchondral sclerosis develops when joint stress causes the bone beneath cartilage to become denser and harder. It's closely related to osteoarthritis as both conditions often occur together, with subchondral sclerosis being both a cause and consequence of osteoarthritic changes.
What are the common symptoms of subchondral sclerosis in weight-bearing joints? Common symptoms include persistent joint pain, stiffness after inactivity, reduced range of motion, and possible swelling. Weight-bearing joints like knees and hips typically show more pronounced symptoms, especially during physical activity.
How is subchondral sclerosis diagnosed through imaging tests like X-rays and MRI? Diagnosis primarily relies on X-rays, which show increased bone density appearing as whiter areas beneath the cartilage. MRI scans provide more detailed images of both bone and surrounding tissues, helping to assess the full extent of joint damage.
What treatment options are available to manage pain and improve joint function with subchondral sclerosis? Treatment options include conservative measures like physical therapy and weight management, medical interventions such as anti-inflammatory medications and injections, and in severe cases, surgical procedures to repair or replace affected joints.
Can lifestyle changes, such as exercise and weight loss, help reduce the symptoms of subchondral sclerosis? Yes, lifestyle modifications can significantly impact symptoms. Regular low-impact exercise strengthens supporting muscles, weight loss reduces joint stress, and proper body mechanics help prevent further damage. These changes, combined with appropriate medical treatment, can help manage symptoms effectively.