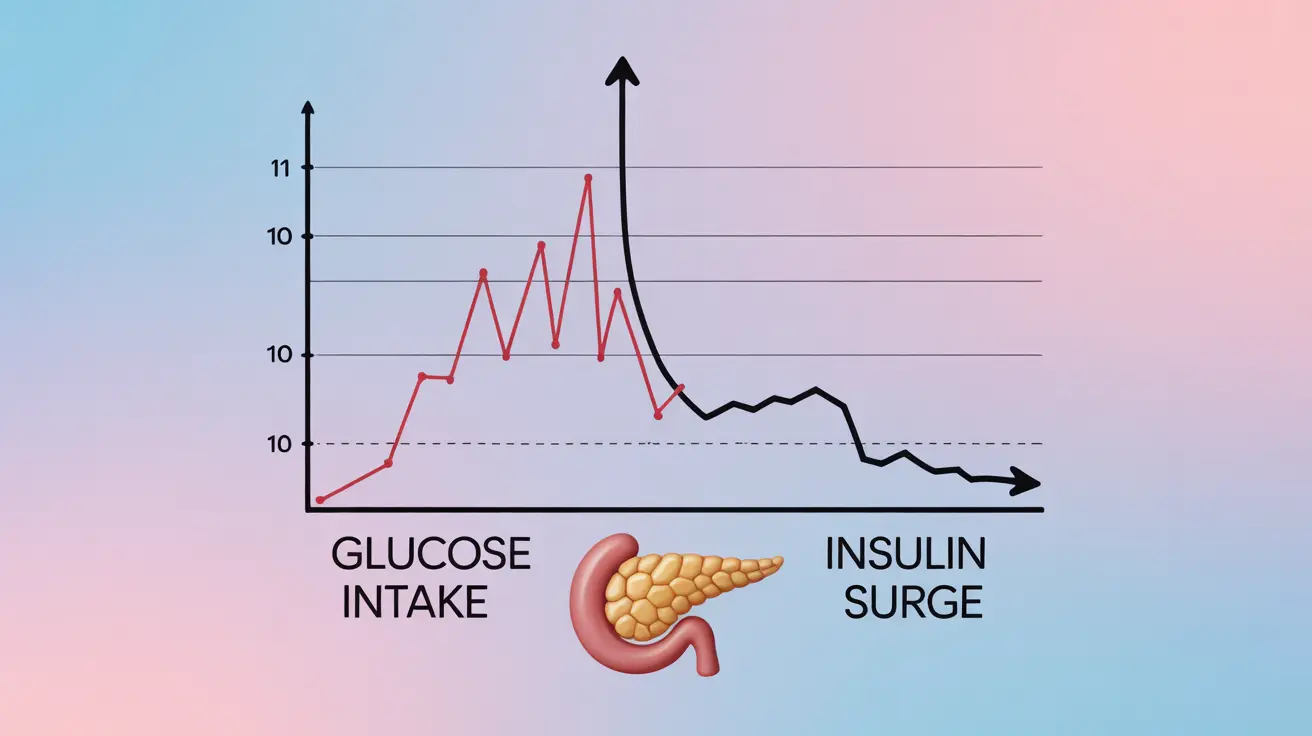
A sugar crash, also known as reactive hypoglycemia, occurs when blood sugar levels drop significantly after consuming high-sugar foods or drinks. This sudden decline can trigger various physical and mental symptoms that affect your daily functioning. Understanding the mechanics behind sugar crashes is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
While many people experience sugar crashes occasionally, frequent episodes may indicate underlying health issues that require medical attention. Let's explore what causes these crashes, how to recognize them, and most importantly, how to prevent them through proper diet and lifestyle choices.
What Causes a Sugar Crash?
Sugar crashes typically occur 1-4 hours after consuming foods high in simple carbohydrates or sugar. When you eat these foods, your blood sugar rises quickly, prompting your pancreas to release insulin to help cells absorb the glucose. Sometimes, this response can be overly aggressive, causing blood sugar to drop below normal levels.
Common triggers include:
- Consuming sugary beverages or snacks on an empty stomach
- Skipping meals
- Eating meals high in refined carbohydrates
- Excessive caffeine consumption
- Individual insulin sensitivity
Recognizing Sugar Crash Symptoms
Sugar crash symptoms can vary in intensity and combination among individuals. Being able to identify these signs is the first step in managing and preventing future episodes.
Physical Symptoms
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shakiness or trembling
- Sweating
- Hunger
- Rapid heartbeat
- Headache
Mental and Emotional Symptoms
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Confusion
- Brain fog
- Mood swings
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
If you experience frequent sugar crashes, your healthcare provider may recommend several tests to determine the underlying cause. These may include:
- Fasting blood glucose test
- Oral glucose tolerance test
- Mixed meal tolerance test
- Continuous glucose monitoring
Prevention Strategies
Dietary Modifications
The most effective way to prevent sugar crashes is through dietary changes:
- Choose complex carbohydrates over simple sugars
- Pair carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats
- Eat regular, balanced meals
- Include fiber-rich foods in your diet
- Stay hydrated with water instead of sugary drinks
Lifestyle Adjustments
Additional preventive measures include:
- Regular exercise to improve insulin sensitivity
- Consistent meal timing
- Adequate sleep
- Stress management
- Portion control
Managing Active Sugar Crashes
When experiencing a sugar crash, take these immediate steps:
- Eat a small, balanced snack containing protein and complex carbohydrates
- Stay hydrated
- Rest if possible
- Avoid sugary foods that could trigger another crash
- Monitor your symptoms
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a sugar crash mean and what causes it? A sugar crash occurs when blood sugar levels drop significantly after consuming high-sugar foods, causing your body to release excess insulin. This overcompensation leads to lower-than-normal blood sugar levels.
What are the common symptoms of a sugar crash or reactive hypoglycemia? Common symptoms include fatigue, shakiness, sweating, irritability, difficulty concentrating, hunger, and anxiety. These symptoms typically appear 1-4 hours after consuming high-sugar foods.
How is a sugar crash diagnosed and what tests might a doctor perform? Doctors may use fasting blood glucose tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, mixed meal tolerance tests, or continuous glucose monitoring to diagnose reactive hypoglycemia and identify underlying causes.
What are effective ways to prevent sugar crashes through diet and lifestyle? Prevention includes eating balanced meals with complex carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats; maintaining regular meal times; staying hydrated; exercising regularly; and getting adequate sleep.
How can sugar crashes be managed or treated if they occur? When experiencing a sugar crash, eat a balanced snack containing protein and complex carbohydrates, stay hydrated, rest if possible, and avoid consuming more sugary foods that could trigger another crash.